D2000 SES (Script Execution Server) process
D2000 SES process ensures the start of virtual SEE processes. The functionality of SES server is implemented in the process event.exe. D2000 SES may service both the remote ESL scripts and the local parts of ESL scripts for TCL. The handling of script types is defined by a start parameter.
--SES_REMOTE
--SES_LOCAL
Example of starting SES server:
event.exe /Sserver_name --SES_REMOTE
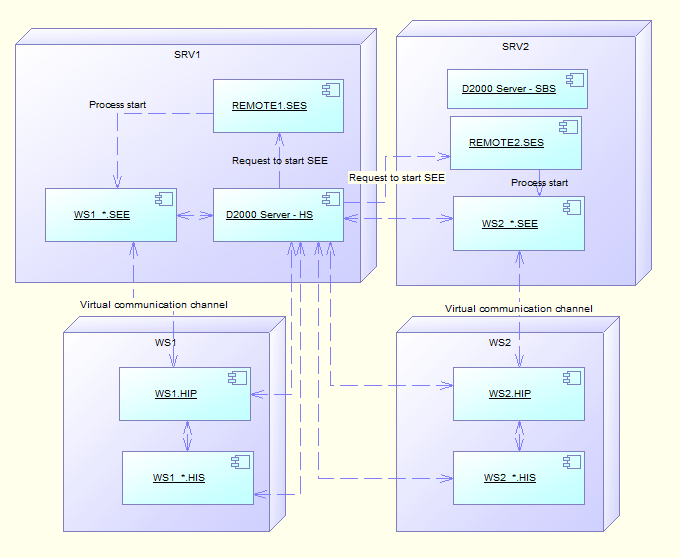
The startup of virtual SEE processes is conditioned upon the request from HIP process. A typical configuration is shown on the following diagram.
| Process | Meaning |
|---|---|
| SRV1, SRV2 | Application server |
| WS1, WS2 | Work station of a client |
| D2000 Server | Server process of D2000 System |
| REMOTE1.SES, REMOTE2.SES | Server that services the virtual SEE processes |
| SRV1.RRS, SRV2.RRS | Resident Remote Services |
| WS1.HIP, WS2.HIP | D2000 HI processes – user console |
| WS1_*.HIS, WS2_*.HIS | ESL Interpret on the Client side |
| WS1_*.SEE, WS2_*.SEE | ESL Interpret on the Server side – Script Execution Engine |
The diagram shows the configuration of a redundant application. The servers SRV1 and SRV2
ensure this redundancy. SRV1 is HS (Hot Server) and SRV2 is SBS.
The connection of WS1.HIP from the client work station and opening
the picture, which contains both the local and remote ESL script, causes that D2000 Server HS
ensures the startup of proper process
WS1_*.SEE.
This startup is done by SES process.
As, there are two running SES processes
in the application, the process with the least running SEE processes will ask
for the start.
This principle enables to use the computing power of both servers (SRV1 and SRV2).
After starting, SES processes must connect to
D2000 Server,
not to the redundant group (they must be started with parameter /S, not /RD or /RS).
Related pages:
Pridať komentár