Supported device types and versions
Communication line configuration
Communication station configuration
I/O tag configuration
Tell commands
Literature
Changes and modifications
Document revisions
Supported device types and versions
Protokol DNP3 is a telemetric protocol designed for communication of a master station (usually SCADA) with outstations (usually PLC, RTU, or other IED - Intelligent Electronic Devices). It was developed while IEC only worked on IEC60870-5 standards (IEC 870-5-101 and IEC 870-5-104).
DNP3 defines multiple object Groups (e.g. Binary Input, Analog Input, Counter) and multiple Variations for each object group (e.g. for Analog Input there are variations 32-bit with flag, 16-bit with flag, 32-bit without flag, 16-bit without flag, Single-precision floating point with flag ..). Each object is defined by a Group and Index (a non-negative number with the size of 1, 2, or 4 bytes).
At the same time, the DNP3 protocol classifies objects into 4 classes (Class 0 - static objects; Class 1..3 - dynamic objects with change registration). Similar to IEC 870-5-101 and IEC 870-5-104, DNP3 supports requesting all values of a particular class (Poll request), in addition to the explicit reading of a particular group of objects with a specified variation (or possibly using variation 0 - automatic variation). When reading, it is possible to request the data of the whole group or to specify an index or the entire range of objects.
The following application functions are supported for the objects:
- Read (1) - reading objects.
- Write (2) - Single-phase write of objects (with numeric code confirming successful write or talking about write error).
- Select (3) + Operate (4) - a two-phase write of objects that virtually excludes the possibility of error due to undetected interference on the line. Each operation returns a group, index, and write value in addition to the return code.
- Direct Operate (5) - single-phase write of objects (except the numeric code, the operation returns a group, index, and write value).
- Direct Operate Non Return (6) - single-phase write of an object without confirmation (least secure).
- Enable Unsolicited Responses (20) - activation of sending spontaneous changes by subordinate stations.
The protocol also supports sending spontaneous changes by outstations - using the application function Unsolicited Response (130).
Data is sent as Data Link Layer packets, also called transport segments. One or more transport segments form an Application Layer fragment. The fragment can be sent as confirmed (Data Link Layer function code 3 - CONFIRMED_USER_DATA) or unconfirmed (Data Link Layer function code 4 - UNCONFIRMED_USER_DATA). The transport segments within one fragment are always confirmed - with the exception of the last one (Data Link Layer function code 0 - ACK).
Table 1: D2000 implementation supports the following groups and their variations:
| Group (highlighted can be configured for I/O tags) | Variations | Supported operations | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binary Input (1) | Packed format (1) | Reading (Read) | Binary inputs |
| Binary Input Event (2) | Without time (1) With absolute time (2) With relative time (3) | Analysis* | Reporting of binary inputs' changes |
| Double-bit Binary Input (3) | Packed format (1) With flags (2) | Reading (Read) | Double-bit binary inputs |
| Double-bit Binary Input Event (4) | Without time (1) With absolute time (2) With relative time (3) | Analysis* | Reporting of double-bit binary inputs' changes |
| Binary Output (10) | Packed format (1) Output status with flags (2) | Reading (Read) | Binary outputs |
| Binary Output Event (11) | Status w/o time (1) Status with time (2) | Reading (Read) | Reporting of binary outputs' changes |
| Binary Command (12) | Control relay output block (CROB) (1) Pattern control block (PCB) (2) Pattern mask (3) | - | Not supported yet |
| Binary Output Command Event (13) | Command status without time (1) Command status with time (2) | Analysis* | Reporting of changes (results of third party commands) |
| Counter (20) | 32-bit with flag (1) 16-bit with flag (2) 32-bit with flag, delta (obsolete) (3) 16-bit with flag, delta (obsolete) (4) 32-bit w/o flag (5) 16-bit w/o flag (6) 32-bit w/o flag, delta (obsolete) (7) 16-bit w/o flag, delta (obsolete) (8) | Reading (Read) | Counters |
| Frozen Counter (21) | 32-bit with flag (1) 16-bit with flag (2) 32-bit with flag, delta (obsolete) (3) 16-bit with flag, delta (obsolete) (4) 32-bit with flag and time (5) 16-bit with flag and time (6) 32-bit with flag and time, delta (obsolete) (7) 16-bit with flag and time, delta (obsolete) (8) 32-bit w/o flag (9) 16-bit w/o flag (10) 32-bit w/o flag, delta (obsolete) (11) 16-bit w/o flag, delta (obsolete) (12) | Reading (Read) | Counters- values captured when the object was frozen |
| Counter Event (22) | 32-bit with flag (1) 16-bit with flag (2) 32-bit with flag, delta (obsolete) (3) 16-bit with flag, delta (obsolete) (4) 32-bit with flag and time (5) 16-bit with flag and time (6) 32-bit with flag and time, delta (obsolete) (7) 16-bit with flag and time, delta (obsolete) (8) | Analysis* | Reporting of counters' changes |
| Frozen Counter Event (23) | 32-bit with flag (1) 16-bit with flag (2) 32-bit with flag, delta (obsolete) (3) 16-bit with flag, delta (obsolete) (4) 32-bit with flag and time (5) 16-bit with flag and time (6) 32-bit with flag and time, delta (obsolete) (7) 16-bit with flag and time, delta (obsolete) (8) | Analysis* | Reporting of counters' changes when the object was frozen |
| Analog Input (30) | 32-bit with flag (1) 16-bit with flag (2) 32-bit w/o flag (3) 16-bit w/o flag (4) Single-prec flt-pt with flag (5) Double-prec flt-pt with flag (6) | Reading (Read) | Analog inputs |
| Frozen Analog Input (31) | 32-bit with flag (1) 16-bit with flag (2) 32-bit with time-of-freeze (3) 16-bit with time-of-freeze (4) 32-bit w/o flag (5) 16-bit w/o flag (6) Single-prec flt-pt with flag (7) Double-prec flt-pt with flag (8) | Reading (Read) | Analog inputs - values captured when the object was frozen |
| Analog Input Event (32) | 32-bit w/o time (1) 16-bit w/o time (2) 32-bit with time (3) 16-bit with time (4) Single-prec flt-pt w/o time (5) Double-prec flt-pt w/o time (6) Single-prec flt-pt with time (7) Double-prec flt-pt with time (8) | Analysis* | Reporting of analog inputs' changes |
| Frozen Analog Input Event (33) | 32-bit w/o time (1) 16-bit w/o time (2) 32-bit with time (3) 16-bit with time (4) Single-prec flt-pt w/o time (5) Double-prec flt-pt w/o time (6) Single-prec flt-pt with time (7) Double-prec flt-pt with time (8) | Analysis* | Reporting of analog inputs' changes when the object was frozen |
| Analog Input Reporting Deadband (34) | 16-bit (1) 32-bit (2) Single-prec flt-pt (3) | Reading (Read) Writing (all functions) | Deadbands of analog inputs |
| Analog Output Status (40) | 32-bit with flag (1) 16-bit with flag (2) Single-prec flt-pt with flag (3) Double-prec flt-pt with flag (4) | Reading (Read) | Reading of analog outputs |
| Analog Output (41) | 32-bit (1) 16-bit (2) Single-prec flt-pt (3) Double-prec flt-pt (4) | Writing (Select+Operate, Direct Operate, Direct Operate No Response, but not Write) | Writing of analog outputs |
| Analog Output Event (42) | 32-bit w/o time (1) 16-bit w/o time (2) 32-bit with time (3) 16-bit with time (4) Single-prec flt-pt w/o time (5) Double-prec flt-pt w/o time (6) Single-prec flt-pt with time (7) Double-prec flt-pt with time (8) | Analysis* | Reporting of analog outputs' changes |
| Analog Output Command Event (43) | 32-bit w/o time (1) 16-bit w/o time (2) 32-bit with time (3) 16-bit with time (4) Single-prec flt-pt w/o time (5) Double-prec flt-pt w/o time (6) Single-prec flt-pt with time (7) Double-prec flt-pt with time (8) | Analysis* | Reporting of analog outputs' changes |
| Time and Date (50) | Absolute time (1) Absolute time and interval (2) Absolute time at last recorded time (3) | Reading (Read) | Current time |
| Time and Date CTO (51) | Absolute time, synchronized (1) Absolute time, unsynchronized (2) | Analysis* | Common timestamp ** |
| Class Objects (60) | Class 0 data (1) Class 1 data (2) Class 2 data (3) Class 3 data (4) | Poll | Requesting values for all objects of the respective class |
| Binary-Coded Decimal Integer (101) | Small (1) Medium (2) Large (3) | Reading (Read) | Reading of 1,2 and 4-byte signed BCD numbers |
| Unsigned Integer (102) | 8-bit (1) | Reading (Read) | Reading of 8-bit unsigned numbers |
| Octet String (110) | Variations 0-255 correspond to octet strings of 0-255 bytes in length | Reading (Read) Writing (Write) | Reading + writing of octet strings |
| Octet String Event (111) | Variations 0-255 correspond to octet strings of 0-255 bytes in length | Analysis* | Reporting of octet strings' changes |
| Virtual Terminal Output Block (112) | Variations 0-255 correspond to strings of 0-255 bytes in length | Writing (Write) | Writing to a virtual terminal |
| Virtual Terminal Event Data (113) | Variations 0-255 correspond to trings of 0-255 bytes in length | Reading (Read) | Reading from a a virtual terminal |
* Note: Operation Analysis means that D2000 KOM can analyze the message and assign values to the appropriate I/O tag. For example, for a Binary Input Event (2) group, values are assigned to the I/O tags from the Binary Input (1) group.
** Note: The outstation can send object values from the Time and Date CTO (51) group, defining the Common Time of Occurrence (CTO) for subsequent events. Afterward, values with relative time are sent - Binary Input Event (2) and Double-bit Binary Input Event (4), using With relative time (3) variations.
Note: D2000 KOM supports sending a message with the writing type outside the range allowed by the standard - e.g. for the Analog Output (41) group, a write operation with Write (2) function can be configured.
The D2000 implementation also supports time synchronization (according to the parameters configured on the station) and browsing. Secure authentication is not supported.
Communication line configuration
Category of communication line:
- Serial
- SerialOverUDP Device Redundant
- MOXA IP Serial Library
- RFC2217 Client
- TCP / IP-UDP: The IP address and UDP port of the outstation are configured on the line (the default port for the DNP3 protocol is 20000). The UDP port on the side of the D2000 KOM process is dynamically assigned. If it needs to be fixed, use the SerialOverUDP Device Redundant line.
- TCP/IP-TCP: The IP address and TCP port of the outstation are configured on the line (the default port for the DNP3 protocol is 20000). The parameter Line number is not used, set it to 0.
Note: if a TCP/IP-TCP line has all stations set to StOFF, TCP connection will be closed. Thus it is possible to control TCP communication from the event using a tell command STSTAT.
Communication line protocol parameters
Configuration line dialog box - tab Protocol parameters.
They influence some of the optional protocol parameters. The following line parameters can be set:
| Keyword | Full name | Description | Unit | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
MA | Master Address | Address of KOM process. The address must be a 16-bit number from interval 0-65 519 (other addresses have special meanings). | - | 1 |
SS | Serialized Stations | Serialization of communication with individual stations on the line. Serialization means that individual stations are queried sequentially (which corresponds to the situation of the stations on the serial line) to avoid conflict when multiple stations try to send a response at the same time. If a D2000 KOM process actually communicates with a single device that contains multiple virtual stations, or a device that is forwarding messages to other stations (in a way that prevents a conflict), or the channel is duplex (TCP, UDP), it is possible to disable serialization. Thus D2000 KOM process will send queries to all stations on the line and then wait for answers. Turning off serialization can speed up communication, but this will cause packet collisions and packet losses on lines with multiple stations where collisions are possible (such as RS-485). | - | YES |
BG | Browse All Groups | The parameter determines whether, in addition to Poll requests for individual classes (Class 0-3), requests for the explicit reading of all supported object Groups should also be sent. The reason for the explicit reading of Groups is that some objects may not be assigned to any of the classes, so Poll requests will not find them. | - | YES |
DTQ | Debug Timeout Queue | The parameter activates advanced debug information about messages in the time queue. | - | NO |
Communication station configuration
- Communication protocol DNP3.
- Station address: a 16-bit number from range 0-65 519 (other addresses have special meanings).
Communication station protocol parameters
The following station parameters can be set:
| Keyword | Full name | Description | Unit | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
PI1, PI2, PI3, PI4 | Poll Interval n (-1=OFF) | Interval for sending Poll requests. It is possible to configure 4 different intervals and for each interval to specify the class to which Poll is sent (Class 0-3). | sec | 10 for PI1-3 600 for PI4 |
PC1, PC2, PC3, PC4 | Poll Class n | The class to be queried within the n-th Poll request. There are four classes according to the standard:
The default order for each parameter (Pol Class 1-4) is Class 1, 2, 3, 0. First, data (events) from the highest priority (Class 1, 2, 3) are read, then Static Data (for all Classes 0-3). | - | Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class 0 |
MF | Max Frame Length | The maximum length of the data packet sent by process D2000 KOM - Data Link Layer packet (also called transport segment). This is data in Header Block, i.e. fields Ctrl (1B), Destination (2B), Source (2B) plus data in Data Blocks (in each max. 16 bytes). The Start (2B) and Length (2B) fields in the header, and the CRC (2B) fields in the header and each data block are not included in the length. The parameter can be in the range 10-255. | Bytes | 250 |
MG | Max Fragment Length | The maximum length of the Application Layer fragment sent by the D2000 KOM process. The Application Layer fragment is a block of octets containing request or response information that is transmitted as one or more consecutive transport segments. The parameter can be in the range 15-1024. | Bytes | 512 |
RT | Response Timeout | Timeout for receiving a response to a request. | sec | 10.000 |
RL | Reset Link States | Message sent to the outstation when establishing a connection. According to the standard, the message RESET_LINK_STATES (0) must be sent if confirmed messages are used (see Confirmation Mode parameter). If the parameter is set to NO, a REQUEST_LINK_STATUS (9) message will be sent. | - | YES |
RO | Read Only | If the parameter is set to YES, the station is in the receive-only mode (no messages are sent to it). | - | NO |
RC | Retry Count | The number of request retries (1-20), if the station is not responding, or its response is corrupted. | - | 3 |
CE | Com Error | The number of errors (missing or corrupted response) after which the station goes into a communication error. | - | 5 |
AU | Activate Unsolicited | The parameter activates the sending of spontaneous changes by outstations - function Unsolicited Response (130). The options are:
Note: Sending spontaneous changes by multiple stations e.g. on the RS-485 bus can cause collisions. | - | Disabled |
CM | Confirmation Mode | The parameter enables confirmation of messages sent by process D2000 KOM. If confirmation is enabled, the outstation must acknowledge each application fragment (by application function 0 - CONFIRM). | - | Unconfirmed |
RSD | Receive-send Delay | The delay between receiving a station response and sending another packet. Delays can be used to artificially slow down communication (reduce/distribute the station's load). | ms | 0 |
RW | Read after Write | The parameter activates verification by reading a value after writing. Readings will only be performed for the I/O tags with Explicit Read configured and a Write Type that does not return a value, i.e. Write (2) and Direct Operate Non Return (6). | - | YES |
SR | Single Request Per Frame | The parameter disables the default cumulation of multiple Read and Poll requests within a single message. By default, the requests are cumulated until the data size reaches Max Fragment Length bytes. | - | NO |
SB | Status Bits Mapping | Mapping of status bits (if they are included in a received message) to the I/O tag value. Options are:
Different variations within different groups have different status bits. All except the ONLINE bit indicate a problem. Individual groups and their variations have the following status bits: (GXvY stands for Group X variation Y, GXvY-Z stands for Group X variation Y through Z - see Table 1) G1v2, G2v1-3, G3v2, G4v1-3, G10v2, G11v1:
G20v1-4, G21v1-8, G22v1-8, G23v1-8:
G30v1-2, G30v5-6, G31v1-4, G30v7-8, G32v1-8, G33v1-8, G40v1-4, G42v1-8:
| - | WEAK + Flags |
OF | Reverse Online Flag | Reverse mapping of the ONLINE flag. Since this is the only flag in the DNP3 protocol that means normal status (all other flags indicate problems), its reversion when mapping to the FLA flag may be useful (so the FLA flag is set if the ONLINE flag is 0, i.e. device is offline). | - | NO |
SF | Separate Frozen Counter | Enables separation of Frozen Counters namespace from Counters - i.e. I/O tags in the Frozen Counter (21) and Frozen Counter Event (23) groups will have separate addresses from the Counter (20) and Counter Event (22) I/O tags. According to the standard, Frozen Counters and Counters share a common space, but a specific implementation of the DNP3 protocol required this separation. | - | NO |
SE | Octet String Encoding | The encoding used to convert objects from Octet String (110) group to text strings. Supported encodings are:
| - | ISO_8859_1 |
DT | Debug I/O Tags | High level of communication logging with information about individual I/O tags. | - | NO |
I/O tag configuration
Possible value types of I/O tag: Ai, Ao, Di, Dout, Ci, Co, Qi, TxtI, TxtO, TiA, ToA, TiR, ToR.
Introduction
The I/O tag corresponds to one DNP3 object.
The minimum I/O tag configuration requires to configure the Group and Index parameters. Such an I/O tag must be placed in one of the dynamic classes Class 1-3, so that changes of its value are sent spontaneously or in a response to the Poll request.
Explicit Read must be configured for static data (assigned to Class 0) or for objects that are not assigned to any of the classes Class 1-3. For instance, according to the standard, objects from the Binary-Coded Decimal Integer (101), Unsigned Integer (102), and Octet String (110) groups may not be in Class 0, and the Analog Input Reporting Deadband (34) is not in Class 0, so its objects must be explicitly read.
When configuring explicit reading, a particular Variation can be specified (or keep the default value <Automatic>, which means that variation 0 is used). Furthermore, it is possible to configure the required address range with the Range parameter and optionally with the From and To parameters (a request generated by a single I/O tag can read data for multiple I/O tags that do not have explicit reading configured, or for items of a structured variable). Using the Read Period parameter, it is possible to configure a custom reading period different from the period specified in the station parameters.
If the I/O tag is of the output type, writing can be configured with the Write parameter. The Write Type parameter then specifies the application function, the Write Group parameter specifies the group and the Write Variation specifies the variation used for writing. If writing is configured for I/O tag, the Range parameter must be specified, and if a particular value of this parameter requires entering From and To parameters, they must have the same value.
The Disable parameter can be used to disable the I/O tag.
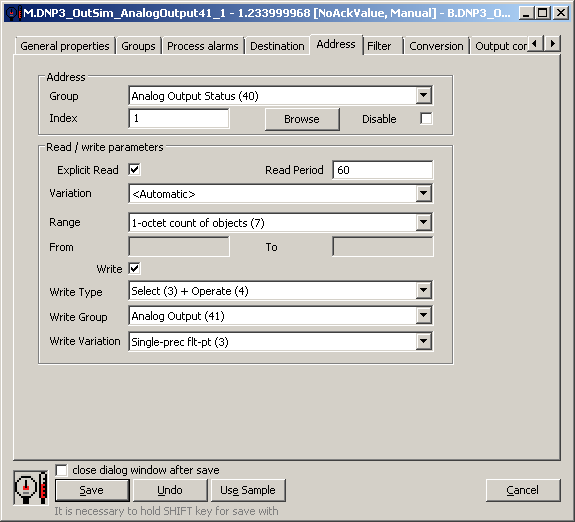
Figure - the configuration of I/O tag address for DNP3 protocol
A detailed description of individual parameters:
Address group
Group: object group to which the I/O tag belongs. The list of supported groups according to the standard is in Table 1 (they are supported if Reading is in the Supported Operations column).
Index: index of an object in the object group. An index is a non-negative number with a size of 1, 2, or 4 bytes. The Group + Index combination specifies the object address in the DNP3 protocol.
Disable: enables to disable the I/O tag, so that it will not acquire values and, in the case of output I/O tags, writing will be disabled too.
Read/write parameters group
Explicit Read: enable explicit reading by the Read (1) application function. It is also necessary to configure the Variation, Range, and, depending on the value of the Range parameter, optionally the From and To indices.
Read Period: a positive real number that indicates the explicit reading period in seconds. If not specified, the period defined on the station is used.
Variation: a preferred variation (group-specific format) used for explicit reading. The <Automatic> variation is sent as a Variation 0 (according to the standard, the master announces that it does not have the preferred format and leaves the selection to outstation).
Range: the range of objects specified for explicit reading or writing. With explicit reading, it is also possible to retrieve all objects in a particular group or a range of objects. The values read in this way will then also be assigned to the I/O tags that do not have explicit reading configured if the Group + Index matches retrieved data. Also, the read values can be assigned to items of a structured variable, if it is configured on the Destination tab.
The following ranges are supported:
| Range | Description |
|---|---|
| 1-octet start/stop index (0) | Usable if both From and To are less than 256 |
| 2-octet start/stop index (1) | Usable if both From and To are less than 65 536 (recommended by the standard) |
| 4-octet start/stop index (2) | Usable if To is greater than 65 535 |
1-octet start/stop virt addr (3): | Indexing with a manufacturer-specific virtual address; usable if both From and To are less than 256 |
2-octet start/stop virt addr (4) | Indexing with a manufacturer-specific virtual address; usable if both From and To are less than 65 536 (recommended by the standard) |
| 4-octet start/stop virt addr (5) | Indexing with a manufacturer-specific virtual address; usable if To is greater than 65 535 |
| No range (6) | The From and To parameters are not used; it is used to retrieve all objects from the group |
| 1-octet count of objects (7) | Usable for writing if Index is less than 256, the number of objects (1) and then Index are specified |
| 2-octet count of objects (8) | Usable for writing if Index is less than 65 536, the number of objects (1) and then Index are specified (recommended by the standard) |
| 4-octet count of objects (9) | Usable for writing if Index is greater than 65 535, the number of objects (1) and then Index are specified |
From, To: specifies a range of indices or virtual addresses for certain values of the Range parameter (0-5). The value of From parameter must be is less or equal to the value of To parameter. If writing is configured for the I/O tag, and the Range value requires From and To parameter to be specified, then their values must be the same.
Note: In practice, we have encountered DNP3 implementations that only supported writing with Range = 7, 8, and 9 (1/2/4-octet count of objects), i.e. they did not support writing specifying Range equal to 0, 1, and 2 (1/2/4-octet start/stop index) using From and To indices, even if they were set to the same value.
Write: enable writing operations function for output I/O tags. The parameters Range, Write Type, Write Group, Write Variation, and optionally - depending on the value of the Range parameter - also From and To must be specified.
Write Type: application function used for writing. The following functions are supported:
| Write function | Description |
|---|---|
| Write (2) | Single-phase writing of objects (with a returned numeric code confirming successful write or specifying a write error). |
| Select (3) + Operate (4) | Two-phase write of objects that virtually excludes the possibility of error due to undetected interference on the line. |
| Direct Operate (5) | Single-phase write of objects. It returns a group, index, and written value in addition to the return code. |
Direct Operate Non Return (6) | Single-phase write of an object without acknowledgment (the least secure but with the least load on the communication medium). |
Table 1 in the Supported Operations column for Write operation indicates which application functions are in compliance with the standard. Our implementation permits using application functions beyond the standard if a specific device supports them.
Write Group: object group used for writing. The list of supported groups according to the standard is in Table 1 (writing is supported if Writing is in the Supported Operations column).
Write Variation: variation used for writing. The list of supported variations for individual groups according to the standard is shown in Table 1 in the Variations column (writing is supported if Writing is in the Supported Operations column).
Browse
For the I/O tags, it is possible to discover the list of objects and their data types, as long as the KOM process is running and communication with an outstation is established.
Clicking the Browse button opens the DNP3 Item Browser window and displays a list of objects that have been read so far. The object list is created dynamically as a result of received messages (responses to Read and Poll requests as well as spontaneously arrived values).
At the same time - if the Browse All Groups parameter is set to YES, the first browsing (as well as browsing when the Refresh button is pressed) generates requests to read all supported object groups.
The list of objects is dynamic, i.e. when a new value arrives in the KOM process or when a new object is detected, it is updated.
Double-clicking on a particular line will cause the Group and Index parameters to be inserted into the configuration of I/O tag from which the DNP3 Item Browser window was opened.
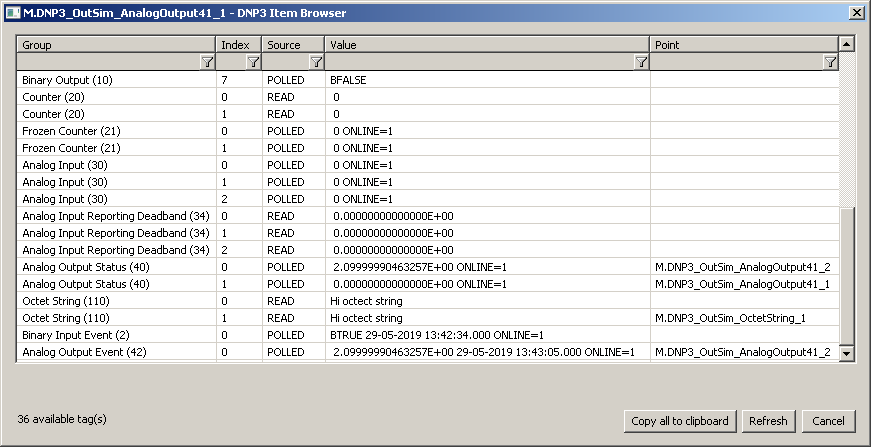
Figure - DNP3 Item Browser window
The window displays the following information:
Group: object group. In addition to the groups configurable for the I/O tags, "event" groups (such as Binary Input Event (2)) may also appear in the list, as long as the KOM process has received a message reporting a change in object value.
Index: index of an object in a group
Source: the source of data:
- READ - data came in response to data read request - Read (1) function
- POLLED - data came in response to a Poll request - reading object group Class Objects (60)
- SPONTANEOUS - data came spontaneously - using Unsolicited Response (130) function
Value: the current value, optionally - depending on a particular object group and variation - with flags and timestamp
Point: the name of the I/O tag that is configured for this object. Names can also be repeated:
- if a column of a structured variable is specified for the Destination column parameter on the Destination tab in the I/O tag configuration
- if an "event" object group and an object group configurable for I/O tag are mapped to the same I/O tag (in the figure above, Analog Output Status (40) and Analog Output Event (42), both with Index=0, display I/O tag M.DNP3_OutSim_AnalogOutput41_2).
Filtering in the list of objects: the browse window allows you to filter by the values displayed in each column. The values don't have to be entered completely. The notation *FILTERED EXPRESSION* is sufficient, where the asterisks represent any text before the start and end of the expression (e.g., *put* covers both input or output).
The total number of objects: the total number of objects in all object groups is displayed at the bottom left of the window.
Meaning of individual options and buttons:
Copy all to clipboard
Copies all displayed objects and details to the Windows Clipboard.
Refresh
The Refresh button can be used to force the object list to be re-read from the device. By default, the KOM process reads the list of objects and their data types only for the first request and stores it in memory. Depending on the number of objects and the speed of the device, this reading may take a longer time. It then sends this stored list to the CNF process(es), so that the next reading of the list in the DNP3 Item Browser window is fast.
Cancel
D2000 Cnf has the recycling of browser windows implemented. If the window is closed by the Cancel button or after selecting an object, it is actually only hidden and is available for browsing for another I/O tag within the same station, so that the list of objects being viewed is preserved. Clicking on the cross at the top right corner will cause the window to actually close.
Tell commands
| Command | Syntax | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| STWATCH | STWATCH StationName | Tell command sends commands for the reading of values of all configured I/O tags. This command sends Poll requests to all Classes according to the station parameter configuration and sends requests for the reading of all I/O tags with the Explicit Read parameter active. |
Literature
IEEE Standard for Electric Power Systems Communications - Distributed Network Protocol (DNP3).
Blogs
You can read a blog about the DNP3 protocol:
Changes and modifications
-
Document revisions
- Ver. 1.0 - May 28, 2019 - the creation of the document
Requirements
| Minimum supported version | D2000 V12.1N |
Related pages:
Pridať komentár