...
Optimisation of old values processing coming from communication (automatically or as a result of TELL command GETOLDVAL) or values of remote tags (as a result of TELL command GETOLDVAL).
If the checkbox is checked, during processing of old value the archive database is queried whether the value is already present there. If it exists, the value is discarded (and recalcs of statistical or calculated archived values which use this primary archive value are not performed either).
Note: Optimisation is useful e.g. for archiving of I/O tags from communication using the protocol IEC62056-21:2002 File I/O. Its communication files contain several historical values (which KOM process sends as old values) and one new value for every I/O tag.
...
- Periodical - writing values into the archive is periodical. The archiving process in defined time moments stores the archive object value into the archive. Timestamp (the value time) is not given by the occurrence time of the archive object value, but by the time of the value storing into the archive.
Reading the values stored periodically by means of D2000 system (ESL: GETARCHARR, GETARCHVAL, D2000 ObjApi: GetArchivData, D2000 VBApi: VBApiGetArchData, D2000 WorkBook) follows the rule that the archive object value out of time moments given by the period, is unknown (invalid). The result of the data reading is therefore given by the oversampling and the begin (BT) and end (ET) time as follows:- oversampling (step) = 0
The reading results are all the values, time of which belong into the interval <BT, ET>. - oversampling (step) <> 0
The reading result is the value array with timestamps continuously:
BT+0*step, BT+1*step, BT+2*step, ..., BT+N*step.
The number of values is given by the end ET of the time interval. The array value without a record with the same timestamps in the archive is invalid. The value with such a record is filled according to it. The above facts imply, that when reading periodical data, it is necessary (advisable):- to adjust BT exactly for some of the object archiving moments given by the period and time offset of the archiving.
- oversampling value (step) must be an integer multiple of the archiving period.
- ET = BT + (N-1)*step, where N is an integer number: the number of values in the final selection.
Note: The statistical archive, from the reading point of view, acts periodically.
- oversampling (step) = 0
On value change - just value changes of the archive object undetected by the value filter are stored into the archive.Kotva sa_filter1 sa_filter1
Reading of values stored by using a filter by means of D2000 system (ESL: GETARCHARR, GETARCHVAL, D2000 ObjApi: GetArchivData, D2000 VBApi: VBApiGetArchData, D2000 WorkBook) follows the rule that the archive object value at any time (t) is given (equal) by the last historical value before the given time (t). The data reading result is therefore given by the oversampling and the begin (BT) and end (ET) time as follows:- oversampling (step) = 0
The reading result are all the values, time of which belongs to the interval <BT, ET> and 1 value before BT time, in case there is no value exactly equal with BT time in the archive. - oversampling (step) <> 0
The reading result is a array of values with timestamps continuously:
BT+0*step, BT+1*step, BT+2*step, ..., BT+N*step.
The number of values is given by the end ET of the time interval. The array value without any record in the archive with the same timestamp will be given by the last value before the time required.
- oversampling (step) = 0
...
If the option Publish values is checked, then the historical value publishes its last archived value in the way, that depends on the object defined by the parameter Historical value as follows:
- For a simple HV - the object of Historical value type you are configuring gets the last value (if the parameter Historical value is not defined).
- When archiving an one-column HV - last archived values of individual items are filled into the relevant items of the column of a Structured variable type object defined by the parameter Target object.
- When archiving a structured HV - last archived values of individual items are filled into the relevant items of a Structured variable type object defined by the parameter Target object.
...
| Function | Meaning |
|---|---|
| None | No function. |
| Average * | Arithmetical average of all archive object values. |
| W-Average * | Weighted arithmetical average of all archive object values. |
| Integral | Time integral of historical values. |
| Sum | Sum of archive object values. |
| Maximum | Maximum of archive object values. |
| Minimum | Minimum of archive object values. |
| Count | Number of archive object values. |
| Filter | Applying a filter for value storing into the statistical archive. |
| Increment | Increment between values. If the newer value is greater than the older one, then the difference between the values, otherwise the newer value (the function is useful to process counter values that oveflow and start from zero again). |
| Delta | Delta between values. Parameter (Compare value) – weight of impulse. The result will be the impulse multiplied by its weight. Weight of 1 will ensure standard behaviour. |
| EcoAvg | Average of the object values within the elapsed time period (Period parameter in Time parameters tab) according the methodology based on flags of individual values entering the statistic. The same purpose is fulfilled by the function %EcoAveR, that is implemented for eval tags. |
| GT Time (>) | The function calculates the time, during which the value of the historical value was greater than the entered constant (Compare value). |
| GE Time (>=) | The function calculates the time, during which the value of the historical value was greater or equal to the entered constant (Compare value). |
| LT Time (<) | The function calculates the time, during which the value of the historical value was lower then the entered constant (Compare value). |
| LE Time (<=) | The function calculates the time, during which the value of the historical value was lower or equal to the entered constant (Compare value). |
| Maximum in time interval | Obsolete - do not use! |
| Minimum in time interval | Obsolete - do not use! |
| Number of local maximums | |
| Number of local minimums | |
| Sum of positive values | Sum of positive values of the historical value. |
| Sum of negative values | Sum of negative values of the historical value. |
| Average of positive values | Arithmetical average of positive values of the historical value. |
| Average of negative values | Arithmetical average of negative values of the historical value. |
| Sum of increments | Sum of increments for given time interval. If the new value is less than the old value, the increment is 0. Parameter (Compare value) – weight of impulse. The result will be the impulse multiplied by its weight. Weight of 1 will ensure standard behaviour. |
| Time slice** | Object value in given time moments. |
| Sample standard deviation | The function calculates the sample standard deviation of all values of the archive object. |
...
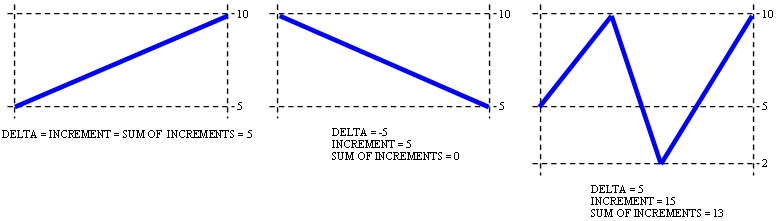
The difference among the functions INCREMENT, DELTA and SUM OF INCREMENTS is shown in the following figures.
In the first case, all three functions are equal to 5 (10-5)
In the second case
- DELTA = 5-10 = -5
- INCREMENT = 5 (because 5 <10)
- ADDITIONAL AMOUNT = 0 (because 5 <10)
In the third case
- DELTA = (10 - 5) + (2 - 10) + (10 - 2) = 5
- INCREMENT = (10-5) + 2 (because 5 <10) + (10-2) = 15
- ADDITIONAL AMOUNT = (10-5) + 0 (because 5 <10) + (10 - 2) = 13
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...