Configuration of communication line of "Serial", "Serial Line Redundant" and "Serial System&Line Redundant" categories
Communication line parameters of "Serial", "Serial Line Redundant", and "Serial System&Line Redundant" categories do not depend on the hardware used for serial communication, because the operation of serial interfaces is solved by means of asynchronous port drivers in Windows system (device drivers) or Linux serial port interface. Definitions are the same either for communication via standard ports COM1 up to COM99, or e.g. via intelligent asynchronous communication adapters DigiBoard, Moxa, VSCOM, or other extension cards or devices. These parameters may be configured in four independent modes. Communication stations can subsequently use one (or even more) of these modes for their communication.
Note: if the D2000 KOM process is running on a Linux/Raspberry PI platform, you must enter the Device parameter value as a full path to the device that corresponds to the serial port (eg /dev/ttyAMA0 or /dev/ttyS0).
Parameters
Baud rate
Setting of the line baud rate. Valid values: 110, 150, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400.
Number of bits
A number of data bits. Valid values: 5, 6, 7, 8.
Number of stop bits
A number of stop bits. Valid values: 1, 1.5, 2.
Illegal combinations:
5 data bits and 2 stop bits,
6, 7, or 8 data bits and 1.5 stop bit.
Parity
Settings of the parity of asynchronous transmission:
- No parity
- Even
- Odd
Handshaking
Configuration of handshaking on the level of Windows driver.
- None
- RTS/CTS - hardware handshake
- XON/XOFF - software handshake
- Custom - own configuration of the handshake
None
It allows setting RTS, DTR signals to required permanent values.
RTS/CTS
RTS signal is used for the standard hardware handshake controlled directly by the serial asynchronous port driver. It allows setting a permanent value of the DTR signal.
XON/XOFF
Software XON/XOFF handshaking is controlled directly by the serial asynchronous port driver.
Custom
At transmission, RTS and DTR signals may be controlled by Receive Delay and Transmit Delay time parameters. Own setting of the handshaking is suitable to use for RS232/485 converters controlled by these signals.
Hardware
DTR/DSR
Custom mode sets DTR as the active signal for the handshaking control.
RTS/CTS
Custom mode sets RTS as the active signal for the handshaking control.
Inverse
For the handshaking of Custom type, controlled signals RTS or DTR are inverted.
RTS=0 (RTS=1)
It sets a constant RTS signal level in case that is not actively used by the selected handshaking type.
DTR=0 (DTR=1)
It sets a constant DTR signal level in case that is not actively used by the selected handshaking type.
WaitTxEMPTY
If the option is enabled, the communication thread is waiting for the transmission to end. The option enables the synchronization of RTS or DTR signal control at the end of the transmission (see Receive delay) in case of the handshake of Custom type. As the standard serial drivers of Windows operating systems allow to get information only about the transmission of the last byte into the transmission shift register of the UART device (but not physically sent out), then in the case of this option, there is 1 character with 0xFF value added to the end of the transmitted message. At the moment of transmission indication of this character into the transmit register, the inherent message is sent out safely, and Receive delay (if nonzero) is starting to tick. See also Note.
Transmit delay
Delay (in milliseconds), that is inserted between the RTS signal setting (Custom handshaking RTS/CTS) or DTR signal setting (Custom handshaking DTR/DSR) and the beginning of message transmission.
Receive delay
Delay (in milliseconds), that is inserted from the end of the transmission to the deactivation of the RTS signal (Custom handshaking RTS/CTS) or DTR signal (Custom handshaking DTR/DSR). For the real starting of this delay at the moment of the transmission end, it is necessary to use the WaitTxEMPTY option.
Other options
ConstOpen
If the option is enabled, then the communication port of the line is permanently opened, otherwise, the port is used only in case of need. The option allows sharing ports with other applications.
CheckError
If the option is enabled, the communication error check will be executed - Parity, Frame, Overrun, Break Error.
Ballast
A number of empty unimportant characters (with 0x00 value), which are inserted before the transmitted message. It is advantageous when controlling modems/radiomodems or converters controlled by their own data signal. See also Note.
Note: Ballast and WaitTxEMPTY options insert special characters before (or behind) the transferred message, which may disable the communication with devices. Further information can be found in the documentation for individual communication protocols that communicate via asynchronous serial ports.
Tell command LNSTAT
The tell command LNSTAT OPEN/CLOSE stops communication (CLOSE) and disconnects the communication port. Communication resumes after the LNSTAT OPEN command or when the communication process is restarted.
Note
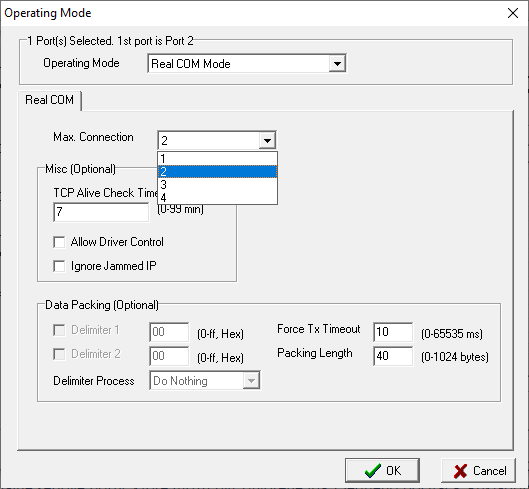
The /DBSH startup parameter for Serial, Serial Line Redundant, and Modem communication lines causes the serial port to be closed if the D2000 KOM process is connected to an SBS Server or if the D2000 KOM process becomes a passive instance. This makes it possible for a redundant D2000 application (or an application with multiple redundant D2000 KOM processes) to use virtual serial ports that can only be opened from one computer. An example of such a serial server is Moxa OnCell. On the other hand, for example, Moxa NPort serial servers allow configuring up to 4 connections per serial port. The following screenshot of the NPort Administrator program shows the configuration of the Moxa NPort serial port in "Real COM Mode" (virtuálny sériový port) with a maximum of 4 connections.
Related pages:
Pridať komentár