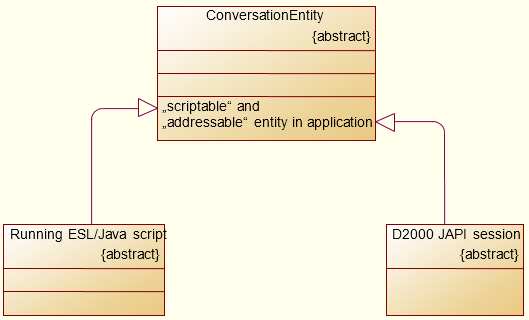
In the D2000 on the system level, there is supported a mechanism that enables to create a conversation between two "scriptable" and "addressable" entities of the applications.
In practice, the conversations should be used wherever on the application level, there is some session (or binding) between the instances of ESL scripts or processes implemented by the D2000 JAPI. In the event that such bindings are made by the conversation, there is possible to resolve this condition where the "other entity" of this session ends.
For example:
A service, which allows clients (other server events, pictures or D2000 JAPI) to be attached to receive the messages, is implemented by server event E.MAIL_SERVER. This connection is done by this method:
RPC PROCEDURE Attach .... END Attach |
The client will subscribe to the messages by calling the appropriate message:
CALL [E.MAIL_SERVER] Attach ON SELF.EVH |
E.MAIL_SERVER implements the next service that enables to send the message to logged-in clients:
RPC PROCEDURE Send(IN TEXT _msg) ... END Send |
When ending the client, it must stop registration by calling this method:
RPC PROCEDURE Detach .... END Detach |
Everything works properly until the moment when a client, who is being ended, do not manage to call the method Detach, which causes that E.MAIL_SERVER will not be informed that the client no longer exists.
The other error could be that if E.MAIL_SERVER was reinitiated for some reason (process restart, a new version of service, ...), no client finds out that it must be registered again by calling the method Attach.
The conversations help to resolve these problematic situations.
Below is the list of entities that may be used in the conversations:

The conversation is a unique session between the entities. It is used as a medium (or transport layer) for mutual asynchronous procedural communication (by calling the RPC procedures and methods of interfaces that they implement) and regards the life cycle. It means that:
RPC procedures are used to create and close conversations and send messages. Handling of unexpected interruption of the transaction is done by calling the RPC procedure of script which participates in the transaction.
For that purpose, we extended the syntax of the declaration of RPC procedures.
RPC PROCEDURE [_hTC, TC_B] NewTransaction(parameters) RPC PROCEDURE [_hTC, TC_E] EndTransaction(parameters) RPC PROCEDURE [_hTC, TC_BE] QuestionTransaction(parameters) RPC PROCEDURE [_hTC, TC_C] UserProc(parameters) RPC PROCEDURE [_hTC, ERROR] TransactionInterrupted |
Variable _hTC is used for identification of conversation (number of conversations is not limited). Within the procedure handling, it is always declared as a local variable of IN INT type.
The extended syntax for calling the procedures.
CALL [objIdent] NewConversation(parameters) ASYNC ... TC_B _hTC CALL [_hTC] EndConversation(parameters) ASYNC ... TC_E CALL [objIdent] QuestionConversation(parameters) ASYNC ... TC_BE _hTC CALL [_hTC] UserProc(parameters) ASYNC TC_C |
Variable _hTC is output within the actions TC_B and TC_BE and input within TC_C and TC_E. All callings are asynchronous.
Keywords TC_B, TC_E, TC_BE, ERROR are used for procedures that manage the life cycle of conversation (handle or initiate the events that changes its status). Keyword TC_C is used to indicate the calling that does not change of conversation status.
Procedure UserProc is a user-defined procedure, which is used to transmit the messages within conversation without change of its status. The name of the procedure is always defined by a user. When calling the procedure of ESL Interface, which implements ESL script, a described syntax is applied.
The syntax for calling the procedure which is implemented by a process:
CALL [(0)] I.Interface^ProcName(parameters) ON ProcesName.EXT |
0 – zero