IEC
...
60870-5-104 communication protocol
Supported device types and versions
Communication partners
Communication line configuration
Communication station configuration
Tell TELL commands
I/O tag configuration
Literature
Document revisions
Supported device types and versions
...
The protocol (known also as IEC 870-5-104 or IEC-104) allows reading and writing data, operating on the basis of TCP network communication. Implementation is, according to the IEC870IEC 60870-5-104 standard, as follows:
- Originator ASDU address is 1 byte, it is defined as the line number.
- ASDU address is 2 bytes, it is defines defined as the station address. ASDU addresses of all stations on one line must be different.
- Cause of transmission is 2 bytes (contains also Originator ASDU address).
- Information object address is 3 bytes, it is defined as an I/O tag address.
- The following ASDU types are implemented in the monitoring course (from controlled station to the D2000 system and also vice-versa in balanced mode):
Table 1| ASDU type | I/O tag type |
|---|
| 1 - Single-point information | Di, Qi (On/Off), Ai, Ci |
| 2 - Single-point information with time tag | Di, Qi (On/Off), Ai, Ci |
| 3 - Double-point information | Qi, Ai, Ci |
| 4 - Double-point information with time tag | Qi, Ai, Ci |
| 5 - Step position information | Ci, Ai * |
| 6 - Step position information with time tag | Ci, Ai * |
| 7 - Bitstring of 32 bits | Ci, Ai |
| 8 - Bitstring of 32 bits with time tag | Ci, Ai |
| 9 - Measured value, normalized value | Ai |
| 10 - Measured value, normalized value with time tag | Ai |
| 11 - Measured value, scaled value | Ci, Ai |
| 12 - Measured value, scaled value with time tag | Ci, Ai |
| 13 - Measured value, short floating-point value | Ai |
| 14 - Measured value, short floating-point value with time tag | Ai |
| 15 - Integrated totals | Ci, Ai |
| 16 - Integrated totals with time tag | Ci, Ai |
| 17 - Event of protection equipment with time tag | Ci, Ai, TiR ** |
| 18 - Packed start events of protection equipment with time tag | Ci, Ai, TiR *** |
| 20 - Packed single-point information with status change detection | Ci, Ai |
| 21 - Measured value, normalized value without quality descriptor | Ai |
| 30 - Single-point information with time tag CP56Time2a | Di, Qi (On/Off), Ai, Ci |
| 31 - Double-point information with CP56Time2a tag | Qi, Ai, Ci |
| 32 - Step position information with CP56Time2a tag | Ci, Ai * |
| 33 - Bitstring of 32 bits with CP56Time2a tag | Ci, Ai |
| 34 - Measured value, normalized value with CP56Time2a tag | Ai |
| 35 - Measured value, scaled value with CP56Time2a tag | Ci, Ai |
| 36 - Measured value, short floating-point value with time tag CP56Time2a | Ai |
| 37 - Integrated totals with time tag CP56Time2a | Ci, Ai |
| 38 - Event of protection equipment with time tag CP56Time2a | Ci, Ai, TiR ** |
| 39 - Packed start events of protection equipment with time tag CP56Time2a | Ci, Ai, TiR *** |
| 40 - Packed output circuit information of protection equipment with time tag CP56Time2a | Ci, Ai, TiR *** |
| 241 - 64-bit floating-point value (Ipesoft & URAP implementation) | Ao |
| 243 - 64-bit floating-point value with time tag CP56Time2a (Ipesoft & URAP implementation) | Ao |
| 251 - Archive data values (Ipesoft's implementation) | none **** |
| 252 - D2000 Unival (Ipesoft's implementation) | all (except Qi) |
Note: Single bites bits of the byte, which informs us on quality (SIQ for ASDU 1,2,30; DIQ for ASDU 3,4,31; QDS for 5..14,20,32..36) are mapped into the flags FLA A (0.bit), FLB B (1.bit) .. FLH H (7.bit) except flags except the bits that are directly set by the value of the variable ( SCO bit 0, DCO and RCS bity bits 0-1). After receiving the answer (a positive/negative one), the flags FLAA .. FLH are H flags are set according to bits of "status" byte.
For example:
for ASDU 4: FLAA=DPI bit 0, FLBB=DPI bit 1, FLCC=0, FLDD=0, FLEE=BL bit, FLFF=SB bit, FLGG=NT bit, FLHH=IV bit.
for ASDU 16: FLAA .. FLE E Sequence number bity bits 0..4, FLFF=CY bit, FLGG=CA bit, FLHH=IV bit.
Moreover:
- if a bit is set to IV (Invalid), the value state will be Invalid
- if some of the bits are set to NT (Not topical), SB (Substituted), BL (Blocked), OV (Overflow), CA (Counter adjusted), CY (Counter overflow) for corresponding ASDU types, the value state will be Weak.
...
* - T-bit of the value of these ASDU types is in the
FI I flag, a number within -64 .. +63 is in a variable of Ci/Ai type.
** - ASDU 17 and 38: SEP byte is in the
flags FLA A (0.bit),
FLB B (1.bit) ..
FLH H (7.bit), the following 2 bytes (CP16Time2a) are in a variable of Ci/Ai type as a positive number (0-60 000) or they are in a variable of TiR type as a relative time (0-60 seconds).
*** - ASDU 18, 39 and 40: SPE(ASDU 18,39) byte respectively OCI (ASDU 40) byte is in the
flags FLI I (0.bit),
FLJ J (1.bit) ..
FLP P (7.bit), QDP byte is in
the the flags FLA A (0.bit),
FLB B (1.bit) ..
.FLH H (7.bit), the following 2 bytes (CP16Time2a) are in a variable of Ci/Ai type as a positive number (0-60 000) or they are in a variable of TiR type as a relative time.
The following ASDU types are implemented in the control course (from D2000 system to controlled station and also vice-versa in balanced mode):
Table 2| ASDU type | I/O tag type |
|---|
| 45 - Single command | Dout |
| 46 - Double command | Dout |
| 47 - Regulating step command | Dout |
| 48 - Set point command, normalised value | Ao |
| 49 - Set point command, scaled value | Co |
| 50 - Set point command, short floating-point value | Ao |
| 51 - Bitstring of 32 bit | Co |
| 58 - Single command with time tag CP56Time2a | Dout |
| 59 - Double command with time tag CP56Time2a | Dout, Co |
| 60 - Regulating step command with time tag CP56Time2a | Dout |
| 61 - Set point command, normalised value with time tag CP56Time2a | Ao |
| 62 - Set point command, scaled value with time tag CP56Time2a | Co |
| 63 - Set point command, short floating-point value with time tag CP56Time2a | Ao |
| 64 - Bitstring of 32 bit with time tag CP56Time2a | Co |
| 250 - Archive data request command (Ipesoft's implementation) | none **** |
| 252 - D2000 Unival (Ipesoft's implementation) | all |
To set the bites bits of "status" byte (SCO for ASDU 45,58; DCO for ASDU 46,59; RCO for ASDU 47,60; QOS for ASDU 48..50,61..63), there are used the flags FLA A (0.bit), FLB B (1.bit) .. FLH H (7.bit) are used, except the bitesbits, which are directly set by the variable value (SCO bit 0, DCO and RCS bites bits 0-1). Having received a response (positive/negative), the flags FLAA .. FLH are H flags are set according to the bites bits of the "status" byte.
When sending commands (ASDU 45-64), the value of 6 [Activation] is send sent as a CauseOfTransmission. Expecting a The expected response from the controlled station depends on the parameter the Command Confirm parameter. There are the following possibilities:
- writing is successful , if the packet with RSN confirming the SSN packet with the logwrite command
- writing is finished, if there is a response with CauseOfTransmission=7 [Activation Confirmation] and/or with 10 [Activation Termination]. Success/Unsuccess failure depends on the setting of the P/N bite in bit in CauseOfTransmission.
**** - ASDU 250 can be used for communication with Ipesoft 870-5-104 Server. The command will ask for historical values (within
any specified interval) from the server, which
get back will arrive as ASDU 251 (or newer ASDU 249 that use 64-bit values for improved precision, if the protocol parameter
D2H64 is enabled on the server). The reading of the archive values can be executed by means of the
TELL GETOLDVAL command
GETOLDVAL with the parameter containing the name of the I/O tag or station (in this case,
there are read the values of all I/O tag
in successive stepsare read gradually, i.e. reading
another of the next tag starts after
termination the reading of
currently read current tag
is done).
Response for ASDU 250 is again ASDU 250 (with CauseOfTransmission=7) and with the return code:
- 0 - the successful start of reading the history
- 1 - the history for the required tag doesn't existsexist
- 2 - the history for the required tag is not available (the archive does not run)
Further follows Next (is the return code was 00) the ASDU 251 with archive data will be sent and the termination ASDU 250 with CauseOfTransmission=10.
Establishing a connection:
process The D2000 KOM process is connecting to the TCP port and sends a StartDT Act U-frame StartDT Act, then a StartDT Con U-frame is waited expected as a reply.
For all the stations with a defined synchronization (see the article below), there is send an ASDU type 103 [Clock synchronisation command] with CauseOfTransmission=6 [Activation] is sent, there is expected and a reply in dependence (depending on the Command Confirm parameter) is expected.
Then there is sent a sequence of 0 up to N I-frames with ASDU 100 [Interrogation Command] and ASDU 101 [Counter Interrogation Command] is sent, both with CauseOfTransmission=6 [Activation]. The I-frames are sent for each station with at least one input I/O tag (i.e. Ai, Di, Qi, Ci). As a response, there is expected (in any order):
- receiving reception of frames with ASDU 100 [Interrogation Command] and with CauseOfTransmission=7 or 10 (depends depending on the Command Confirm parameter)
- receiving reception of frames with ASDU 101 [Counter Interrogation Command] and with CauseOfTransmission=7 or 10 (depends depending on the Command Confirm parameter)
- receiving reception of current values of all I/O tags.
The other side can also sent send frames with ASDU TypeIdentificator=100 and CauseOfTransmission=10 [Activation Termination]. However, but the process D2000 KOM process does not consider it to be an error , if such no frames will not receive. are received. The order of sending ASDU 100 and 101 sending order as well as disabling their sending is defined by the parameters Order of IC and Order of Counter IC parameters.
Clock synchronisation: Sending ASDU type 103 [Clock synchronisation command] is performed during initialization (after sending StartDT and before sending Interrogation Command). The synchronization is sent for the stations, with the checked parameter Enable in the tab Enable parameter checked in the Time parameters tab. ASDU type 103 is sending sent regularly with a defined period.
Forced disconnection: If all stations on the line are in the simulation mode or the communication is stopped for them, the line will be disconnected (communication socket will be closed). If the simulation is disabled for at least one station and the communication is not stopped for it (the the Parameters tab Parameters of Station type object), the line will be connected again (and there will be sent Interrogation Command and/or Counter Interrogation Command will be sent to the active station). After turning on every next stationenabling communication for further stations, Interrogation Command and/or Counter Interrogation Command will be sent to the stationthese stations, see the next articleparagraph.
Forced sending of Interrogation Command and/or Counter Interrogation Command: If a station is in the simulation mode and the communication is not stopped for it (the the Parameters tab Parameters of Station type object), the process D2000 KOM process sends Interrogation Command and/or Counter Interrogation Command (see the parameters Order of IC, Order of Counter IC).
The D2000 system also supports the a balanced mode. In the mode, the task of controlled and control stations is changed. That time, symmetrical. In this mode, the D2000 system receives commands and confirms them. The balanced mode may be used only when it is supported by the partner station. An advantage is that the D2000 system sends the current status of output I/O tags (defined as ASDU 1-40) as a reply to ASDU 100 [Interrogation Command] and 101 [Counter Interrogation Command] requests. It is still suitable to configure single-shot commands as ASDU 45 - 64; they are not repeated after re-establishing the connection.
As the protocol supports the balanced mode (partly it is a server), there are valid the rules of server protocols apply to it.
The output tags, which are configured as ASDU 1-40, do not switched to go through the Transient status (i.e. they are considered as if in the configuration of I/O tag, tab Output controlcontrol tab, the I/O tag output mode is set on to Command). The record writing is considered to be successful if there is the a connection with the server at the time of recordwriting, otherwise, the record writing is unsuccessful.
Communication partners
...
- ABB MicroScada. Note: The value of the parameter Maximum message length in the ABB MicroScada settings must be changed from 253 similar to 230 (+/- a few bytes). Default value of the parameter causes rewriting the communication buffer and it is expressed by sending a corrupted message.
- PLC Bernecker & Rainer, protocol implementation: URAP-AUTOMATIZÁCIA s.r.o. (Ltd.)
- LFC terminals of Slovenské Elektrárne, a.s. (Inc.), protocol implementation: Energodata/ABB
- RS Unicon 4, UniControls
| Kotva |
|---|
| komunikacna_linka |
|---|
| komunikacna_linka |
|---|
|
Communication line configuration
...
- Communication line category: TCP/IP-TCP or TCP/IP-TCP Redundant.
- TCP parameters - server parameters are mandatory:
- Host: string containing at most 80 characters – server name in form of INET (name or numerical address a.b.c.d). In the case of redundant systems, multiple names/addresses separated by commas can be entered.
- Port: TCP port number (0..65535)
- Line number: is to be used as the Originator ASDU address (1 byte, 0-255)
| Kotva |
|---|
| komunikacna_stanica |
|---|
| komunikacna_stanica |
|---|
|
Communication station configuration
...
- Communication protocol: IEC870-TCP.
- Station address a decimal number within the range of 0..65535 , defines the ASDU address.
Note 1: After saving a station in process D2000 CNF, the process D2000 KOM automatically sends ASDU 100 and ASDU 101 (Interrogation and Counter Interrogation Commands) to this station, if enabled.
Note 2: The protocol supports sending long time stamps (CP56Time2a tag) in local time or UTC time with defined offset (see the parameter Use monotonic UTC time +).
Note 3: Starting with D2000 version 7.02.004 if a TCP Redundant line category is used, the C and D flags FLC and FLD are used in the value of communication stations for an indication of the functionality of primary (FLCC) and secondary (FLDD) communication path. If these flags are set, the respective communication path is non-functional. For example, if the value of the communication station is StON and C flag FLC is is set it means that only the secondary communication path is functional.
For lower versions of D2000 only partial detection of a broken communication path is available when using the parameter the Strict Redundancy Connection Signalisation parameter.
The Browse button opens a browsing dialogue for the station address. If the communication is functional, a dialogue with the ASDU addresses received so far is displayed. The Refresh button can be used to clear the list of received ASDU addresses.
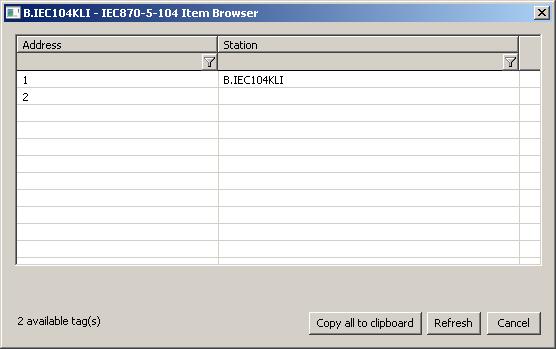 Image Added
Image Added
Station protocol parameters
Table 3
| Full name | Meaning | Unit | Default value |
|---|
|
Asymetric Asymmetric Redundancy Mode Periodicity | The parameter can be used for a TCP Redundant line with defined backup servers (see the parameters AS1, AP1, BS1, BP1 ..). |
Non| The non-zero value of ARMP parameter means that if this number of ASDUs is received (after a successful reconnect), both |
connection | connections are checked whether they're not going through the same network ( |
IP a | IPs and ports defined in the line settings or ASx:APx and BSx:BPx). If they do, the connection to the standby server (see |
the parameter Asymetric following next IP address will be tried (i.e. Alternate Server 1, Alternate Server 2, line IP, Alternate Server 1, etc).
Note: When the parameter |
Asymetric | Asymmetric Redundancy Mode Periodicity is enabled, the second connection is established to "B-Alternate Server 1":"B-Alternate Port 1" and not to the IP address and port defined for the line after running the |
process | D2000 KOM process (so that it wouldn't be immediately closed). | - | 0 |
|
Asymetric Asymmetric Redundancy Mode Slave Detection |
Detection | The detection method of standby server for |
Asymetric least significant bit - bit 0 of the 3rd Control Field byte set to 1
- 2 - if ASDU in CauseOfTransmission contains
|
a bit set to 8 | - | 0 |
Alternate Server 1/Alternate Port 1/Alternate Server 2/Alternate Port 2/ | Extension for redundant systems: |
beside | besides the IP address defined in the configuration of the Line, it is possible to define 2 alternative IP addresses. In case of a connection failure, the |
process D2000 KOM process is attempting to connect to the next address in the list.
Note 1: All IP addresses and ports must be defined |
stepwise gradually for one station (i.e. at first "Alternate Server 1", "Alternate Port 1" and then "Alternate Server 2", "Alternate Port 2").
Note 2: These parameters are obsolete |
, | since it's possible to define several IP addresses in the configuration of the line (separated by comma or semicolon, e.g. 10.0.0.1;10.0.0.2). | - | - |
B-Alternate Server 1/B-Alternate Port 1/B-Alternate Server 2/B-Alternate Port 2/ | Can be used when the protocol IEC 870-5-104 is configured for a TCP redundant line. The meaning of the parameters is the same as for the primary connection, but they are valid for the backup connection.
Note 1: All IP addresses must be defined stepwise for one station (i.e. at first "Alternate Server 1", "Alternate Port 1" and then "Alternate Server 2", "Alternate Port 2").
Note 2: These parameters are obsolete |
, | since it's possible to define several IP addresses in the configuration of the line (separated by comma or semicolon, e.g. 10.0.0.1;10.0.0.2). | - | - |
| Confirmation of control ASDU.
If Command Confirm=0, the |
process | D2000 KOM process is not waiting for confirmation of control ASDU from the partner station using |
backward sending other | a different CauseOfTransmission |
, consider | considered to be confirmed |
, there is received a packet containing the corresponding ReceiveSequenceNumber is received.
If Command Confirm=1, the |
process D2000 KOM process is waiting for confirmation with CauseOfTransmission=7 (Activation Confirmation).
If Command Confirm=2, the |
process D2000 KOM process is waiting for confirmation with CauseOfTransmission=10 (Activation Termination).
If Command Confirm=3, the |
process D2000 KOM process waiting for confirmation with CauseOfTransmission=7 or 10 (if both of them are received, only the first of them is taken into account).
Having received corresponding confirmation means that writing is finished (the Transient attribute of written value is |
evaluated cleared and the "Wait Timeout Tn" timeout stops elapsing).
If |
there is received other CauseOfTransmission, as the process | a CauseOfTransmission different from the one the D2000 KOM process expects |
for, is received, it will be ignored.
Writing is successful |
, if the received ASDU contains the P/N bit set to 0. Otherwise, writing is unsuccessful.
Value from received ASDU is |
backwardly | written back into a particular I/O tag and is sent to the system. E.g. if an ASDU of type 50 (short floating point) with the value of 1200.0 is sent and the partner station sends an ASDU of type 50 as a reply, P/N bit=0, the value of 999.0 (e.g. due to physical limitations of the given parameter) as a response, then the value |
is to be send by process D2000 KOM | will be sent to the D2000 system by the D2000 KOM process. | - | 1 |
|
The These parameters are intended for the configuration of a communication station for communication between two D2000 systems |
with using ASDU 252 - D2000 Unival (Ipesoft's implementation). more ... |
| A mask for debug levels of input data. The meaning of bits is as follows: |
1- 0.bit - displays a number of incoming values during General Interrogation
|
2- 1.bit - displays all incoming values
|
3- 2.bit - balanced mode: requesting Interrogation command was received
| - | 0 |
| A mask for debug levels of output data. The meaning of bits is as follows: |
1- 0.bit - balanced mode: displays a number of outgoing values during General Interrogation
|
2- 1.bit - displays all outgoing values
| - | 0 |
| Extension for ABB MicroScada: If End of initialization=1, having received ASDU 70 (End of initialisation) resends Interrogation Command and/or Counter Interrogation Command. | - | 0 |
| If Force Master Time=True, then the |
process | D2000 KOM process will accept ASDU 103 (Clock synchronisation command) with CauseOfTransmission=6 [Activation] or 3 [Spontaneous] from the server and |
saves it will save the time difference between the server's time and its time. If CauseOfTransmission=6, it replies with CauseOfTransmission=7 [Activation Confirmation].
Then the time of all values, which are received with timestamps, is decreased by this difference, i.e. a correction to the time of D2000 is made.
The parameter allows |
to solve | solving the problem when some values from the server are received with the timestamps and others without timestamps and times from D2000 and server differ. In this case, without parameter Force Master Time=True the values received without timestamps are |
specified | tagged by D2000 time and the values with the timestamps are |
specified | tagged by the server time. With parameter Force Master Time=True the time, sent by the server, is corrected to D2000 time using the time difference, which is computed from the received ASDU 103 (Clock synchronisation command). | - | False |
| Extension for ABB MicroScada: If Force Slave Time=True, then the |
process D2000 KOM process will accept ASDU 103 (Clock synchronisation command) with CauseOfTransmission=6 [Activation] or 3 [Spontaneous] from the server and saves the time difference between server time and its time. If CauseOfTransmission=6, it replies with CauseOfTransmission=7 [Activation Confirmation].
Then all values, which are received with no timestamps, are to be marked by the current time plus time difference (if the station is not configured to use the communication computer time).
|
The parameter | The Force Slave Time parameter allows |
to solve | solving the problem, that |
having sent | after receiving ASDU 100 or 101 |
there are sent values with no timestamps, but they | sends "interrogated" values without timestamps. However, during the communication, the values are sent with the |
time stamps during the communication - problems can occur, when there are not synchronized | timestamps - which may cause problems if the times of the MicroScada and the D2000 system are not synchronized. | - | False |
| If GI Send New=True, then the |
process the command | the General Interrogation command, sends also values with more recent times than |
is | the time when the command |
is | was received. The value of |
the parameter | the GI Send New parameter must be True to send values with |
more recent times using the command General Interrogation| future times as a reply to the General Interrogation command. | - | False |
Ignore Control Field 3 bit 0 | Determines |
behaviour| behavior, when ASDU contains Control Field with the lowest bit ( |
10) of the 3rd-byte set to 1.- if Ignore Control Field 3 bit 0=False (default), ASDU content is to be processed
- if Ignore Control Field 3 bit 0=True, ASDU content is to be ignored
The feature can be used when creating a redundant TCP connection (TCP Redundant line + IEC 870-5-104 protocol). |
Hot | The active server should send ASDU with the lowest bit of the 3rd Control Field byte set to 0, |
standby | the passive server should send ASDU with the lowest bit of the 3rd Control Field byte set to 1. | - | False |
Ignore Invalids on Interrogation | Balanced mode: if this parameter is set on a station, the |
process | D2000 KOM process will not send as a reply for ASDU 100 and 101 (Interrogation / Counter interrogation command) values of I/O tags which are Invalid or Unknown. |
Parameter | The parameter can be used e.g. when controlling |
, | if sending Invalid values causes a breakdown of control. | - | False |
| Determines |
behaviour| behavior, when ASDU contains |
bit 8 (testthe highest 7th bit (Test) set in CauseOfTransmission.- if Ignore Tests=0 (default), ASDU content is to be processed
- if Ignore Tests=1, ASDU content is to be ignored
- if Ignore Tests=2,
|
weak - a Weak attribute is to be set
The feature can be used for creating a redundant TCP connection (TCP Redundant line + IEC 870-5-104 protocol). |
Hot | An active server should send ASDU with the Test bit=0, |
standby | a passive server should send ASDU with the Test bit=1. | - | 0 |
| If Ignore Unknown Addresses=TRUE, the |
process | D2000 KOM process will not show an error on its console or write it into log files in case that incoming value has the address not matching any of the addresses of I/O tags defined in the D2000 system. | - | False |
| Balanced mode: After connecting to the IEC104 server, the |
process | D2000 KOM process sends the values of all variables without waiting for ASDU 100 or 101 [Interrogation/Counter Interrogation Command] requests. | - | False |
Interrogation Covers Counter Interrogation | Balanced mode: As a reply to Interrogation, also values of I/O tags configured as ASDU 15, 16, 37 (Integrated Totals) are sent. (They are normally requested by ASDU 101 [Counter Interrogation].) | - | False |
Interrogation WithOut Timestamps | If Interrogation WithOut Timestamps=True, then values sent as a response to ASDU 100 [Interrogation Command] in balanced mode will be sent as ASDUs without timestamps.
For example instead of ASDU 2 (Single-point information with time tag) or ASDU 30 (Single-point information with time tag CP56Time2a) ASDU 1 (Single-point information) will be sent.
This |
behaviour | behavior is suitable in the situation when the values have been invalidated as a result of communication error and after the communication is reestablished the values come with old timestamps which causes problems in the archive (if the values change only rarely, calculated archives depending on them will be also invalid till a new value arrives). At the same time, this behavior is strictly according to the IEC standard, which says that the response to Interrogation should not use ASDUs with time stamps. | - | False |
| Sending window size i.e. number of I-frames sent by the |
process | D2000 KOM process without receiving a confirmation (S-frame or I-frame). According to the standard, the default value is 12. | - | 12 |
| The parameter may be used to read |
archive historical values for communication with LFC terminals or other devices that support ASDU 250 defined by Ipesoft. Unlike the primary use of ASDU 250, the LFC terminal can only transmit one value for interval begin time, while the end time is ignored. The value |
is to be received as ASDU 251 but as one of the standard ASDU with |
time stamp. What is morea timestamp. Moreover, the values (with the same |
time stamptimestamp) of other tags may be received along with the value of the required tag. LFC terminal does not send ASDU 250 (with CauseOfTransmission=7, 10) as part of the response to ASDU 250 and the |
process treats process considers the reading |
as done as soon as it gets the value of the required |
IO Reading archive values is considered as unsuccessful but connection to LFC terminal is not closed until If the value is not received |
in within the time defined by the |
parameter T1T1 parameter, the reading of historical value is considered unsuccessful, however, the connection to the LFC terminal is not closed. If the values of other I/O tags are received along with the value of the required I/O tag, they must be received before the value of the required tag is received, otherwise, they are not considered as |
archive historical values (because reading is |
consider considered to be done after the value of required I/O tag is |
donereceived).
Example: After the request for the values of I/O tags with the addresses of 1,2..16, the LFC terminal always sends the values of all the tags in the order of 1,2..16, therefore we must |
require ask for the value of the I/O tag with the address of 16. If the parameter is not defined or LFC History=0, reading |
archive are is defined by Ipesoft (D2000 IEC104 Server partner is assumed). If LFC History=1, then the value |
the time of which belongs into the time interval specified by the action GETOLDVAL (and transferred through ASDU 250) is considered to be historical |
one is be stored in and but not to the I/O tag, etc.) if its timestamp belongs to the time interval specified by the GETOLDVAL action (and is received as ASDU 250). If LFC History=2 then |
see description above behavior is as for LFC History=1 except if the |
time timestamp of the received value is |
later newer than the timestamp of the current value of the I/O tag, the received value |
is to process D2000 Server process as a new one and not as a historical one. Note: When reading |
archive historical data of the LFC terminal, |
the GETOLDVAL may not contain the station name ( |
the statIdent) but the I/O tag name. If the action contains a station name, ASDU 250 |
is to will be sent for one I/O tag only. | - | 0 |
| Maximum acceptable time difference (in hours) between the time of received data and the time of |
process | the D2000 KOM process. If the partner station sends a value with a timestamp older or |
latter then | later than MDT hours, the value |
is to | will be ignored and an error |
report is to generated | written into the line's trace file. If |
the parameter | the Maximum Time Difference parameter is a negative value (e.g. Maximum Time Difference=-5), |
there is used | its absolute value is used and the system |
tag is | will be generated as well. If the parameter's value is zero, the time difference |
is to | be checked. | hrs | 0 |
| If the parameter is True, then the status |
bit byte of incoming ASDUs is ignored and not saved into the |
flags FA.FHH flags. Flags of output I/O tags are also ignored and they are not |
set bitbyte. | - | False |
| Order of sending ASDU 100 [Interrogation Command] during connection initialization. If |
OIC<OCIC| Order of IC < Order of Counter IC, ASDU 100 will be |
send OIC| Order of IC=0, ASDU 100 will not be sent. The parameter can be set extra for each station. | - | 1 |
| Order of sending ASDU 101 [Counter Interrogation Command] during connection initialization. If Order of Counter IC < Order of |
Counter | IC, ASDU 101 will be sent before ASDU 100. If Order of Counter IC=0, ASDU 101 will not be sent. The parameter can be set extra for each station. | - | 2 |
|
Number | The number of repetitions, after which the IP address not responding to the ping is |
known as considered non-functional.
See |
the parameter other than then | it defines the timeout (in milliseconds) of server response for ping (ICMP echo) packet. In the background, |
the process | the D2000 KOM process sends ping packets to all defined IPs - Line IP address and Alternate Server 1, Alternate Server 2, B-Alternate Server 1, B-Alternate Server 2. If some of the addresses |
does response for | respond Ping Count-times, it is designated as non-functional. If the line is connected to this IP address, the connection is terminated. |
New | A new connection is established |
just | only to a functional IP address. If the parameter Ping TimeOut=0, sending the ping packet to IP addresses is disabled. | ms | 0 |
| A delay between receiving StartDT Con response and sending Interrogation Command and/or Counter Interrogation Command in the |
initialisation | initialization phase. | ms | 0 |
| A delay before connecting |
and | or reconnecting (after starting the |
process | D2000 KOM process and after communication break-up). | ms | 0 |
|
Initial | The initial Send sequence number after the TCP connection is established. According to the standard, having established the connection the Send sequence number is set to 0, other than zero could be appropriate e.g. for testing. | - | 0 |
|
Number The number of values that must be identical in the Smart Redundancy Minimum mode to consider the connections synchronized. The following parameters are taken into account:- I/O tag and station addresses
- value
- time
- flags (
|
FAFH process the | identical values go via the both connection of the TCP Redundant line in the same order. The |
process | D2000 KOM process is attempting to synchronize the connections. If |
the D2000 KOM process receives | a number of identical values defined by |
the parameter synchronisation synchronization is done, the value that comes earlier is taken into account, the same value via the other connection is ignored.
When the TCP connection is broken or two different values |
comes synchronisation synchronization is broken.
Compared to the detection |
hotstandby | passive partner by means of "Ignore Tests"/"Ignore Control Field 3 bit 0", an advantage is that after communication failure with the |
hot | active server, there is no data loss |
, | because the communication is still working with the |
standby | passive partner and the D2000 KOM process is attempting to recover the connection with the |
hot active server.
Having recovered the connection (if the second connection is working), there are ignored the values which are acquired by the command General Interrogation. | - | False |
| If True, after changing the status of |
process process | D2000 KOM process is connected to) from Hot into Standby state |
(| (in a redundant system), connection with the IEC104 server will not be closed. | - | False |
Standby Set Control Field | If TRUE, after changing the status of |
process process | D2000 KOM process is connected to) from Hot to Standby state (in |
the | a redundant system), the lowest bit of the 3rd Control Field byte of information APDUs (APDU containing data or commands) will be set to 1 instead of the standard value of 0. The |
behaviour | behavior does not strictly follow the standard and we recommend |
you to use parameter | Standby Set Test Bit parameter instead of this parameter if it is possible. | - | False |
| If True, the Cause Of Transmission will have a Test bit set if the |
process | D2000 KOM process is connected to the Standby server (in a redundant system) or is a passive instance. | - | False |
| If True, after changing the status of |
process process | D2000 KOM process is connected to) from Hot into Standby state (in a redundant system), |
there | the new values will be sent |
new values| to the IEC104 server. | - | False |
Station Communication Error |
Number | The number of unsuccessful connection attempts after the communication failure after which the station status is changed to St_CommErr. For redundant lines, the communication must be either failed on both TCP connections or only a TCP connection to |
standby-server must be the | such a server are ignored. | - | 2 |
| The status of all stations on the line is changed into the |
state St_HardErr state if the following conditions are met:- number of unsuccessful connection attempts reaches the value of
|
ST_HE - Station Hard Error or higher,
- an attempt to restore the communication lasts at least the time defined by the
|
parameter - Time filter parameter (maximum value of all stations on the line is taken into account),
- for redundant lines, the communication must be either failed for both TCP connections or
|
there is working only standby- the the - such a server are ignored.
| - | 5 |
Stop Data Confirm Ignored | Workaround |
due to | for the MetsoDNA server error: after connecting to the IEC870-5-104 server from the |
firm | Metso company, the server sends a StopDT Con U-frame |
STOPDTcon confirms interruption in | confirming the end of sending data). If the |
parameter | Stop Data Confirm Ignored parameter is True, this frame will be ignored and the communication will continue. Without the |
parameter | Stop Data Confirm Ignored parameter set, the connection will be aborted. | - | False |
Strict Redundancy Connection Signalisation | Determines |
behaviourbehavior, when the protocol is used for TCP Redundant line- if Strict Redundancy Connection Signalisation=False, the line is
|
in order - ok (TRUE), if at least 1 connection is working
- if Strict Redundancy Connection Signalisation=True, the line is in error state (FALSE), if both connections are working
| - | False |
| The parameter is implemented for use on OpenVMS platforms only. If it is other than zero, then defines the timeout (in seconds) for opening a new connection to the IEC104 server. For OpenVMS, the default value is 75 seconds, for Windows, it is 20 seconds. When the timeout expires, the connect procedure returns an error. | - | 0 |
| Setting Tcp No Delay parameter causes low-level socket option TCP_NODELAY being set, thus turning off the default packet coalesce feature. | - | False |
|
Number | The number of received I-frames, after which the |
process a | an S-frame confirmation. According to the standard, the default value is 8. The relation W < K must be true, the standard recommends W = 2/3 * K. | - | 8 |
| Timeout for receiving the confirmation of a sent I-frame (either confirmation within the I-frame or the S-frame itself) or a U-frame. If the |
process get in the time T1| T1 time, it closes the TCP connection. According to the standard, the Wait Timeout T1 default value is 15000 ms. | ms | 15 000 |
| Timeout for sending the confirmation of a received I-frame. Wait Timeout T2 < Wait Timeout |
T2 other | another I-frame (which confirms the received I-frame) is not sent |
in the time | within Wait Timeout T2 time since the I-frame was received, |
so process a | an S-frame confirming the received I-frame to the partner. According to the standard, the Wait Timeout T2 default value is 10000 ms. | ms | 10 000 |
| Timeout for sending test frames ( TEST ACT U-frame |
TEST ACT| ). If no data are sent in any direction for a long time, |
an TEST ACT to process D2000 KOM after | expiration of the Wait Timeout T3 time |
and there | by the D2000 KOM process, and a TEST CON U-frame is expected ( |
in the | within Wait Timeout T1 time after sending) |
receiving a U-frame TEST CON| . If the Wait Timeout T3 on the partner side is set to a lower value, it sends the test frames, and the |
process reply process replies to them. According to the standard, the Wait Timeout T2 default value is 20000 ms.
Setting the value to 0 disables sending test frames. | ms | 20 000 |
| Timeout for receiving the confirmation of a sent value. Receiving e.g. S-frame with RSN (Receive Sequence Number) confirming, that the other party received the previous I-frame doesn't mean, that the I-frame was processed. |
In Timeout Tn| Timeout No answer time interval, the |
process | D2000 KOM process waits for receiving the response (e.g. after sending ASDU with TypeIdentificator=45 [Single Command] with CauseOfTransmission=6 [Activation] |
there is expected , the receiving of Single Command with CauseOfTransmission=7 [Activation Confirmation] is expected.
After the expiration of the Wait Timeout Tn, the |
process | D2000 KOM process closes the TCP connection. | ms | 60 000 |
Defined parameters, except for Order of IC, Order of Counter IC, and Force Slave Time, are valid for the entire line - i.e. it is enough to define them for one station on the line.
...
TELL commands
...
Table 4
| Command | Syntax | Description |
| STCOMMAND | STCOMMAND StationName DISCONNECT |
Tell | TELL command closes immediately the active TCP connections of the communication line (a parent of "StationName"). Then the connection is restarted and |
re-connected| reconnected. |
| STWATCH | STWATCH StationName | TELL command sends Interrogation Command and/or Counter Interrogation Command to the station (depending on station parameters). |
Examples of configurations
...
Example 1: Client communicating with the server SrvA
...
on a redundant network.
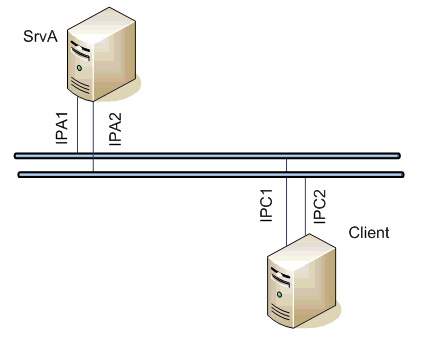 Image Modified
Image Modified
Server settings - line: TCP/IP-TCP(Host ALL, port 2404)
- protocol: IEC 870-5-104 Server
- parameters: none
| Client settings - line: TCP (Host IPA1, IPA2, port 2404)
- protocol: IEC 870-5-104
- parameters: none
|
If a communication segment drops out (e.g. IPA1 failure) the client establishes a connection with the server SrvA using the address IPA2.
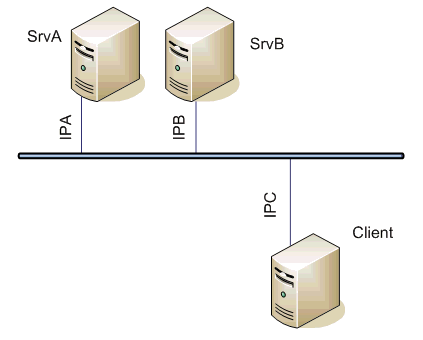 Image Modified
Image Modified
Servers' settings - line: TCP/IP-TCP (Host myName or ALL, port 2404)
- protocol: IEC 870-5-104 Server
- parameters: SKO=TRUE; SWV=False; SSCF3=True;
| Client settings - line: TCP/IP-TCP Redundant (Primary host IPA, Secondary host IPB, both ports 2404)
- protocol: IEC 870-5-104
- parameters: SKO=True;ICF3=True;
|
The client communicates both with the hot server and with the standby active and passive server, connection with the standby passive server continues to be open, but new values are send sent by the hot active server only.
Note: If a symbolic name myName is used in the configuration of the IEC104 Server, it should be defined as IPA in the hosts file of the 1-st server and as IPA and IPB in the hosts file of the 2-nd server as IPB.
...
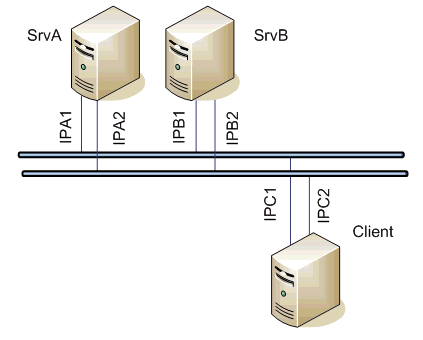 Image Modified
Image Modified
Servers' settings - line: TCP/IP-TCP(Host ALL, port 2404)
- protocol: IEC 870-5-104 Server
- parameters: SKO=True; SWV=False;SSCF3=True;
| Client settings - line: TCP/IP-TCP Redundant (Primary host IPA1, IPA2, Secondary host IPB1, IPB2, both ports 2404)
- protocol: IEC 870-5-104
- parameters: ICF3=True
|
The client communicates with both the servers. If one network segment drops out (e.g. IPA1 failure), the client establishes a connection with the SrvA server SrvA using the IPA2 address IPA2.
...
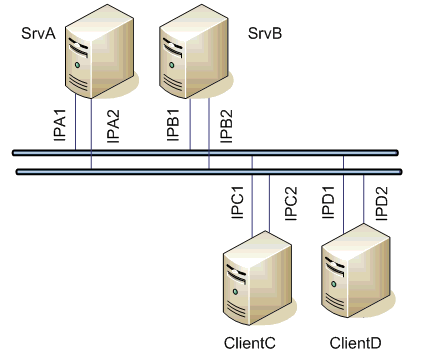 Image Modified
Image Modified
Servers' settings - line: TCP/IP-TCP(Host ALL, port 2404)
- protocol: IEC 870-5-104 Server
- parameters: SKO=True; SWV=False;SSCF3=True;
| Clients' settings - line: TCP/IP-TCP Redundant (Primary host IPA1, IPA2, Secondary host IPB1, IPB2, both ports 2404)
- protocol: IEC870-5-104
- parameters: SKO=True; SWV=False;ICF3=True
|
The clients communicate with both the servers. If one network segment drops out (e.g. IPA1 failure), the clients establish a connection with the SrvA server SrvA using the IPA2 address IPA2. After switching the hotactive/standby passive statuses of the clients ClientC and ClientD clients, they keep communicating with the servers, however, but only the active client only sends commands. New values are sent by the active server.
I/O tag configuration
...
Possible I/O tag types: Ai, Ao, Ci, Co, Di, Dout, Qi
- I/O tag address is mapped on to the Information object address, i.e. it has 3 bytes and must within the range of 0..16777215.
- Input tags must be of particular types (Ai, Ci, Di, Qi) for received ASDU, see the see table 1 and also the table 2 in the balanced mode.
- For a particular type of output tag (Ao, Dout, Co), it is necessary to set a an ASDU type, that has to be used, see the see table 2.
- Archive for providing historical values: if the client asks for historical values through ASDU 250, the server sends:
- the values of the historical value specified by this input entry field,
- if the input entry field is not filled, then the values of the historical value that archives the I/O tag,
- if given the specified historical value does not exist, then the values of the I/O tag that archives the control object of given the specified I/O tag,
- if the control object does not exist (or the archive is not available), the server returns an error.
Specification of a historical value allows user to set configuring e.g. sending 10-minutes averages instead of sending all changes of given I/O tag.
Literature
...
| Info |
|---|
|
You can read blogs about the IEC 870-5-104 protocol (for now, in Slovak language only): |
Document revisions
...
- Ver. 1.0 – July 30th, 2003
- Ver. 1.1 – November 19th, 2003: extension of supported ASDU, new parameters
- Ver. 1.2 – March 20th, 2004: added ASDU for reading archive data
- Ver. 1.3 – June 20th, 2004: extension - redundancy support
- Ver. 1.4 – December 1st, 2004: extension - support of balanced mode
- Ver. 1.5 - December 12th, 2012 - updating, tell TELL commands
...




