...
- Communication line category: OPC.
- OPC parameters:
- OPC Host: Only Remote entrance requires itRequired for Remote OPC server only. Computer, where the program program D2000 OPC Server is installed in - it is defined for OPC server type "Remote" only (maximum string: 50 characters). You can define names according to the UNC convention (e.g. \\server or server), DNS domain names (e.g., domain.com, example.company.com), or IP address (196.54.23.113).
- Backup Host: Only Remote entrance requires itRequired for Remote OPC server only. It is a backup OPC host. If the parameter is defined, after the communication has failed, the process process D2000 KOM is attempting to establish a connection alternately with the OPC host Host and the Backup hostHost.
- OPC Server: Name (ProgID) of the OPC server (maximum string: 50 characters).
- Server Type: according to the server type – InProc, Local, or Remote.
Communication line parameters
Following The following communication line parameters can be configured for protocol "OPC Data Access 2.05 & 3.0":
Tab. No. 1
| Name | Description | Unit | Default value | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPC HDA server name (ProgID), if it is available. Leave empty if OPC HDA functions are are not to be activated, use empty textused. | - | ||||||||||||||
| Sets the NumItems parameter for the synchronous reading of historical "raw" values. The implicit value 0 (zero) means all values in the given interval. | - | 0 | |||||||||||||
Authentication Level | Authentication level used when establishing a connection to the OPC server. The OPC standard defines the following levels:
Note: The default value RPC_C_AUTHN_LEVEL_CONNECT (2) may no longer be sufficient. Microsoft has implemented security hardening to address the security issues described in CVE-2021-26414. See "KB5004442—Manage changes for Windows DCOM Server Security Feature Bypass (CVE-2021-26414)" for more details. | - | 2 | |||||||||||||
| Starts the sequencing of calling the function Refresh2 of interfaces Async I/O 2.0 and Async I/O 3.0. The calling executes after the first calling has been finished (after it gets the values). | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||||
| Starts the sequencing of calling the function Refresh2 of interfaces Async I/O 2.0 and Async I/O 3.0. The calling executes after the first calling has been finished (after it gets the values). | YES/NO | NO | | Kotva | rfga | rfga | Repeat Failed Group Activation | Failed OPC group activations will be attempted again after a delay specified by the parameter "Group reactivation delay". | YES/NO | YES | ||||||
| A delay after which a failed OPC group activations activation is repeated if repetition is enabled by the parameter "Repeat failed group activation". | sec | 30 | |||||||||||||
| When an OPC group activation fails, KOM disconnects from the OPC server and reestablishes a connection. The parameter is relevant in a configuration of redundant OPC servers (after a disconnect from an OPC server follows , a reconnect to an alternate OPC server follows, where group activation may be successful). | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||||
| Period of executing the call of GetGroupState of interface the interface IOPCGroupStateMgt. This synchronous call is repeated periodically and detects to detect the problems which that could occur in communication with the OPC Server. | sec | 10 | |||||||||||||
| All the errors returned by calling of the "GetGroupState" function of interface interface IOPCGroupStateMgt are considered to be fatal (they will result in a disconnect from the OPC server and in a reconnect, or in a restart of the KOM process). An example of an error message returned by "GetGroupState": | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||||
| Allows stopping the KOM process when a fatal error occurs in communication. See the Note. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||||
| Only the active KOM process (i.e., the active instance connected to the HOT server) communicates with the OPC server. The KOM process, which becomes passive (by changing the active instance or switching the redundancy), closes the connection to the OPC server. Note: This parameter allows the reduction of the OPC server load in redundant D2000 systems, as well as solving problems with the license limitation on the number of OPC clientsAllows stopping the KOM process when a fatal error occurs in communication. See the Note. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||||
dp | Disconnect On Passive
| The parameter causes the first value of each I/O tag received after connecting to the OPC server to be ignored if it is invalid (it has a 'BAD' status). This parameter was implemented to suppress undesirable behavior of the OPC.SimaticNET server Only the active KOM process (i.e., the active instance connected to the HOT server) communicates with the OPC server. The KOM process, which becomes passive (by changing the active instance or switching the redundancy), closes the connection to the OPC server.Note: This parameter allows to reduce the OPC server load in redundant D2000 systems as well as to solve problems with license limitation of the number of OPC clients . | YES/NO | NO |
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Fatal abort of communication with the OPC Server causes the COM/OPC errors at callings:
...
- OPC Group Name - maximum string: 80 characters. This name is only formal in most cases and has no direct relation to the addressing scheme of devices communicating with the OPC server. The name of the group must be unique, ; two stations cannot have the same same OPC Group Name within one linkline.
- Type - data access type. You can choose one of the Async I/O 2.0, Async I/O 3.0, and Synchronous I/O options. The Async I/O 2.0 option - the asynchronous OPC interfaces IOPCAsyncIO2 and IOPCDataCallback (OnDataChange and OnReadcompleted call-back callback procedures) are used for data reading. The Synchronous I/O 2.0 option - OPC interface IOPCSyncIO is used. The Async I/O 3.0 option - OPC interfaces IOPCAsyncIO3 and IOPCDataCallback (OnDataChange and OnReadCompleted call-back callback procedures) are used for value reading of OPC items
- Create Active - if the option is checked, the OPC group is active, and OPC items in this group get values. If the option is not checked, the OPC group and items are initialized, but the OPC items do not get values. It is possible to block the OPC group - station temporarily. The option controls the pActive parameter of the SetState call of the OPC interface IOPCGroupStateMgt.
- Update Rate - it is given in milliseconds and defines the maximum speed of OPC item value changes for the option Async I/O 2.0 or Async I/O 3.0. It is transferred as pRequestedUpdateRate parameter of as the pRequestedUpdateRate parameter of the SetState call of the OPC interface interface IOPCGroupStateMgt. Warning - the information, set in tab the Time parameters tab in dialog window the Communication station - configuration dialog box, defines the read rate of OPC items.
- % Deadband - the parameter range is from 0.0 up to 100.0%. The parameter can only be only used for an analog type of items and determines the minimal change of the item for sending the value from the server to clients. For calculation, the OPC server uses the range defined by parameters High EU and Low EU, which can be get obtained by using the interface IOPCItemProperties. The default value of this parameter is 0.0. Value of % Deadband is transferred by means of parameter the pPercentDeadband of parameter of the SetState call of the OPC interface IOPCGroupStateMgt.
Note: The protocol OPC Client described in this topic does not support the OPC interface IOPCItemProperties. For further information, read up the document listed in the section section Literature. - Time Bias - If the OPC server and OPC client do not run in the same time zone, the parameter (given in minutes) will be used for the correct calculation of the time of the value of the "timestamp" OPC item. The default value of the parameter is 0 (zero). For further information read up the documents listed in the section Literature.
...
| Name | Description | Unit | Default value | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allows verifying the value after the recording by synchronous reading. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||
| Allows writing data into the OPC Server only by the synchronous interface IOPCSyncIO2. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||
| Using the Async I/O 3 option allows writing data by the WriteVQT function of the IOPCASyncIO3 interface (i.e., the write that transfers the quality and the timestamp together with the value). | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||
| Activates the debug list. It increases the number amount of information about the communication operation. It is recommended to use it only for the detection of the problems and debugging. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||
| Special mode for communication with OPC Servers made by the Merz company. The conversion to/from from MS DOS Date Time Format (2 x WORD) is used for values of TiA and ToA type. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||
| Delay which is A delay artificially inserted between the the AddItems callings calls to slow down the initialization phase. | ss:mss | 0 | |||||||||||
| An integer value of the "ERROR" state for conversion into Qi - quaternary input. | 0,1,2,3 | 3 | |||||||||||
| An integer value of "OFF" state for conversion into Qi - quaternary input. | 0,1,2,3 | 2 | |||||||||||
| An integer value of "ON" state for conversion into Qi - quaternary input. | 0,1,2,3 | 1 | |||||||||||
| An integer value of "TRANS" state for conversion into Qi - quaternary input. | 0,1,2,3 | 0 | |||||||||||
| If the quality of the OPC item changes into to "BAD", the value of the I/O tag will be valid with a a Weak flag. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||
| Blocks the effort to call AddItems which still repeats after its failurerepeated calls of AddItems, should adding a specific I/O tag address fail. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||
| Activates all the items of a group by a single call. It can speed - up the OPC communication start. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||
| All callings calls of the Write and Refresh2 functions as are registered as separate transactions. If they do not end up finish (successful successfully or unsuccessfulunsuccessfully) within this timeout, the error message will occur in the trace file of communication. | sec | 120 | |||||||||||
| Timeout, which delays repetitions of failed operationoperations:
| sec | 5 | |||||||||||
| Enables synchronous reading of the item value before the writing if the KOM process does not know the item data type (i.e., if there is a default value of data type "Empty/Default (VT_EMPTY)" and if the value must be written). | YES/NO | YES | |||||||||||
| Address of OPC Item (OPC Item ID), which contains the OPC server or OPC group error status (e.g., depending on the state of communication). An I/O tag with this address must also be configured. If the status reports an error, it will affect the values of all I/O tags on the station (they will have the Weak flag set). The Status Item Inverted Operation parameter specifies what value corresponds to the error status. | - | - | |||||||||||
| Interpretation of the OPC Item Status Item Name with an error status of the OPC server or the OPC group. The NO value means that the False or 0 reports values mean the correct state, and True respectively or non-zero value reports values mean an error. The YES value means that the False or 0 means values mean the error state, and True respectively or non-zero value reports correct statusvalues mean the correct state. | YES/NO | NO | |||||||||||
| Mapping the "Non Specific " OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of the I/O tag value. | None, FA, FB, FC, FD, FE, FF, FG, FH, FI, FJ, FK, FL, FM, FN, FO, FP | None | |||||||||||
| Mapping the "LocalOverride" OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of the I/O tag value. | |||||||||||||
| Mapping the "Config Error" OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of the I/O tag value. | |||||||||||||
| Mapping the "Not Connected" OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of the I/O tag value. | |||||||||||||
| Mapping the "Device Failure" OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of the I/O tag value. | |||||||||||||
| Mapping the "Sensor Failure" OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of the I/O tag value. | |||||||||||||
| Mapping the "Last Known" OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of the I/O tag value. | |||||||||||||
| Mapping the "Comm Failure" OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of the I/O tag value./td> | |||||||||||||
| Mapping the "Out Of Service" OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of I/O tag value. | |||||||||||||
| Mapping the "Waiting For Initial Data" OPC DA quality flaginto the attributes of I/O tag value. | |||||||||||||
| Mapping the "Last Usable" Last Usable" OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of the I/O tag value. | |||||||||||||
| Mapping the "Sensor Cal" OPC DA quality flaginto the attributes of the I/O tag value. | |||||||||||||
| Mapping the "EGU Exceeded" OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of the I/O tag value. | |||||||||||||
| Mapping the "Sensor CalSub Normal" OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of the I/O tag value. | |||||||||||||
| Mapping the "EGU Exceeded" OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of the I/O tag value. | |||||||||||||
| Kotva | f_sn | f_sn | Map SubNormal as FlagMapping the "Sub Normal" OPC DA quality flag into the attributes of the I/O tag value. | |||||||||||
| Kotva | raec | raec | Reconnect After Error CountIf a consecutive number of errors during reading equals the value of this parameter, reinitialization of OPC connection will be performed. Value of zero means that reinitialization will not be performed (default behavior). The current implementation handles only errors in synchronous mode (type setting to "Synchronous I/O" in tab Address of Station object). | - | 0 |
...
Possible I/O tag types: Ai, Ao, Ci, Co, Di, Qi, Dout, TiA, ToA, TiR, ToR, TxtI, TxtO.
I/O tag address requires to define OPC Item ID (maximum string: 200 characters). If the OPC server supports the IOPCBrowseServerAddressSpace interface, the "OPC Item ID" address may be selected directly from the address list supported by the OPC server (by clicking the "Browse Items..." button, see the Browsing of OPC server address space section.
Note: if the I/O tag's address is specified as %IGNORE, such an I/O tag will be ignored.
Further required parameters (OPC Item Parameters) are:
- Type - required data type (VARIANT). The default value is Empty/Default (VT_EMPTY), - the OPC server makes a decision on the VARIANT type of the item.
- Item Active - if the option is checked, the item will be active and get values from the server. The option is transferred by the parameter bActive of the pItemArray structure into the AddItems call of the OPC interface IOPCItemMgt.
- Bit Index - bit number. It is defined as a number within the range of 0..31. It can be only used for the Di and Dout value types. Value received from the OPC server will be converted to 32-bit unsigned number and the binary value of the I/O tag is the value of a particular Bit Index. The conversion is allowed only for the VARIANT values of integer types (e.g. VT_UI1, see the Type parameter ).
- Array Index - the option (a number within the range of 0..32767) determines the index in the array of received VARIANT value from the OPC server of the Array type. Array value on the defined position is assigned to the value of the I/O tag.
The protocol supports the configuration of the Destination tab of the I/O tag. If the value of the OPC item is of Array type, the communication protocol copies the values of the array, starting with the ArrayIndex item, into a column of a structured variable. The size of the structured variable is taken into consideration. If the VARIANT array is smaller than the number of structured variable rows, the empty rows of the structured variable will be invalidated. If the number of structured variable rows is smaller than the VARIANT array, the values which are over the limit will be ignored.
...
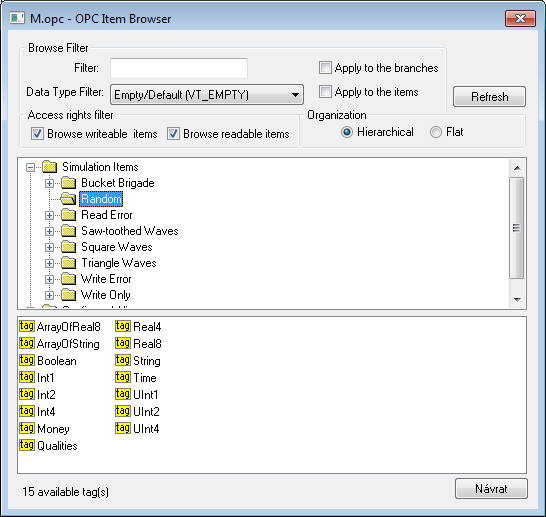
Clicking on the "Browse Items..." button in the Address tab of the I/O tag dialog box opens another dialog window "OPC Item Browser".
Here the user can choose the items from the OPC server address space. The item representation can be "Hierarchical" or "Flat". Some of the OPC servers do not support the "Hierarchical" representation (the button "Hierarchical" is disabled). If both the representations are supported the "Hierarchical" may be switched over to "Flat" and vice-versa.
- Hierarchical - enables browsing of the OPC server address space according to the logical hierarchical groups and subgroups. The dialog box "OPC Item Browser" is divided into two parts:
- hierarchical tree structure (top part)
- list of OPC items (OPC tags) belonging to the selected branch (bottom part)
- Flat - displays all the available OPC items in one linear list.
OPC Item ID may be selected by double click on it. This item then occurs in the text field OPC Item ID in the Address tab of the I/O tag dialog box and the "OPC Item Browser" dialog window will be closed. To close the window without changes click on the "Cancel" button.
On the top part of the dialog window, there are filter options. Text "Filter" allows showing only the items according to the mask (some of the OPC servers support the so-called star convention).
"Data Type Filter" allows showing the items of a specified data type. The "Empty/Default" option is the default and enables viewing all the items.
The user must define whether the filter should be applied on the hierarchical tree structure (check the "Apply to the branches" button) or also on the OPC items (check the "Apply to the items" button).
According to the access rights, only readable items are displayed (check the "Browse readable items" button) or writable ones (check the "Browse writeable items" button). Default settings - both possibilities are enabled.
The changed conditions come into effect by clicking the "Refresh" button.
Copying tags
A keyboard shortcut Ctrl+C copies the names of tags in a selected branch into the Windows clipboard. All tags will be copied unless a specific tag is selected.
A keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Shift+C copies the names of tags in all browsed branches into the Windows clipboard.
Note: In versions from 20th December 2018 and newer, recycling of browser dialog has been implemented. If the dialog is closed by the Close button or after selecting a tag, it is actually only hidden and it is available for browsing by another I/O tag within the same station so that the tree structure of the browsed objects is preserved. Clicking on the close icon at the top right corner will cause the dialog to be really closed.
...
Implementation of this protocol partially supports the specification of OPC HDA (Historical Data Access). The synchronous reading of raw data is supported. TELL command GETOLDVAL activates the reading of historical values. The asynchronous option IOPCAsyncIO of mode for OPC DA should be set to continuously read both the historical data and the current one.
...
| If a consecutive number of errors during reading equals the value of this parameter, reinitialization of the OPC connection will be performed. A value of zero means that reinitialization will not be performed (default behavior). The current implementation handles only errors in synchronous mode (type set to "Synchronous I/O" in the Address tab of the Station object). | - | 0 |
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Possible I/O tag types: Ai, Ao, Ci, Co, Di, Qi, Dout, TiA, ToA, TiR, ToR, TxtI, TxtO.
I/O tag address requires defining the OPC Item ID (maximum string: 200 characters). If the OPC server supports the IOPCBrowseServerAddressSpace interface, the "OPC Item ID" address may be selected directly from the address list supported by the OPC server (by clicking the "Browse Items..." button, see the Browsing of OPC server address space section.
Note: if the I/O tag's address is specified as %IGNORE, such an I/O tag will be ignored.
Further required parameters (OPC Item Parameters) are:
- Type - required data type (VARIANT). The default value is Empty/Default (VT_EMPTY), - the OPC server makes a decision on the VARIANT type of the item.
- Item Active - if the option is checked, the item will be active and get values from the server. The option is transferred by the parameter bActive of the pItemArray structure into the AddItems call of the OPC interface IOPCItemMgt.
- Bit Index - bit number. It is defined as a number within the range of 0..31. It can only be used for the Di and Dout value types. Value received from the OPC server will be converted to a 32-bit unsigned number, and the binary value of the I/O tag is the value of a particular Bit Index. The conversion is allowed only for the VARIANT values of integer types (e.g., VT_UI1, see the Type parameter ).
- Array Index - the option (a number within the range of 0..32767) determines the index in the array of received VARIANT value from the OPC server of the Array type. The array value at the defined position is assigned to the value of the I/O tag.
The protocol supports the configuration of the Destination tab of the I/O tag. If the value of the OPC item is of Array type, the communication protocol copies the values of the array, starting with the ArrayIndex item, into a column of a structured variable. The size of the structured variable is taken into consideration. If the VARIANT array is smaller than the number of structured variable rows, the empty rows of the structured variable will be invalidated. If the number of structured variable rows is smaller than the VARIANT array, the values that are over the limit will be ignored.
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Clicking on the "Browse Items..." button in the Address tab of the I/O tag dialog box opens another dialog window, "OPC Item Browser".
Here, the user can choose the items from the OPC server address space. The item representation can be "Hierarchical" or "Flat". Some of the OPC servers do not support the "Hierarchical" representation (the button "Hierarchical" is disabled). If both the representations are supported the "Hierarchical" may be switched over to "Flat" and vice-versa.
- Hierarchical - enables browsing of the OPC server address space according to the logical hierarchical groups and subgroups. The dialog box "OPC Item Browser" is divided into two parts:
- Hierarchical tree structure (top part)
- List of OPC items (OPC tags) belonging to the selected branch (bottom part)
- Flat - displays all the available OPC items in one linear list.
OPC Item ID may be selected by double-clicking on it. This item then occurs in the text field OPC Item ID in the Address tab of the I/O tag dialog box, and the "OPC Item Browser" dialog window will be closed. To close the window without change, click on the "Cancel" button.
On the top part of the dialog window, there are filter options. Text "Filter" allows showing only the items according to the mask (some of the OPC servers support the so-called star convention).
"Data Type Filter" allows showing the items of a specified data type. The "Empty/Default" option is the default and enables viewing all the items.
The user must define whether the filter should be applied on the hierarchical tree structure (check the "Apply to the branches" button) or also on the OPC items (check the "Apply to the items" button).
According to the access rights, only readable items are displayed (check the "Browse readable items" button) or writable ones (check the "Browse writeable items" button). Default settings - both possibilities are enabled.
The changed conditions come into effect by clicking the "Refresh" button.
Copying tags
A keyboard shortcut Ctrl+C copies the names of tags in a selected branch into the Windows clipboard. All tags will be copied unless a specific tag is selected.
A keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Shift+C copies the names of tags in all browsed branches into the Windows clipboard.
Note: In versions from 20th December 2018 and newer, recycling of browser dialog has been implemented. If the dialog is closed by the Close button or after selecting a tag, it is actually only hidden and it is available for browsing by another I/O tag within the same station, so that the tree structure of the browsed objects is preserved. Clicking on the close icon in the top right corner will cause the dialog to be closed.
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Implementation of this protocol partially supports the specification of OPC HDA (Historical Data Access). The synchronous reading of raw data is supported. TELL command GETOLDVAL activates the reading of historical values. The asynchronous option IOPCAsyncIO of mode for OPC DA should be set to continuously read both the historical data and the current one.
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Command | Syntax | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| STWATCH | STWATCH StationName | The command sends commands for the synchronous reading of values of all configured I/O tags (regardless of whether data access type is set to “Async I/O 2.0”, "Async I/O 3.0", or “Synchronous I/O”) |
| STCOMMAND | STCOMMAND StationName DISCONNECT | The command closes the active OPC connection of the line (the parent of "StationName"). Then, the system is restarted and the connection is reinitiated. If remote access is used and a backup OPC host is configured, the servers are interchanged ("OPC Host" for "Backup Host" or vice-versa). |
| STCOMMAND StationName CONNECT_PS | Closes the active OPC connection and enforces connection to the primary OPC server "OPC Host". It is important only for remote access. | |
| STCOMMAND StationName CONNECT_BS | Closes the active OPC connection and enforces connection to backup OPC server "Backup Host". It is important only for remote access. |
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Remote browsing/local registration of the OPC server
D2000 KOM Process (version 7.01.020 rel. 055 and higher) supports getting GUID OPC Servers from ProgID on remote computers through the DCOM interface by OPCENUM utility (remote browsing). The local registration of the OPC server on the local PC is not required if the OPCENUM utility/Windows service has been installed (both on the local PC with the D2000 KOM process as an OPC client and on the remote PC with the OPC server) and the access rights allow the remote browsing. The OPCENUM utility is a part of the "OPC Core Components Redistributable" package available on http://www.opcfoundation.org or as a part of the OPC Server installation package.
If this error occurs (see the section COM/OPC errors record):
ERROR: OPCServerName caused COM/OPC error 80040153H on CoCreateInstanceEx(IID_OpcServerList), Error string : Invalid value for registry
It is necessary to install the OPC Core Components Redistributable also on the OPC client (KOM process). The registration of the OPC Server is optional. To register, use one of the two ways:
- Some OPC servers are supplied together with installation programs supporting the connection of OPC clients (third party) to the remote OPC server. These installation programs have names such as "OPC Server Connect" and the like. After installation, the OPC server (ProgID) appears in the list of OPC servers on the client's computer. D2000 OPC client uses this information for the acquisition of CLSID from the given ProgID (see the section Communication line configuration). An OPC server registered in this way, of course, can't be run on the client's side.
- Manual registration of the OPC server on the client's side. Proceed as follows:
- Copy the OPC server (from the computer where it has been installed) into an auxiliary directory on the client's side (computer).
- Run the command line from the directory.
- Register the OPC server. If the OPC server name is e.g., OPCSERVER.EXE, then enter a command:
OPCSERVER.EXE /regserver
and press ENTER. If the OPC server is only a .dll, use the regsvr32 system utility. - The auxiliary directory and files can be deleted.
Always study the OPC server manual from its manufacturer in detail and compare it with the procedures described above.
Setting the access rights to the OPC Server
As the OPC DA standard uses COM/DCOM technology, the connection to the remote OPC server is checked for Windows operating system access rights. On both the local (OPC client) and remote (OPC Server) computer, the same user must be created (with the same password) and the user must be logged on the client computer, or the KOM process (running as a Windows service) must be started with this user's credentials.
- On the command line, on the computer where the OPC server is installed, start the "Component Services" configuration tool (in the "Administrative Tools" folder or by starting the "dcomcnfg" command on the command line).
- Select "Component Services" -> "Computer" -> "My Computer", select the "Properties" menu.
- Check that DCOM is enabled by checking the "Enable Distributed COM on this computer" option in the "Default Properties" tab.
- On the "COM Security" tab, check the limits for "Access Permissions" and "Launch and Activation Permissions". Press "Edit Limits..." and verify the DCOM access rights for your user, or for the "Distributed COM Users" user group. Verify the "Remote Access", "Remote Launch", and "Remote Activation" permissions. Note that these are limit settings. The "Security" settings on a specific component cannot override the "COM Security" limit settings, although it can be configured to do so.
- Check that the user is a member of the "Distributed COM Users" User Group. Open "Control Panel" -> "Administrative tools" -> "Computer Management" -> "Local Users and Groups" -> "Groups" and find the "Distributed COM Users" group. If the user under whom you access the OPC server is not in this group, add it to it.
- In the list of components ("DCOM Config" branch under "My Computer"), find the desired OPC server and open its parameters window (menu "Properties"). Open the "Security" tab.
- Switch "Launch And Activation Permissions" to "Customize" and click the "Edit..." button.
- Check whether the desired user or user group "Distributed COM Users" is in the list, and if not, add it.
- Enable the "Remote Launch" and "Remote Activation" options.
- Do the same for "Access Permissions".
- In the "Identity" tab, check whether the
...
Remote browsing/local registration of OPC server
D2000 KOM Process (version 7.01.020 rel. 055 and higher) supports getting GUID OPC Servers from ProgID on remote computers through the DCOM interface by OPCENUM utility (remote browsing). The local registration of the OPC server on the local PC is not required if the OPCENUM utility/windows service has been installed (both on the local PC with D2000 KOM process as an OPC client and on the remote PC with the OPC server) and the access rights allow the remote browsing. The OPCENUM utility is a part of the "OPC Core Components Redistributable" package available on http://www.opcfoundation.org or as a part of the OPC Server installation package.
If this error occurs (see the section COM/OPC errors record):
ERROR: OPCServerName caused COM/OPC error 80040153H on CoCreateInstanceEx(IID_OpcServerList), Error string : Invalid value for registry
it is necessary to install the OPC Core Components Redistributable also on the OPC client (KOM process). The registration of the OPC Server is optional. To register, use one of the two ways:
- Some OPC servers are supplied together with installation programs supporting the connection of OPC clients (third side) to the remote OPC server. These installation programs have names such as "OPC Server Connect" and the like. After installation, the OPC server (ProgID) appears in the list of OPC servers on the client's computer. D2000 OPC client uses this information for acquisition of CLSID from given ProgID (see the section Communication line configuration). An OPC server registered by this way, of course, can't be run on the client's side.
- Manual registration of the OPC server on the client's side. Proceed as follows:
- Copy the OPC server (from the computer where has been installed) into an auxiliary directory on the client's side (computer).
- Run the command line from the directory.
- Register the OPC server. If the OPC server name is e.g. OPCSERVER.EXE, then enter a command:
OPCSERVER.EXE /regserver
and press ENTER. If the OPC server is only a .dll, use the regsvr32 system utility. - The auxiliary directory and files can be deleted.
Always study the OPC server manual from its manufacturer in detail and confront it with the procedures described above.
Setting the access rights to OPC Server
As OPC DA standard uses COM/DCOM technology, the connection to the remote OPC server is checked for Windows operating system access rights. On both the local (OPC client) and remote (OPC Server) computer, the same user must be created (with the same password) and the user must be logged-on the client computer, or the KOM process (running as a Windows service) must be started with this user's credentials.
- On the computer with the OPC server, use the "dcomcnfg" command to start "Component Services" (or start it in "Administrative Tools").
- Select "Properties" menu in "Component Services" -> "Computer" -> "My Computer".
- Make sure that DCOM is enabled, i.e. parameter "Enable Distributed COM on this computer" on the "Default Properties" tab is checked.
- In the list of components (branch "DCOM Config" under "My Computer"), select the required OPC server and open the dialog box containing its parameters (Properties). Click the Security tab.
- The parameter "Launch And Activation Permissions" set to Customize and click the Edit... button.
- Find the required user and if is not in the list, add him/her into..
- Enable the options "Remote Launch" and "Remote Activation".
- The parameter Access permission set to Customize and click the Edit... button.
- In the "Identity" tab check whether "The launching user" or "This user" option is enabled, which is also the checking of set, and if so, the user account that you configure. Typically, we we are configuring is also listed. We usually recommend the setting "The launching user". If some problems occur, in case of problems, try the direct setting "This user". In any case, be careful about with the setting "The interactive user", which is absolutely not recommended! The OPC server can be accessible and started only if some we strongly do not recommend this! In this case, the OPC server is only available and started if a user is interactively logged in on the computer machine with the OPC server. This setting leads to the problems such as with the unavailability of an OPC server being unavailable, e.g., after its starting until any restart, while no user is logged onin.
- If you must it is necessary to use the setting "The system account (services only)", i.e. ., when the OPC server works operates as a Windows service, watch monitor the level of access rights of the "SYSTEM" user according to the rules above-mentioned rules.
Wrong setting of access rights will probably cause an error (see the section Errors and problems - COM/OPC error reports):
...
The problem can be partially solved when you add the Everyone group into to Launch Permissions and Access Permissions. To ensure , that the OPC server will be run under some user (not under the SYSTEM account), open the tab Identity and define the data for the option This user. In this case, the OPC server is not safe.
If the KOM process runs as a Windows service, it cannot use the "/X1" or "/X2" parameters, because it does not work under the logged-on user but under the SYSTEM account, and access rights verification executed by the OPC server fails. Use the "/X4" start-up parameter.
...
For users working under Windows XP with ServicePack2 Service Pack 2 or later operating systems, it is recommended to change the parameter Network access: Let Everyone permissions apply to anonymous users (Local Security Policy -> Local Policies -> Security Options) to the value of Enabled.
...
|E|> ERROR: ServerName caused COM/OPC error 80070005H on Advise(IID_IOPCDataCallback), Error string : E_ACCESSDENIED Access is denied.
then it is necessary to add a user in the context of whose the communication runs. In "Component Services" on the computer with OPC client (KOM process) add this user to the list of users on the "COM Security" tab -> "Edit Limits", for both "Access Permissions" and "Launch and Activation Permissions" parameters and enable "Remote Access" / "Remote Activation". It is a problem connected with establishing the call-back callback connection with the OPC server. In this case, the roles are reversed, and the OPC client (i.e., KOM process) works as a DCOM server. Adding this user and enabling the remote access enables establishing the call-back callback procedures between the OPC client and the OPC server. Call-back procedures are necessary for acquiring the values from the OPC server in the "Async I/O 2.0" and "Async I/O 3.0" asynchronous modes.
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
If the OPC server is configured to run under "The interactive user" on the last Identity tab Identity of the "Properties" dialog window, it may cause the OPC server to be available only when a user is logged on to the computer. We recommend changing this setting to "The launching user", "This user", resp. respectively "The system account". |
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
In the specific case for the OPC communication to work, it was required:
|
...
When starting or during the course of communication, the following error reports could occur. For easier identification of the problem, set the communication tracking level at least to the level Monitor, or temporarily to the level Monitor & disk in the configuration dialog box of a particular communication line. If you select the level Monitor & disk, the file line_name.LOG containing all debug and error logs will be created in the subdirectory /TRACE of the application directory on the computer with running process the D2000 KOM process.
| Error: | WriteAsync - FAILED (transactionID) - Item : 'OPCItemID' |
| Description: | Attempt to write the value using the Write function call of the OPC interface IOPCAsyncIO2 failed. |
| Error: | ShutDown OPC Server : 'ServerProgID' ! |
| Description: | The OPC server was stopped, probably in the correct way, even though it has active clients. |
| Error: | OPC Server 'ServerProgID' is unavailable ! |
| Description: | The remote DCOM OPC server is unavailable. Process D2000 KOM as a client is still attempting to connect to the server. Check the PC with the installed OPC server (if it is running and is correctly connected to the local network). |
| Error: | SetCallBack - FAILED, Group : 'OPCGroupName', Server : 'ServerProgID' ! |
| Description: | Fatal error - call-back procedures of the OPC interface OPCDataCallback could not have been initialized for the OPC group. Contact the Ipesoft's technical support. |
| Error: | SetGroupState - FAILED, Group : 'OPCGroupName', Server : 'ServerProgID' ! |
| Description: | Fatal error - SetStatefunction call of the OPC interface IOPCGroupStateMgt failed. Contact the Ipesoft's technical support. |
| Error: | EnableSubscribe - FAILED, Group : 'OPCGroupName',Server : 'ServerProgID' ! |
| Description: | Fatal error - SetEnable function call of the OPC interface IOPCAsyncIO2 failed. Contact the Ipesoft's technical support. |
| Error: | RefreshAllAsync - FAILED, Group : 'OPCGroupName', Server : 'ServerProgID' ! |
| Description: | Fatal error -Refresh2 function call of the OPC interface IOPCAsyncIO2 failed. Contact the Ipesoft's technical support. |
| Error: | OPCConnectToServer - FAILED, Server : 'ServerProgID' ! |
| Description: | Fatal error - it is not possible to connect to the OPC server. Check the OPC server parameters - the tab OPC in the configuration dialog box of the communication line and the tab Address in the configuration dialog box of the communication stations. |
| Error: | OPCAddGroup - FAILED, Group : 'OPCGroupName', Server : 'ServerProgID' ! |
| Description: | Fatal error - the OPC group could not be created by calling the AddGroup function of the OPC interface IOPCServer. Contact the Ipesoft's technical support. |
| Error: | ReadSync - FAILED, Item : 'OPCItemID' ! |
| Description: | Read call of the OPC interface IOPCSyncIO failed. |
| Error: | AddItems - FAILED (Group not connected), Item : 'OPCItemID' ! |
| Description: | The OPC item could not have been initialized, because creating the OPC group has failed. Contact the Ipesoft's technical support. |
| Error: | Write - FAILED (transactionID) , Item : 'OPCItemID' ! |
| Description: | Writing the value into the OPC server failed. Writing is performed by the Write function called by the interfaces IOPCSyncIO or IOPCAsyncIO2, according to the parameter Type (data access type) of the OPC group. |
| Error: | Write - FAILED, OPC Server is disconnected, Item :'OPCItemID' ! |
| Description: | The value could not have been written into the OPC server, because the OPC server is disconnected. |
| Error: | Group parameters error, Group: 'OPCGroupName', Server : 'ServerProgID' ! |
| Description: | OPC group configuration parameters are wrong. Check the OPC parameters - the tab Address in the configuration dialog box of a particular communication station. |
...
- OPC FOUNDATION, Data Access Custom Interface Standard, Version 2.05A, June 28, 2002.
- OPC FOUNDATION, Data Access Custom Interface Standard, Version 3.00, March 4, 2003.
- OPC FOUNDATION, OPC Common Definitions and Interfaces, Version 1.0, October 27, 1998.
- OPC FOUNDATION, Using OPC via DCOM with Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 2, (C) 2004 OPC Foundation Inc.
The othersOther sources:
- OPC DCOM White Paper, Richard C. Harrison, Intellution Inc. © Intellution Inc. 1998
...
- January 3rd, 2003 - added the parameter UPDATE_RATE, value arrays.
- January 23rd, 2004 – revised parameters group/item, error reports, and DCOM.
- November 22nd, 2005 - new protocol parameters implemented.
- October 10th, 2007 - parameters of protocol Async I/O 3.0 update
- December 3rd, 2007 - added the information about the destination column
- March 2009 - added the support of HDA
- February 2010 - OPC Item browsing
- March 2013 - tell commands
- July 2021 - added support for working with 64-bit INT / UINT
...
- Ver. 1.0 – February 9th, 2000
- Ver. 1.1 - January 3rd, 2002
- Ver. 1.2 - January 23rd, 2004
- Ver. 1.3 - November 22nd, 2005
- Ver. 1.4 - October 10th, 2007
- Ver. 1.5 - December 3rd, 2007
- Ver. 1.6 - March 13th, 2009
- Ver. 1.7 - February 8th, 2010
- Ver. 1.8 - March 5th, 2013
- Ver. 1.í 9 - July 16th, 2021
- Ver. 1.10 - Feb 7th, 2021 - added parameter "Authentication Level"
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
...