An authentication Authentication is a process of verification of the user's identity, i.e. the verification that the user is who he says he is. The authentication of the user is performed based on something the user knows (user's name and password), what he owns (USB token, personal chip card with encryption and identification PKI key), or user's measurable biometric characteristic (fingerprint, iris scan).
...
- to use the same password to log into D2000 and Windows (NTLM authentication),
- to use the same name and password to log into several D2000 systems; the password can be changed in one system and is valid for all systems - the password into Windows (NTLM authentication),
- automatic logon into D2000 without entering the name and password based on user's logon to Windows (Kerberos authentication),
- to secure the logon of the user into D2000 by hardware means (USB token, personal chip card with encryption and identification PKI key) in such a way that these hardware means are used to log the user into Windows and then the Kerberos authentication is used for logon into D2000,
- to disable to logon of the user into D2000 by Windows user management tools,
- to set policy policies and parameters for D2000 password by Windows user management tools.
Note for Linux and Raspberry PI platforms: as of D2000 version 12.2.65 (patches from 27.5.2020 and later), Kerberos authentication is also available on Linux x64 and Raspberry PI platforms. The following steps must be performed to make it work:
- joining of Linux/Raspberry PI server to Windows domain
(with the command realm join domain_name, e.g. realm join IPSTEST.SK) - enabling access of the D2000 Server (kernel) to the /etc/krb5.keytab file. One option is to configure the D2000 Server to run as root, another - less dramatic - is to configure access rights for the group under which the D2000 Server is running. For example, if the d2users group is used, you need to run:
chgrp d2users /etc/krb5.keytab
chmod 640 /etc/krb5.keytab
On the Linux platform, authentication within one domain (IPSTEST.SK) and between two domains was tested (hi.exe run under a user in the IPESOFT.SK domain, D2000 server on a Linux server in the IPSTEST.SK domain. In both cases, the value of the AuthSecPrinc parameter was set to SRVAPP$@IPSTEST.SK, where SRVAPP is the name of a Linux computer joined in the Windows domain.
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Authentication method | Meaning | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
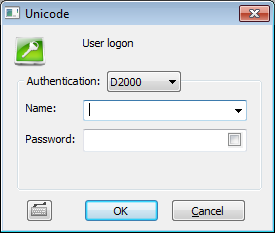
| The authentication of the user's name and password is performed by the process D2000 Server. This is the standard authentication method. It uses name and password which are saved in configuration of object User. Logon dialog displays user's name and password: | ||||||||||
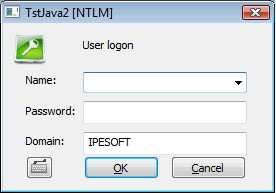
| The authentication subsystem Windows NTLM (NT LAN Manager) verifies the user's name and password. This subsystem is available from the Windows NT 4.0 version and the authentication is done in the domain defined by configuration parameter Domain. After the authentication D2000 Server will obtain the information about successful / unsuccessful verification of user's name and password in the domain. If the authentication is successful it will look for the object of User type with the same user name and check whether the NTLM authentication (parameter Authentication methods) is allowed, the domain name is the same and the logon is enabled. Dialog box contains: user name and password, name of application, text [NTLM] in the title and the name of Windows domain the user is logging into. Note: NTLM authentication is available on standalone computer with locally defined users (in this case Domain is computer's name) as well as in Windows domain (Domain is the name of domain). If the connection to an authentication authority failed, the user is not logged on. The NTLM authentication will change to D2000 authentication and this warning occurs: "NTLM authentication has failed. Enter your login name and password from D2000." | ||||||||||
| The authentication of the user's identity is made by the authentication subsystem Windows Kerberos (available from the version Windows 2000). It verifies the identity of the user which is logged into Windows so that the logon into D2000 System is automatic without Logon dialog or entering name and password. D2000 Server will obtain the information about user's name and domain from Windows Kerberos authentication subsystem. If the domain name matches the user's configuration parameter Domain then it will look for the object of User type with the same user name and check whether the Kerberos authentication (parameter Authentication methods) is allowed and the logon is enabled. Note: Using Kerberos authentication method is almost as risky as using the start parameters /AN and /AP which allow to start HI process and perform auto logon without entering user's name and password if the user leaves the workstation and does not lock the desktop (usage of the start parameters /AN and /AP is even more hazardous because they allow to steal the password for later misuse, while Kerberos permits only immediate misuse but not stealing of the password). Therefore we recommend:
| ||||||||||
| Authentication method available for D2000 versions above 12.00.061. The authentication of the user's identity is made performed by the Windows Kerberos authentication subsystem Windows Kerberos (available from the version Windows 2000). It verifies the identity of the user which who is logged into Windows so that the logon into D2000 System is automatic without Logon dialog or and without entering name and password. Note: SPNEGO authentication is available only in Windows domain, not on standalone computer, because it requires a software infrastructure which is installed only as a part of Windows domain controller. | ||||||||||
auth_tcl | TCLThe authentication of the user's identity is performed between internet browser and properly configured web server using Windows Kerberos authentication subsystem. It verifies the identity of the user which is logged into Windows so that the logon into D2000 System is automatic without Logon dialog or entering name and password. After the authentication ends successfully the information about user's name and domain is sent to the process D2000 Server. If the domain name matches the configuration parameter Domain then it will search the object of User type with the same user name and check whether the TCL authentication (parameter Authentication methods) is allowed and whether the logon is enabled. Note: If the user is not logged to Windows domain or Kerberos authentication cannot be successfully performed, the login window asking for username and password will be displayed. The username and password will be used for login using D2000 authentication. Kotva |
| This method is available from D2000 version 9.1.30. The user is identified by scanning the RFID card. RFID authentication works if RFID tag is installed on the client work station on some of serial COM ports, D2000 HI is running with the parameters (parameters of console) that ensure the handling of the RFID tag (see Console preferences - RFID parameters). After scanning the RFID card, there can occur two situations:
|
...
| Parameter | Meaning | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default method of authentication the process D2000 Server requires from all users. Possible values of parameter are:Note: The method TCL cannot be set as the value of this parameter - this method is implicitly permitted for Thin clients and forbidden for all other processes. | ||||||
| Security principal of authentication. Parameter is mandatory for Kerberos and SPNEGO authentication. Security principal can be the name of account which the process D2000 Server runs under. By default (kernel.exe runs as service under account Local System), the Security principal is the computer account in domain. Its name is the same as the name of computer and at the end is the symbol $. If the process kernel.exe has been run manually (from a command line) the Security principal is the account of the user in domain. Example: Domain is MyCompany, server is SrvApp1, process kernel.exe runs as service on account LocalSystem. Parameter AuthSecPrinc can be srvapp1$ or srvapp1$@MyCompany. If users belongin to a different domain OtherCompany want to be authenticated, AuthSecPrinc must be srvapp1$@MyCompany and moreover the domain MyCompany must trust the domain OtherCompany. Note: inter-domain autentication was tested on server srvapp114v belonging to domain ipstest.sk, AuthSecPrinc=srvapp114v$@ipstest.sk. HI was run on a computer belonging to domain IPESOFT, domain ipstest.sk trusted the domain IPESOFT. Example: Domain is MyCompany, process kernel.exe has been started from the command line by user D2User. Parameter AuthSecPrinc can be d2user or d2user@MyCompany. Note: Security principal can be defined also by the tools for Active Directory management so that it is independent from user name under which the process kernel.exe runs. More information can be obtained from Active Directory documentation and the instructions for the utility ktpass.exe on Microsoft web site. |
...