...
DLMS
...
COSEM communication protocol
Supported device types and versions
Communication line configuration
Station configuration
Station parameters
Settings of transmission parameters
I/O tag configuration
I/O tag address
Literature
Changes and modifications
Document revisions
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
This protocol executes implements a serial communication with the devices by binary HDLC protocol according to the DLMS/COSEM standard.
Two modes of addressing of I/O tags are supported:
- "Short Name (SN) referencing" using 16-bit object addresses
- "Logical Name (LN) referencing" using 6-byte OBIS codes
Communication was tested with the following devices:
- EMH LZQJ (SN referencing)
- Landis ZMD400 (SN referencing)
- Iskraemec Iskra Iskraemeco Iskra MT880-M (LN referencing)
- ADDAX NP73E.2-18-1 (LN referencing)
Protocol The protocol supports time synchronization, the period is configured in the station configuration dialog.
...
- Supported line categories: Serial, SerialOverUDP Device Redundant, TCP/IP-TCP, TCP/IP-TCP Redundant, MOXA IP Serial Library, RFC2217 Client, MODEM.
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
- Upper MAC Address is used for addressing a Logical Device addressing, i.e. separately addressable entity within the physical device.
- Lower MAC Address is used for addressing of a Physical Device addressing, i.e. multi-drop address on the line.
Upper MAC Address is required. An implicit value, which is set when missing the station address is missing, is a reserved address Upper MAC Address = 1 (Management Logical Device).
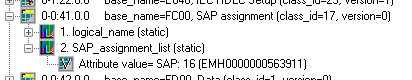
In ordinary situations, when the physical device is identical with the logical one (one physical device = one logical device), you need not change this address does not need to be changed. If the physical device integrates more logical devices, you should monitor the registry content or "0-0:41.0.0" register of "SAP assignment" class (class_id=17, attribute 2 "SAP_assignment_list") in the dialog box "DLMS SN Object List" dialog box. This dialog box shows the list of logical devices that are integrated in the a physical one.
This is the example of a value representation of the attribute "SAP_assignment_list" attribute of the class "SAP assignment" class in the device which contains one logical devices device with Upper MAC Address 16.
See also the protocol parameter "Client MAC address" and a document "DLMS UA 1000-2 Ed. 7.0", chapter 8.4.2.3 "Reserved special HDLC addresses".
...
Note: for Iskraemec Iskra MT880, Upper MAC Address = 1, Lower MAC Address = 16 + last two digits of the serial number (if, for example, the serial number is 72211943, then Lower MAC Address = 16 + 43 = 59).
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Communication Communication station configuration dialog box - Protocol parameters tab.
It They influences some optional protocol parameters. The following station protocol parameters can be set:
Table 1
| Parameter | Meaning | Unit / sizeSize | Default value | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| --- DLMS/HDLC parameters --- | ||||||||||||||||
| Setting The setting of the "Application Context" parameter of the DLMS/COSEM protocol. Short_Name_Referencing_No_Ciphering context is supported for "Short Name (SN) referencing". Logical_Name_Referencing_No_Ciphering context is supported for "Logical Name (LN) referencing". Next The next two contexts with encryption are not supported. | Logical_Name_Referencing_No_Ciphering Short_Name_Referencing_No_Ciphering Logical_Name_Referencing_With_Ciphering Short_Name_Referencing_With_Ciphering | Short_Name_Referencing_No_Ciphering | |||||||||||||
| HDLC MAC address of a client (i.e. D2000 KOM process). A The default value is 10H which is the reserved value "Public client". See "DLMS UA 1000-2 Ed. 7.0" document, chapter 8.4.2.3 "Reserved special HDLC addresses". | 0 .. 7FH | 10H | |||||||||||||
| Maximal The maximum length of one HDLC frame packet on the receiver from the device's side. When occurring some communication problems occur (e.g. checksum error and so onetc.), we recommend you to decrease decreasing the value of this parameter. | 250 | ||||||||||||||
| Maximal The maximum length of one HDLC frame packet on the transmitter to the device. When occurring some 's side. When communication problems occur (e.g. checksum error and so onetc.), we recommend you to decrease decreasing the value of this parameter. | 250 | ||||||||||||||
| Maximal The maximum length of PDU (data packet). One PDU can be divided into more HDLC frame packets according to settings of HDLC protocol parameters MaxHDLC Max_info_field_length-receive parameter and and HDLC Max_info_field_length-transmit parameter. Note: a specific electrometer (Landis ZMD400) only accepted a value of 0, otherwise it returned a rejected-permanent error during connection establishment. | 0 .. 65535 | 1200 | |||||||||||||
| A Disconnect request will not be used after the readout of values from a device is finished. During the next readout, a connection establishment phase is omitted (HDLC mode-setting request and AARQ negotiation request). | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||||
| Device password. If entered, the "Low Level Security" authentication with the entered password is used within the AARQ Association Request. | |||||||||||||||
| Ban of online Online address selection from the list of objects, directly on the device, through the DLMS Object List dialog box in the configuration of the I/O tag address will be disabled. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||||
| Several electrometers implement optimization of time data when reading from profiles (class_id=7). The optimization means that only the first row of data contains a timestamp, others contain null. The time stamp timestamp of each row is equal to the previous row's time stamp timestamp plus the value of the capture_period (4) attribute. If the value of this parameter is YES, the value of the capture_period attribute is read prior to reading the profile data. If the value of this parameter is NO, the content of the capture_period attribute is not read, but the KOM process relies on all profile rows to contain timestamps. If this is not the case, the profile data is not read, and the line logs contain error messages "turn on station parameter 'Profile Data Optimization'". | YES/NO | YES | |||||||||||||
| Opening mode of connection with the device. If the device is configured so that it directly uses DLMS/COSEM protocol on the given interface, set this parameter to "Direct HDLC". Mostly (e.g. when reading through IR opto optical interface by an optical reading head) you must open the connection by in IEC protocol in so-called "mode E" and then transfer to HDLC binary protocol (i.e. DLMS/COSEM). "Mode E", according to the specification of IEC protocol, uses the following setting settings of the transmission parameters:
If "Opening Mode" is set on to "IEC mode E", the above-mentioned transmission parameters must be set. As for the Serial communication line, the parameters must be set in the line parameters "Mode 1". See the protocol parameter "Software 7E1". The setting of the baud rate on to 300 Baud is usually not required when using the line of MODEM category. It uses A so-called DTE speed , is used between a PC and a modem. If this speed is higher than 300 Baud, you have to activate the "handshaking" parameter on RTS/CTS in proper line mode. If the parameter value is set to "Direct HDLC" is set, any a dynamic change of transfer transmission parameters is not expected. You can use any Serial line mode and set it by parameter the "Line mode" parameter on the station. More information is mentioned in IEC 62056-21, Electricity metering - Data exchange for meter reading, tariff and load control - Part 21: Direct local data exchange, Annex E: "METERING HDLC protocol using protocol mode E for direct local data exchange". See also chapter "Setting of transmission parameters". | Direct HDLC IEC mode E | Direct HDLC | |||||||||||||
| --- IEC Parameters --- | ||||||||||||||||
| It is an address of a station address (device) and is used only if the Opening mode is set on to "IEC Mode E". The This parameter is optional. It identifies the address of the device at the beginning of communication via the IEC protocol. If this parameter is not defined, the address will not be set at the communication via the IEC protocol and the device will must always respond. If several devices are connected to one line (e.g. RS485 bus), the IEC address of a device must be set so that the devices could be identified and avoid a collision. A device address is max. 32 characters consisting of figures (0...9), capital letters (A...Z), small letters (a...z), or a blank space ( ). Zeros in front of valid figure are ignored (i.e. address 10203 = 010203 = 000010203). "IEC Device Address" is a serial number of the device. This In OBIS addressing, this register has an address "0-0:C.1.0" - Device ID 1, manufacturing number in OBIS addressing. The picture below shows the front panel of the EMH LZQJ device. There is a serial number, i.e. IEC address (563911). If the device contains a display, this value may be usually displayed as you can see on in the picture. | - | ||||||||||||||
| This parameter is used only if the Opening mode is set on to "IEC Mode E". It defines baud rate for the communication through HDLC protocol DLMS/COSEM after the changeover from IEC mode E to the HDLC binary communication. As for the Serial line, this parameter must set the baud rate on to "Mode 2" of the line. AUTO option sets the baud rate according to the value from offered by a device. If this baud rate can not be identified, you should trace check the diagnostic communication logs. You can find there the following messageThe following message can be found there:
and set the baud rate according to it. HDLC binary communication through DLMS/COSEM protocol, unlike the opening IEC step, is realized by different parameters which have to be set in "Mode 2" of the Serial line category:
See also the parameter "Software 7E1" parameter and the chapter Settings of transmission parameters. | 300 600 1200 2400 4800 9600 19200 AUTO | AUTO | |||||||||||||
| It This parameter is used if "Opening mode" is set on to "IEC Mode E". YES option switches Setting it to YES activates an SW emulation of transfer transmission parameters of 7 data bits , and even parity when the transfer the transmission parameters of 8 data bits and none parity are set , none parity (i.e. emulation of 7E1 when 8N1 is set). It enables to the use of the "IEC mode E" option for SerialOverUDP lines that do not support a dynamic changes of transfer transmission parameters. See the chapter Settings of transmission parameters. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||||
| It is This parameter is used if "Opening mode" is set on to "IEC Mode E". Nonzero value activates the sending of a so-called "wake-up message" which activates the communication interface of battery-powered devicedevices. The null characters (0x00) are sent according to the quantity that is characterized defined by the parameter value. The baud rate must be 300 Baud (select configured in "Mode 1" for Serial lines). More information is mentioned available in IEC 62056-21, Electricity metering - Data exchange for meter reading, tariff and load control - Part 21: Direct local data exchange, Annex B: "Wake-up methods for battery-operated tariff devices". | 0 .. 120 | 0 | |||||||||||||
| It is used This parameter is used if "Opening mode" is set on to "IEC Mode E". If a so-called "wake-up" message is activated, this parameter defines a delay after sending of a "wake-up" message even , before the beginning of communication. As for In the case of a Serial line, we recommend to set setting the "WaitTxEMPTY" parameter in particular a specific line mode. According to the document IEC 62056-21, you should set this parameter on between 1,5 up to and 1,7 sseconds. | ms | 0 | |||||||||||||
| --- Send/receive parameters --- | ||||||||||||||||
| Delay The delay after sending the request but before reading the response. | ms | 100 ms | |||||||||||||
| Delay The delay between reading readings of the till response until its completion. | ms | 200 ms | |||||||||||||
| Retry A retry count of reading response till until its completion. | 1 .. 100 | 20 | |||||||||||||
| Delay The delay between the request retry retries if the a communication error communication occurs. | ms | 500 ms | |||||||||||||
| Retry A retry count of request as far as the error communicationa request if a communication error occurs. | 1 .. 20 | 3 | |||||||||||||
| --- Modem parameters --- | ||||||||||||||||
| Phone The phone number for modem connection with a device (only for MODEM lines). | |||||||||||||||
| Maximum waiting time for dial-up modem connection (only for MODEM lines). | 1 .. 600 s | 60 s | |||||||||||||
| Maximum A maximum retry count of dial-up modem connection (only for MODEM lines). | 1 .. 20 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Delay before attempting to dial after an unsuccessful connection attempt (only for MODEM lines). | 1 .. 600 s | 30 s | |||||||||||||
| Time delay after the dial-up connection has been established (only for MODEM lines) but before the beginning of communication. It is used to stabilize the modem connection mostly as far as the for old types of modems. After this timeout passeselapses, all the redundant symbols received data (the residues of AT modem communication) will be read and ignored. | 0 .. 30 s | 5 s | |||||||||||||
| A special initial string of modem 1 (only for MODEM lines). | AT&FE0V1Q0B0X3L0M0 | ||||||||||||||
| A special initial string of modem 2 (only for MODEM lines). Explanation of recommended settings: S37=5 1200bps DTE-DTE speed - limits the speed for modems. Many devices use modems with limited transfer transmission speeds and this setting can speed-up the connection establishment process. Higher transfer transmission speeds must be negotiated individualyindividually. &D2 DTR drop to hangup - for matching with tha the parameter of modem line (line configuration, tab "Modem - parameters", check the option "Use DTR for Hangup" option). S0=0 Disable auto-answer. Auto-answer will not be used. S30=2 20 sec inactivity timeout - automatic hangup after idle timeout expired. Necessary for assuring connection termination after the communication with the last device is over.
| ATS37=5&D2S0=0S7=60S30=2 | ||||||||||||||
| --- Debug parameters --- | ||||||||||||||||
| This parameter activates debug information from the HDLC protocol level. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||||
| This parameter activates full communication monitoring. It enables to display displaying of the I/O tag values and other debug information. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||||
...
To understand the object addressing in DLMS/COSEM protocol, you should know a so-called OBIS standard according to the IEC standard 62056-61 Object Identification system (OBIS), chapter "Annex A - Code presentation".
The "Logical Name (LN) referencing" mode uses OBIS addresses mode directly uses the OBIS address of objects.
The "Short Name (SN) referencing" mode does not use the OBIS address but a 16-bit numerical address in the range of 16 bits..
The individual data entities are presented in so-called COSEM objects (Companion Specification for Energy Metering), which are the instances of COSEM classes (COSEM interface classes, COSEM IC). The Individual types of COSEM classes are specified in the document "COSEM Identification System and Interface Classes, Ed. 10.0", i.e. so-called DLMS Blue Book. Each type of COSEM class has its own identification number ("class_id") and the attributes with the sequence number. Each class has a set of attributes that have sequence numbers. The attribute helps to get facilitates the reading of a specific parameter of given a data entity.
Each instance has its initial beginning SN address (base_name), which is also the address of the first attribute of a class. The "logical_name" is the first attribute of all COSEM classes. When By reading this attribute, a user can obtain an OBIS address of a data entity that is presented by given a specific class can be obtained. The address addresses of other further attributes are calculated according to this formula in the "Short Name referencing" mode:
short_name = base_name + ((attribute_index - 1) * 0x08)
The attributes can be static or dynamic depending on whether their value is static (i.e. unchanging, set by a producer or in the configuration of the device) or dynamic (changing). In the D2000 System, we recommend to configure configuring only the dynamic attributes because , as the own value of the measured data entity is in dynamic attributes. If it is necessary , for the interpretation of a value in a dynamic attribute (mostly the "value" attribute), other static or dynamic attributes can be are read automatically. See more information in the section Supported COSEM classes.
In the following tables, you can find the supported COSEM classes. The attributes that represents own value represent the value of the data entity (i.e. value that is important for a user) are characterized marked as "Yes, the value of an entity" in the column "Support in D2000". The static attributes are read automatically and characterized as "Automatically read".
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Data class_id = 1, version = 0 | Basic The basic class that contains data entity accessible via attribute "value". | ||||
| Attribute | Attribute value type | Attribute description | Support in D2000 | ||
| 1. | logical_name (static) | octet-string (text) | OBIS address of the data entity which is represented by an instance of this class. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 2. | value (dynamic) | CHOICE (see supported types of attribute values) | Own The value of the data entity. | Yes, the value of an entity | |
| Register class_id = 3, version = 0 | A class with data entity value that is accessible via attribute "value". The multiply multiplication coefficient, which is gained by a static attribute "scaler_unit", is used automatically. | ||||
| Attribute | Attribute value type | Attribute description | Support in D2000 | ||
| 1. | logical_name (static) | octet-string (text) | OBIS address of the data entity which is represented by an instance of this class. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 2. | value (dynamic) | CHOICE (see supported types of attribute values) | Own The value of the data entity. | Yes, the value of an entity | |
| 3. | scaler_unit (static) | - | Technical units and multiply coefficient. | Automatically read | |
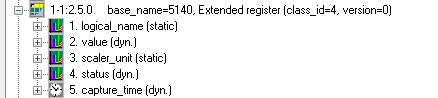
| Extended register class_id = 4, version = 0 | class with data entity value that is accessible via attribute "value". The multiply multiplication coefficient, which is gained by a static attribute "scaler_unit", is used automatically. A time stamptimestamp, which has been gained by the reading of dynamic attribute "capture_time", is added to the entity value. | ||||
| Attribute | Attribute value type | Attribute description | Support in D2000 | ||
| 1. | logical_name (static) | octet-string (text) | OBIS address of the data entity which is represented by an instance of this class. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 2. | value (dynamic) | CHOICE (see supported types of attribute values) | Own The value of the data entity. | Yes, the value of an entity | |
| 3. | scaler_unit (static) | - | Technical units and multiply coefficient. | Automatically read | |
| 4. | status (dynamic) | CHOICE (see supported types of attribute values) | Status of the value. The standard does not specify the interpretation of this value. Mostly, it is a numerical value and you can find necessary information about its interpretation in a device manual. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 5. | capture_time (dynamic) | date_time | Time stamp The timestamp of data entity value. | Automatically read | |
| Demand register class_id = 5, version = 0 | A register for measurement of accumulation energy supply in a given period. See more info in DLMS Blue Book. | ||||
| Attribute | Attribute value type | Attribute description | Support in D2000 | ||
| 1. | logical_name (static) | octet-string (text) | OBIS address of the data entity which is represented by an instance of this class. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 2. | current_average_value (dynamic) | CHOICE (see supported types of attribute values) | Current situation of energy supply that is accumulated since the beginning of the period. | Yes, the value of an entity | |
| 3. | last_average_value (dynamic) | CHOICE (see supported types of attribute values) | Value of energy accumulated in the last period. | Yes, the value of an entity | |
| 4. | scaler_unit (static) | - | Technical units and multiply coefficient. | Automatically read | |
| 5. | status (dynamic) | CHOICE (see supported types of attribute values) | Status of the value. The standard does not specify the interpretation of this value. Mostly, it is a numerical value and you can fined find necessary information about its interpretation in a device manual. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 6. | capture_time (dynamic) | date_time | Time stamp The timestamp of data entity value in the attribute "last_average_value". | Automatically read | |
| 7. | start_time_current (dynamic) | date_time | Time stamp The timestamp of the beginning of accumulated energy measurement with current status in the attribute "current_average_value". | Automatically read | |
| 8. | period (static) | double-long-unsigned | Interval The period of an interval between two changes in data entity value in the attribute "last_average_value". The value is in seconds. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 9. | number_of_periods (static) | long-unsigned | Period count The number of periods that are used for calculation of data entity value in the attribute "last_average_value" attribute. If "number_of_periods" > 1, the "last_average_value" represents "sliding demand". If "number_of_periods" = 1, the "last_average_value" represents "block demand". | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
...
| Clock class_id = 8, version = 0 | Current time and other time parameters. | ||||
| Attribute | Attribute value type | Attribute description | Support in D2000 | ||
| 1. | logical_name (static) | octet-string (text) | OBIS address of the data entity which is represented by an instance of this class. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 2. | time (dynamic) | date_time | Current local time. | Yes, the value of an entity | |
| 3. | time_zone (static) | long | Deviation of local time from UTC in minutes. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 4. | status (dynamic) | unsigned | Time status: bit 0 (LSB): invalid value, bit 1: doubtful value, bit 2: different clock base, bit 3: invalid clock status, bit 4: reserved, bit 5: reserved, bit 6: reserved, bit 7 (MSB): daylight saving active | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 5. | daylight_savings_begin (static) | date_time | Time of passing transition from local time to daylight saving time (DST). | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 6. | daylight_savings_end (static) | date_time | Time of passing transition from daylight saving time (DST) to local time. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 7. | daylight_savings_deviation (static) | integer | Deviation of DS time from standard time in minutes within the range +/- 120 minutes. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 8. | daylight_savings_enabled (static) | boolean | TRUE = DST enabled, FALSE = DST disabled | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 9. | clock_base (static) | enum | Type of source type of exact time: (0) not defined, (1) internal crystal, (2) mains frequency 50 Hz, (3) mains frequency 60 Hz, (4) GPS (global positioning system), (5) radio-controlled | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
...
| SAP assignment class_id = 17, version = 0 | Information about an assignment of logical devices. | ||||
| Attribute | Attribute value type | Attribute description | Support in D2000 | ||
| 1. | logical_name (static) | octet-string (text) | OBIS address of data entity which is represented by an instance of this class. For this case, it is always "0-0:41.0.0". | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 2. | SAP_assignment_list (static) | asslist_type | asslist_type is a structure an array of structures with addresses and a text description "logical device name". It can be only in text format, i.e. I/E O tag must be of TxtI type. See information about the station configuration. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
...
| IEC local port setup class_id = 19, version = 1 | Information about the configuration of communication interface for the communication according to IEC 62056-21. | ||||
| Attribute | Attribute value type | Attribute description | Support in D2000 | ||
| 1. | logical_name (static) | octet-string (text) | OBIS address of data entity which is represented by an instance of this class. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 2. | default_mode(static) | enum | It defines the protocol that is used by a device on the a specific port: (0) protocol according to IEC 62056-21 (modes A…E), (1) protocol according to Clause 8 of DLMS UA 1000-2 Ed. 7.0. Using this enumeration value all other attributes of this IC are not applicable, (2) protocol not specified. Using this enumeration value, attribute 4, prop_baud is used for setting the communication speed on the port. All other attributes are not applicable. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 3. | default_baud (static) | enum | Baud rate in so-called "opening sequence": (0) 300 baud, (1) 600 baud, (2) 1 200 baud, (3) 2 400 baud, (4) 4 800 baud, (5) 9 600 baud, (6) 19 200 baud, (7) 38 400 baud, (8) 57 600 baud, (9) 115 200 baud | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 4. | prop_baud (static) | enum | Baud rate which is suggested by a device. The values are the same as for "default_baud" attribute above. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 5. | response_time (static) | enum | It defines the minimal time between the receiving of a request (the end of request telegram) and the sending of response (the beginning of response telegram): (0) 20 ms, (1) 200 ms | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 6. | device_addr (static) | octet-string | Device address for the IEC 62056-21 protocol. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 7. | pass_p1 (static) | octet-string | Password 1 according to IEC 62056-21. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 8. | pass_p2 (static) | octet-string | Password 2 according to IEC 62056-21. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 9. | pass_w5 (static) | octet-string | Password W5 reserved for national applications. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
...
| IEC HDLC setup class_id = 23, version = 1 | |||||
| Attribute | Attribute value type | Attribute description | Support in D2000 | ||
| 1. | logical_name (static) | octet-string (text) | OBIS address of the data entity which is represented by an instance of this class. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 2. | comm_speed (static) | enum | Communication speed on the proper on a specific port: (0) 300 baud, (1) 600 baud, (2) 1 200 baud, (3) 2 400 baud, (4) 4 800 baud, (5) 9 600 baud, (6) 19 200 baud, (7) 38 400 baud, (8) 5 7 600 baud, (9) 115 200 baud | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 3. | window_size_transmit (static) | unsigned | The maximum number of frames that a device or system can transmit before it needs to receive an acknowledgement from a corresponding station. During logon, other values can be negotiated. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 4. | window_size_receive (static) | unsigned | The maximum number of frames that a device or system can receive before it needs to transmit an acknowledgement acknowledgment to the corresponding station. During logon, other values can be negotiated. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 5. | max_info_field_length_transmit (static) | long-unsigned | The maximum information field length that a device can transmit. During logon, a smaller value can be negotiated. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 6. | max_info_field_length_receive (static) | long-unsigned | The maximum information field length that a device can receive. During logon, a smaller value can be negotiated. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 7. | inter_octet_time_out (static) | long-unsigned | Defines the time, expressed in milliseconds, over which, when any character is received from the primary station, the device will treat the already received data as a complete frame. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 8. | inactivity_time_out (static) | long-unsigned | From the primary station, the device will process a disconnection. When this value is set to 0, this means that the inactivity_time_out is not operational. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
| 9. | device_address (static) | long-unsigned | Contains the physical device address of a device. In the case of one byte addressing: 0x00 NO_STATION Address, 0x01…0x0F Reserved for future use, 0x10...0x7D Usable address space, 0x7E ‘CALLING’ device address, 0x7F Broadcast address In the case of two byte addressing: 0x0000 NO_STATION address, 0x0001..0x000F Reserved for future use, 0x0010..0x3FFD Usable address space, 0x3FFE ‘CALLING’ physical device address, 0x3FFF Broadcast address | Yes, separate I/O tag | |
...
The reading of historical data from load profiles is made by performed using the instances of COSEM classes "Profile generic" (class_id = 7), i.e. the configuration of by configuring an I/O tag in with an attribute 2 ("buffer"). This I/O tag always contains the an invalid valued value in D2000 System but , however, it enables to read reading a buffer of the a specific instance of COSEM class "Profile generic".
| Profile generic class_id = 7, version = 1 | |||||||
| Attribute | Attribute value type | Attribute description | Support in D2000 | ||||
| 1. | logical_name (static) | octet-string (text) | OBIS address of the data entity which is represented by an instance of this class. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |||
| 2. | buffer (dynamic) | array | Data of stored objects. | Yes, see the description above mentioned | |||
| 3. | capture_objects (static) | array | List of object, whose values of which are stored. | Automatic or separate I/O tag of TxtI type | |||
| 4. | capture_period (static) | double-long-unsigned | Period of data storage in seconds. if the value = 0, data are stored by a trigger, not automatically. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |||
| 5. | sort_method (static) | enum | Method to sort data in profile: (1) fifo (first in first out), (2) lifo (last in first out), (3) largest, (4) smallest, (5) nearest_to_zero, (6) farest_from_zero | Yes, separate I/O tag | |||
| 6. | sort_object (static) | It specifies the object or time according to which the data are sorted in a profile. | Yes, separate I/O tag | ||||
| 7. | entries_in_use (dynamic) | double-long-unsigned | Number of records that have been saved into a buffer of profile. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |||
| 8. | profile_entries (static) | double-long-unsigned | Maximum The maximum number of records that can be stored into the buffer. | Yes, separate I/O tag | |||
Data about objects that are accessible by the reading of attribute "capture_objects" are stored into in the buffer. D2000 System automatically searches for I/O tags (its address parameters) that match the objects from attribute "capture_objects" (by their address parameters). The objects are searched by these parameters : "logical_name", "class_id", and "attribute_index".
The TELL command GETOLDVAL or ESL action GETOLDVAL start the reading of all the configured load profiles on the station. The time interval with data is always read by from the load profile according to the parameters of the TELL command or ESL action from the load profile..
Example: I/O tag with address::
- class_id = 7
- attribute_index = 2
- logical_name = 1-0:P.1.0
After a tell command GETOLDVAL B.ELMER_125 "06-07-2020 00:00:00" "06-07-2020 01:00:00", the KOM process queries a list of objects in a profile (by reading attribute 3):
09:44:39.558 06-07-2020|D|DLMS> Composing getRequest for LN ClassID=0007 InstanceID=1-0:P.1.0 AttributeId 3, InvokeID 65and displays a list of received objects:
09:44:40.710 06-07-2020|D|DLMS> Received capture_objects attribute for I/O tag 'M.ELMERY_T125_1_25_PROFILE' (class_id=7, logical_name=1-0:P.1.0, attribute_index=3) are:
09:44:40.710 06-07-2020|D|DLMS> 1. logical_name=1-0:1.5.0, class_id=4, attribute_index=2
09:44:40.710 06-07-2020|D|DLMS> 2. logical_name=1-0:2.5.0, class_id=4, attribute_index=2
09:44:40.710 06-07-2020|D|DLMS> 3. logical_name=1-0:32.7.0, class_id=3, attribute_index=2
09:44:40.711 06-07-2020|D|DLMS> 4. logical_name=1-0:3.5.0, class_id=4, attribute_index=2
this reading is performed only once and the result is cached. Subsequently, data blocks containing historical values are read:
09:44:42.924 06-07-2020|D|DLMS> Block 1 complete, reading next
09:44:42.925 06-07-2020|D|DLMS> Composing Get-Request-Next for block-number 2
..
09:44:51.203 06-07-2020|D|DLMS> Get-Data-Block-Result: raw-data [0], length 88:
09:44:51.203 06-07-2020|D|DLMS> Last Block complete, going to parse 1614 bytes
The values are parsed and assigned to the I/O tags. If the I/O tag with the required address does not exist, a warning is displayed:
09:44:51.205 06-07-2020|D|DLMS> > Old value for I/O tag 'M.ELMERY_T125_1_25_APm_15p', (double_long_unsigned) 992660, Re=99266, Tm=06-07-2020 00:00:00 Local
09:44:51.205 06-07-2020|D|DLMS> > Old value for I/O tag 'M.ELMERY_T125_1_25_APm_15m', (double_long_unsigned) 0, Re=0, Tm=06-07-2020 00:00:00 Local
09:44:51.205 06-07-2020|W|DLMS> Cannot find I/O tag logical_name=1-0:32.7.0, class_id=3, attribute_index=2 to assign profile data!
09:44:51.205 06-07-2020|W|DLMS> Cannot find I/O tag logical_name=1-0:3.5.0, class_id=4, attribute_index=2 to assign profile data!
Note: it is necessary to configure a non-zero delay in the time parameters of the station, otherwise the reading of profiles will never get to the run (periodic reading has a higher priority). If there are several stations on the line, the delay must be higher than the duration of the periodic reading of the values of all the stations.
| Kotva | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Kotva | |||
|
| Type | Description, meaning | Supported conversion into D2000 value types |
| null-data | no data | all, as an invalid value |
| boolean | boolean (true/false) | Di, Ci, Ai, TxtI |
| bit-string | unsupported | - |
| double-long | 32-bit number signed number | Di, Ci, Ai, TxtI |
| double-long-unsigned | 32-bit unsigned number unsigned | Di, Ci, Ai, TxtI |
| octet-string | string of bytes | TxtI |
| visible-string | string (text) | TxtI |
| UTF8-string | UTF8 string (text) | TxtI |
| bcd | unsupported | - |
| integer | 8-bit signed number signed | Di, Ci, Ai, TxtI |
| long | 16-bit signed number signed | Di, Ci, Ai, TxtI |
| unsigned | 8-bit unsigned number unsigned | Di, Ci, Ai, TxtI |
| long-unsigned | 16-bit unsigned number unsigned | Di, Ci, Ai, TxtI |
| long64 | 64-bit signed number signed | Di, Ci, Ai, TxtI |
| long64-unsigned | 64-bit unsigned number unsigned | Di, Ci, Ai, TxtI |
| enum | enumerated type | Di, Ci, Ai, TxtI |
| float32 | float 32-bit float | Di, Ci, Ai, TxtI |
| float64 | float 64-bit float | Di, Ci, Ai, TxtI |
| date-time | date + time | TxtI, TiA |
| date | date | TxtI, TiA |
| time | time | TxtI, TiA, TiR |
...
The following picture shows a configuration dialog box of the I/O tag address.
Example for Short Name (SN) referencing:
...
The meaning of the parameters in the dialog box:
| 1 | Selection of referencing: Short Name (SN) or Logical Name (LN). Based on the value of the station parameter Application Context, only the I/O tags with either SN or LN referencing will be handled. |
| 2 | SN referencing: a required parameter, it is the initial address of the class instance. It is an integer number within the range 0 up to 65520 (0xFFF0 hexadecimal). LN referencing: an unused (disabled) parameter. |
| 3 | Required A required parameter, it is an identification number of COSEM class. |
| 4 | Required A required parameter, it is an index of the attribute (a serial number starting from 1). |
| SN referencing: the parameters base_name, class_id, and attribute_index are mandatory. The parameters base_name and attribute_index are used to calculate Short Name (SN) address according to the formula which helps . Short Name is used to get the value of an attribute from a device. Class_id shows a type of COSEM class. Attribute_index identifies the type of data type that were was received from a device. LN referencing: parameters class_id,attribute_index, and logical_name are mandatory. | |
| 5 | SN referencing: the he Hex checkbox Hex enables to enter the address enables entering the base_name address in a hexadecimal form (checked) or decimal (unchecked). When editing the an existing I/O tag, this checkbox is marked depending on the address that was entered in the first configuration of the I/O tag (i.e. hexadecimal or decimal). The change of status (checked/unchecked) does not convert automatically the value base_name from hexadecimal to decimal and vice-versa. LN referencing: an unused (disabled) parameter. |
| 6 | SN referencing: the parameter logical_name is optional. It is an OBIS address that belongs to the Short Name address, configured by parameters base_name, class_id, and attribute_index. It is in a text format according to the OBIS specification of the object address. |
| 7 | In the bottom part, there is information about the object address. Their Its meaning is only to inform the user about a configured object. The information is initialized after choosing the address in the DLMS Object list dialog box. |
| 8 | Clicking on the Browse button Browse enables to select selecting the address from the DLMS Object List dialog box. There are two methods on for how to configure the addresses of I/O tags:
|
...
If these conditions are fulfilled - the device is connected to D2000 System, a communication station exists and the device communicates, you can define the parameters of the I/O tag address by the selection of the object from the list of all objects on the device. List A list of objects is queried from the device:
...
There is no need to configure any other I/O tags, just click on the button the Browse button.
First loading The first reading of the list takes upto up to several minutes depending on the baud rate. The window displays the information "Waiting for data...".
After data loadingis read, the list of objects and their descriptions will show in the window:
...
- each row represents one instance of COSEM class,
- the OBIS address of the object follows the icon of class,
- then there is the information about the SN address (base_name) of a particular instance of COSEM class and about its type (class_id and version),
- COSEM classes, which are supported in the D2000 System, can be expanded by clicking on the symbol (+).
When expanding a specific instance of the COSEM class, the supported attributes of the class will be displayed:
The information about attribute includes:
- attribute index (attribute_index) - a sequential number of the attribute, it is displayed next to the icon,
- attribute name (e.g. logical_name, value, scaler_unit, time_zone ...),
- static or dynamic attribute.
There can be an "expand" symbol (+) near the icon. When opening it and clicking on the row "Attribute value=" row, the current value of the attribute will be retrieved from the device:
...
This feature enables fast browsing of the attributes of all supported COSEM classes. The dialog window works as both "Object List" and "Value Browser".
The bottom part of the dialog box contains these check-boxes:
- Show hexadecimal - shows all the addresses of base_name classes as hex number hexadecimal numbers or decimal oneones.
- Show inactive objects
- Show unsupported classes - enables to display the instances of unsupported COSEM classes.
To close the dialog box without any changes, click on the Cancel button.
To insert the addressing parameters of the attribute of an instance into the address of I/O tag, double-click on the particular row. This closes the b the "DLMS SN Object List" dialog and the parameters will be set for of the I/O tag will be configured based on the selection.
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
- Value group A defines the energy type (0=abstract objects, 1=electricity, 7=gas),
- Value group B defines a channel number,
- Value group C defines a measured physical value,
- Value group D defines a type of processing,
- Value group E defines next further processing or classification according to the algorithm,
- Value group F defines the storage of processed historical data.
Value group A up to F represents the integer a positive number within in the range from 0 up to 255.
For Value group C and D you can enter also the character values:
...
The address is written in text format:
A-B:C.D.E*F
Value group groups C, D, and E must always contains contain the value. Other blank unspecified values will be set on to zero (0).
For more information see "List of standard OBIS codes and COSEM objects" on http://www.dlms.com, the document "List of standardized OBIS codes, DLMS UA, V2.3, (c) Copyright 1997-2005 DLMS User Association".
...
- DLMS User Association, COSEM Architecture and Protocols, Seventh Edition, (c) Copyright 1997-2009 DLMS User Association (Green book).
- DLMS User Association, COSEM Identification System and Interface Classes, Ed. 10.0, (c) Copyright 1997-2010 DLMS User Association (Blue book).
- International Standard IEC 62056-21, Direct Data Local Exchange, First edition 2002-05.
- International Standard IEC 62056-61, Object Identification System (OBIS), Second edition 2006-11.
- List of standardized OBIS codes, DLMS UA, V2.3, (c) Copyright 1997-2005 DLMS User Association.
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
You can read blogs about the DLMS protocol (for now, in Slovak language only): Communication - DLMS/COSEM protocol |
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
- Ver. 1.0 - May 30, 2011 - creation of document created.
- Ver. 1.1 - January 30, 2019 - suppor support for LN referencing.
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
...