...
Ethernet/IP protocol is one of the most widespread communications protocols in the US designed for communication with PLCs, motors, and other process-level devices. The protocol is managed and developed by ODVA, which includes companies such as Rockwell, Honeywell, or Schneider Electric.
Ethernet/IP protocol is an adaptation of the Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) for the Ethernet bus.
...
- communication via TCP
- explicit messages (request/response type of communication)
- standard addressing of objects (Class/Instance/Attribute)
- symbol addressing of objects (proprietary Rockwell implementation)
- optimisation optimization of symbol objects addressing - so-called Symbol Instance Addressing
...
The communication was tested againstwith:
- Allen-Bradley Micro820
- 1769 CompactLogix 5370 Controller (1769-L18ER/A)
- ControlLogix EtherNet/IP bridge Module (1756-EN2TR/C) connected to 1756-L85E ControlLogix 5580 Controller (1756-L85E/B)
...
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Categeory Category of communication line: TCP/IP-TCP
- TCP parameters - server parameters are mandatory:
- Host: server name in form of INET (name or numerical address a.b.c.d). In the case of redundant systems, multiple names/addresses separated by commas can be entered.
- Port: TCP port number (0..65535). Standard The standard port of Ethernet/IP procotol protocol is 44818
- Line number: unused, set to 0
Note: if all of the stations are in StOFF mode on a TCP/IP-TCP line, the TCP connection will be closed. Thus it is possible to control TCP communication from the event using a tell STSTAT tell command STSTAT.
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
parameters
...
Configuration line dialog box - tab Protocol parameters.
They influences influence some of the optional protocol parameters. The following line parameters can be set:
Table 1
| Key wordKeyword | Full title | Description | Unit | Replacement value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Read Wait Timeout | Waiting between individual reads of data from the communication if no data has been received.. | sec.mss | 0.010 | ||||||
| Send Delay | Waiting after sending one message. The purpose is not to overload the device with too many messages. Note: while testing the Micro820 device, problems were encountered when sending approximately 200 messages (browsing instances of the class File Object [0x37] with zero delay. Waiting for 1 ms solved the problem. | sec.mss | 0.001 | ||||||
| Write Symbolic: Array Elements | Methods of writing array using symbolic adressing addressing (Rockwell). There are three supported modes:
| - | 0 .. Array Index | ||||||
| Optimized write of array element | Optimized write is used when only one array element is written. Optimization consists of writing only one specific element and specifying its index (in the protocol specified as Member ID). Note: the tested Micro820 device supported the optimization, testing the test software server did not. | - | False | ||||||
| Max Packet Size | The maximum size of Ethernet/IP messages (Unconnected Explicit message) - according to the standard 504 bytes. Note: in symbolic mode (Rockwell) it is also possible to work with larger arrays using proprietary services Read Tag Fragmented Service and Write Tag Fragmented Service. | Bytes | 504 | ||||||
| Response Timeout | Timeout to receive an answer for a request. If the response for a request is not received within this time, this is considered an error, and the TCP connection will be closed. | sec.mss | 10.000 | ||||||
| Optimized Work with Symbolic Names | Optimization of work in a symbolic mode (Rockwell) - so-called Symbol Instance Addressing. Instead of using symbolic names, a Symbol Instance ID is used for reading. The Symbolic name is converted to the Instance identifier by the same service which is used for browsing. Note: Not every device or Rockwell firmware version supports this optimization (tested Micro820 with firmware 10.0.12 or 11.0.11 did not support this optimization). In this case, if the device returns the Service not supported [0x08] error code, the optimization will be disabled until the KOM process is restarted or the configuration of the respective line is re-saved. | - | False |
...
- Communication protocol: Ethernet/IP.
- Station The station address is not configured. Multiple stations may be configured on a single line (e.g. because of different time parameters of individual stations).
...
Communication station - configuration dialog box - tab Protocol parameters.
These parameters influence some optional parameters of the protocol. You can set the following station parameters:
...
| Parameter | Meaning | Unit / size | Default value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| An octet string representing the parameter Route_Path (of padded EPATH type, that is, the number of octets in each segment must be even). If this parameter is specified, the protocol messages (Get_Attribute_Single, Set_Attribute_Single, Read Tag [Fragmented] Service, Write Tag [Fragmented] Service) will be wrapped in an Unconnected Send message that is used for routing. It was not necessary to change this parameter when communicating with Micro820 and CompactLogix devices. When communicating with ControlLogix via the ControlLogix EtherNet/IP bridge Module (1756-EN2TR/C), it was necessary to set the parameter to 01 00, which according to protocol documentation means Port 1 (which represents the backplane) and slot 0 (where the Central Processor was located). To communicate with the processor in slot 1, the parameter had to be set to 01 01, so the general syntax for accessing a slot XX would be 01 XX. A more complicated configuration consisting of 3 segments:
so the whole Route Path string is: 01 00 12 0C 31 37 32 2E 32 35 2E 35 38 2E 31 31 01 01 (in the syntax of Rockwell OPC server it is "1,[0,2,172.25.58.11, 1], 1") | octet string | |||||||
| Setting the parameter to YES causes the protocol messages (Get_Attribute_Single, Set_Attribute_Single, Read Tag [Fragmented] Service, Write Tag [Fragmented] Service) to be packaged in a Multiple Service Packet Service message. In the future, this parameter can be used for communication optimisation optimization (wrapping multiple messages into one), in the current implementation, each message is packaged separately, therefore we recomment recommend not to use this parameter. | YES/NO | NO |
...
Possible value types of I/O tag: Di, Ai, Ci, TxtI, TiR, TiA, Dout, Ao, Co, TxtO, ToR, ToA
The addressing of the I/O tag can be either standard or symbolic (Rockwell).
...
Within these messages, an item is addressed by the class number (Class), the instances within the class (Instance), and the attribute number of the particular instance (Attribute).
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
By clicking the Browse button, a browse dialog can be opened and a list of classes and instances within the class can be retrieved as long as the communication with the device is established. When opening, only a list of classes (rows with the folder icon) are is read for speed reasons. Double-click on a class retrieves a list of instances (if the number of instances was determined, i.e. it is not zero or unknown - "???"). Double-clicking on a specific instance (lines with the tag icon) copies the class and the instance to the configuration dialog of the I/O tag.
Note 1: the number of actually retrieved class instances may be less than the number displayed within the list of classes.
Note 2: browsing attempts to read all instances of 1 .. Max Instance, where Max Instance is detected when reading a list of classes. However, if Max Instance > 1000, only the first 1000 instances are tested during browsing. Reading of all instances can take up to several tens of seconds. When it is finished, the folder icon is changed from closed to open.
Note 3: In versions from 20th December 2018 and newer, the recycling of browser dialog has been implemented. If the dialog is closed by the Close button or after selecting an instance, it is actually only hidden and it is available for browsing by another I/O tag within the same station so that the tree structure of the browsed objects is preserved. Clicking on the close icon at the top right corner will cause the dialog to be really closed.
The Refresh button is used to repeatedly retrieve the list from the device. The KOM process caches a list of classes and instances, so the second and subsequent opening of the browse dialog or reading of the list of instances for a specific class is significantly faster than the first one during which the data is being read from the device.
...
This addressing method is supported for by Rockwell devices. It uses Proprietary Rockwell messages:
...
Symbolic name - a symbolic name. It can be simple (Test) or contain the address of a specific item of one-dimensional array (Test [3]), multidimensional (Test [1] [2]), item of a structure (Test.MyItem1), or item of an array of structures (Test[2].MyItem1).Kotva symbolic_name symbolic_name
Item count - number of elements in the case of an array of values.This number may be less than or equal to the actual size of the array in the device.If it is not specified, one element is read.Kotva item_count item_count
Fragmented read - indicationthat the Read Tag Fragmented Service message should be used for reading , because the entire array does not fit into a message with the length specified by the Max Packet Size parameter.
Note: If the reading using Read Tag Service message returns an error code Partial Transfer [0x06], next reads will use the Read Tag Fragmented Service message as if the Fragmented read indication was set.
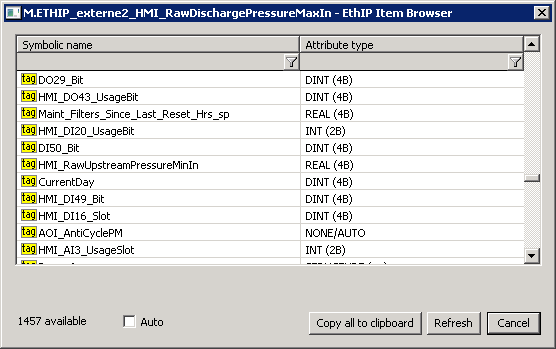
By clicking the Browse button, a browse dialog can be opened and a list of symbolic names retrieved as long as the communication with the device is established. For each symbolic name, its type is also read. In the case of structures or arrays of structures, the type is identified as "STRUCTURE (---)". D2000 cannot presently use such complex types - it is necessary to specify an address of a particular item as a symbolic name (e.g. MyStruct.MyItem or MyArr [1] .MyItem).
The Auto option is used to set the NONE/AUTO attribute type (autodetect). If this option is off, the attribute type is copied to the I/O tag along with the symbolic name after double-click on a specific line in the list of symbolic names.
The Refresh button is used to repeatedly retrieve the list from the device. The KOM process caches a list of symbolic names, so the second and subsequent opening of the browse dialog is significantly faster than the first one during which the data is being read from the device.
Note: symbolic names beginning with the underscore are related to system objects of Rockwell device, other names are user-defined.
Atribute type - the type of attribute. In the case of standard addressing, it is necessary to enter a specific type. In the case of symbolic addressing, it is possible to leave the type of the attribute as NONE/AUTO (autodetect), since proprietary Rockwell messages contain both the value and the attribute type. An exception is if the I/O tag is write-only - then the attribute type must be specified.
Note: not all types of attributes from the offered list have read/write implemented. All numeric types, time types, strings (SHORT_STRING, STRING, STRING2), and numeric and time array types are supported. International string (STRINGI) type is supported for reading.
Array index - index of an element in an array, if the attribute is an array. In the Ethernet/IP protocol, an array is indexed from zero, so if Item count is equal to 3, indices 0, 1, and 2 are allowed.
Note: if Array index + 1> Item count, then Array index + 1 element will be read instead of Item count.
Bit (1..n) - if an attribute type is an unsigned number (BOOL, USINT, UINT, UDINT, ULINT, DATE, TIME_OF_DAY, BYTE, WORD, DWORD, LWORD, ENGUNIT, and arrays of these types) it is possible to enter a specific bit (1 to 64, depending on the number of bits for a specific type).
...
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
You can read blogs about the Ethernet/IP protocol: |
...
- Ver. 1.0 - November 28, 2018 - Creating of the document.
- Ver. 1.1 - January 2, 2019 - Improved browsing, testing with 1769 CompactLogix 5370 Controller
...