D2000 system processes can communicate with the process D2000 Server in two ways:
- through shared memory (i.e. processes running on the same computer as D2000 Server is)
- through TCP/IP or Dual TCP/IP communications
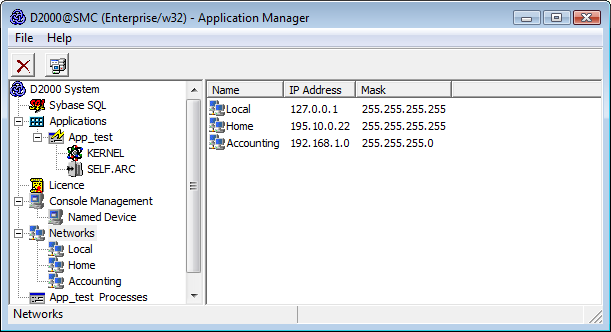
For processes that communicate as described in 2nd option, the process D2000 Application Manager provides the feature to specify the IP addresses of computers for accessing the D2000 Server process. Nowadays, there can be defined 10 networks in D2000 Systems at most.
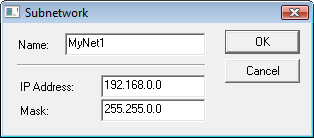
A network is specified by its name, IP address and network mask. The following window is used to specify (or modify) network settings. To open the window select the New SubNetwork item from the popup menu opened by right-clicking the Networks item.
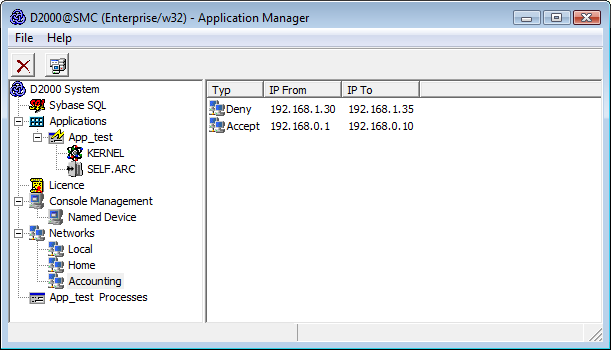
Each network can contain multiple so-called access ranges, i.e. specifications of IP addresses that are to be accepted or rejected to log on.
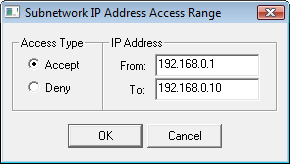
Access range is defined in the following dialog window that is opened by selecting the New IP Access Range item from the popup menu displayed by righ-clicking given network's name.
The process D2000 Server checks the IP addresses of clients (processes) that connect to it through TCP/IP or Dual TCP/IP communications as follows:
- if no network has been specified in D2000 Application Manager, IP addresses is not checked at all,
-
if at least one network has been configured, the incoming client is checked whether it belongs to one of
the specified networks:
- if it doesn't, the connection will be rejected,
- if it does, it has to be verified, whether all the networks, the client belongs to, meet one of the following conditions:
- there are no access ranges specified in the network
- the network contains at least one access range of Accept type and no access range of Deny type, which the client's IP address belongs to
The client will be connected if one of the conditions is met, otherwise the connection is rejected and the error log "Client rejected with error PROCES_TCPIP_DENY" is written into the log file of the process D2000 Server (the kernel.log file).
WARNING
- The process D2000 Server must be running to define or edit a network or access range.
- To edit or define a network or access range in application with the redundancy of application server the process D2000 Server must be in the HS state (HOT Server). After the editing is finished, all the changes are sent to the STANDBY Server.
Example:
| SubNetwork | IP Address | Mask | Range | Possible connections | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local | 127.0.0.1 | 255.255.255.255 | none | local clients | |||||||||
| Production | 192.168.0.0 | 255.255.255.0 | none | clients with the IP addresses of 192.168.0.1 to 254 | |||||||||
| Accounting | 192.168.1.0 | 255.255.255.0 |
|
clients with the IP addresses of 192.168.1.1 to 100, except clients with the IP addresses of 192.168.1.30 to 35 | |||||||||
| Director_Home | 195.10.0.22 | 255.255.255.255 | none | client with the IP address of 195.10.0.22 |
Note 1:
The process D2000 Application Manager connects to the process D2000 Server via TCP/IP by default.
Therefore the network with the IP address 127.0.0.1 and mask 255.255.255.255 must be defined before configuration
of the process D2000 Application Manager. If that network is not defined and the D2000 Application Manager
is restarted, it cannot connect to the process D2000 Server (an error message PROCES_TCPIP_DENY will
be displayed). In this case, run the process D2000 Application Manager using the start parameter /M
that allows to connect to D2000 Server through the shared memory.
Note 2:
The procedure described above doesn't work with Windows Terminal Services. One of the following alternatives
can be used there:
- connect the console session (mstsc.exe /console) and run the process D2000 Application Manager with the parameter /M,
- modify manually the ConsolesInfo.txt file located in the installation directory - delete the [SUBNET] and [IPACCESS] sections and either restart the process D2000 Server or use the TELL command REFRESH_LICENCE.
Pridať komentár