...
A text string describing the historical value. Maximum: 128 characters.
Possibility to use the Dictionary (to open click the CTRL+L).
...
Technical units of the historical value. Maximum: 12 symbols. Possibility to use the Dictionary (to open click the CTRL+L).
...
Values of the individual limits determine the state of the historical value according to its value. The relation value- limits gives give six possible states.
| Limit | Object state according to relation Value - Limit |
| Above VHL (object value > VHL) | |
| VHL | |
| Above HL (HL < object value < VHL) | |
| HL | |
| Normal (LL < object value < HL) | |
| LL | |
| Bellow LL (VLL < object value < LL) | |
| VLL | |
| Bellow VLL (object value < VLL) |
...
- Archive object values - (primary archives) allows to archive implement archiving of values of D2000 system objects. Archiving can be either periodical or on value change.
- Calculate archived values by statistical function (statistical archives) - allows implement applying of a statistical function to a defined object of Historical value.
- Calculate archived values by defined statement (evaluated archives) - allows support defining a custom formula on top of existing objects of Historical value type. The formula is defined in the Statement tab. The results of the calculation are again values , that will be archived.
- Fill archive from the script (Value storage) - values can be written either from an ESL script or manually from the process D2000 HI.
Note: all types of Historical values (also primary, statistical, and evaluated) can be modified from an ESL script or manually from the process D2000 HI).
...
Definition of a D2000 system object, values of which are to be archived. The object may be defined either by typing its name into the input edit field or by selecting it from the list of objects. To open the list of objects, click the button right from the input field.
...
- An object, the value of which is a simple type (Integer, Boolean, Real,...) - just one value is archived, therefore such archived object is called a simple historical value.
- An item of an object of Structured variable type - there is also just one value archived, therefore such archived object is called a simple historical value, too.
- A column of an object of Structured variable type (e.g. SV.Strct[0]^ColName) - there are archived all values of the column. Such an archived object is called a one-column historical value.
- An entire object of Structured variable type (e.g. SV.Struct) - there are archived all values of the object. Such an archived object is called a structured historical value.
...
- Periodical - writing values into in the archive is are periodical. The archiving process stores the archive object value into the archive in defined time moments. Timestamp (the time of value) is not determined by the timestamp of the archived object value (e.g. an I/O tag), but by the time when the value is periodically written into the archive.
Reading the values stored periodically by means of the D2000 system (ESL: GETARCHARR, GETARCHVAL, GETARCHROW, GETARCHCOL, GETARCHSTRUCT, D2000 ObjApi: GetArchivData, D2000 VBApi: VBApiGetArchData, D2000 WorkBook) follows the rule that the archive object's value out of time moments given by the period, is unknown (invalid). The result of the data reading is therefore given by the resampling and the begin (BT) and end (ET) time as follows:- resampling (step) = 0
The reading results are all the values, the time of which belong into to the interval <BT, ET>. - resampling (step) <> 0
The reading result is an array of values with timestamps contiguously:
BT+0*step, BT+1*step, BT+2*step, ..., BT+N*step.
The number of values is given by the end of the time interval (ET). The value of the array item is invalid if a record with the same timestamps does not exist in the archive database. If such a record exists, it is returned as a value of the array item. The above facts imply that when reading periodical data, it is necessary (advisable):- to adjust BT exactly to some of the object archiving moments, given by the period and time offset of the archiving.
- resampling value (step) must be an integer multiple of the archiving period.
- ET = BT + (N-1)*step, where N is an integer number: the number of values in the final selection.
Note: The statistical archive, as far as reading is concerned, behaves as a periodical archive.
- resampling (step) = 0
On value change - all the value changes of the archive object, which are not filtered out by the value filter, are stored in the archive.Kotva sa_filter1 sa_filter1
Reading of values stored by using a filter by means of the D2000 system (ESL: GETARCHARR, GETARCHVAL, GETARCHROW, GETARCHCOL, GETARCHSTRUCT, D2000 ObjApi: GetArchivData, D2000 VBApi: VBApiGetArchData, D2000 WorkBook) follows the rule that the archive object's value at any time (t) is given by (equals to) the last historical value at or before the given time (t). The data reading result is therefore given by the resampling and the begin (BT) and end (ET) time as follows:- resampling (step) = 0
The reading results are all the values, the time of which belongs to the interval <BT, ET> and one value before BT time, in case there is no value with a time exactly equal to BT time in the archive. - resampling (step) <> 0
The reading result is an array of values with timestamps continuously:
BT+0*step, BT+1*step, BT+2*step, ..., BT+N*step.
The number of values is given by the end ET of the time interval. If a record with the same timestamps does not exist in the archive database, the value of the array item will be equal to the last value before the specific required (however, the timestamp will be set accordingly).
- resampling (step) = 0
...
The input field is enabled if the Publish values option is checked. It allows you to define an object, that will contains values of the historical value. When archiving a simple historical value, the target object must not be defined. However, it must be defined for one-column historical value, and for structured historical value - the size of the target object must be the same as the size of the object defined by the parameter Object to archive.
...
- For a simple historical value - the object of the Historical value type you are configuring gets the last value (unless the parameter Historical value is defined).
- When archiving a one-column historical value - the last archived values of individual items are published in the relevant items of the column of a Structured variable type object defined by the Target object parameter.
- When archiving a structured historical value - the last archived values of individual items are published in the relevant items of a Structured variable type object defined by the Target object parameter.
Note: To ensure the correct functionality of the Publish values feature for a one-column historical value (structured HV) the number of rows (columns) of the structured variable defined in the Target object parameter must be the same as the number of rows (columns) of the object defined by the Historical value parameter.
...
- Create an object of Eval tag type, that adds together the values of the I/O tags and then archive archives it.
- Create an object of Historical value type with the expression of „H.Flow1 + H.Flow2“.
...
- If it is not defined, the historical value is a simple one.
- The historical value is a one-column one if the parameter contains:
- column of a structured historical value (e.g. H.Struct[0]^ColName)
- one-column historical value (e.g. H.ColArchiv)
- column of an object of Structured variable type (e.g. SV.Struct[0]^ColName)
- The historical value is a structured one if the parameter contains:
- structured historical value
- an object of Structured variable type
...
In the top part of the tab, an input edit filed field is placed. It serves for entering the expression, that determines the value of the historical value. The expression can contain functions, constants, attributes - but objects of Historical value type only. The expression may also contain extended syntax.
...
If checked, all invalid values of the objects defined in the expression will be replaced with the value of 0. The feature can be used to prevent the expression from getting invalid values. Only the values of input objects are replaced, and invalid values of intermediate data are not replaced. Values of inputs input objects are converted as follows:
...
The parameter can be defined for the archive method Filter. It allows restricting the number of evaluations of a given expression so that the expression will be evaluated once within a defined time . It is used especially in cases when the values of the objects defined in the expression are often changed, and calculating the expression is not required immediatelyto reduce CPU and disk I/O usage. It is used especially in cases when the values of the objects defined in the expression are often changed, and calculating the expression is not required immediately.
...
- Continuous - continuous (on the fly) calculation. Result values are calculated on the fly and they are automatically available (depending on the system load). A disadvantage of the method is a higher demand for computing power (especially for frequent changes of primary historical values that enter into the expression).
- On demand - the calculation is executed and the result is stored in the archive on demand. The demand can be generated by the CALCONDEMANDSTAT action or by the RECALC Tell command command ).
Note: historical value values calculated "on-demand" should not have any depending on historical values calculated continuously, because the result because their results would be wrong. - On read - the calculation is executed as a result of a read request. An advantage of this method is that values are not stored in the database so they don't occupy any disk space. There is no possibility of re-calculation in case of writing delayed data into the archive. A disadvantage is the necessity to read source data and calculate it for each read request. This method should be used for objects whose values are rarely needed.
Note: historical value calculated "on-read" should not have any depending historical values calculated continuously or "on-demand", because the result could be wrong in some cases (due to delayed data) or the calculation could be ineffective (multiple calculations of a single "on-read" object if it is used by several other historical values).
...
Archiving time (Months : Days : Hours). The parameter determines the archiving time depth. It is the minimal time period, during which the data will be stored in the on-line online archive. The older data are being erased from the archive.
...
For periodical data archiving, it is defined, defines what time data with the value for the given period will be stored into in the archive. The time data can present either the beginning time - the "Period begin" option , or the end time of the interval (period) - the "Period end" option.
...
Definition of the condition causing the start archiving of the given historical value.
The object representing the archiving start condition may be defined by in several ways:
- by writing the object in to into the input field,
- by selecting the object from the list of objects - the list is opened after clicking the button right from the input field,
- by creating a new object - the "Create new object button" button.
Also, it is necessary to define, for what state of the given object is the condition is valid. In the list under the object entry field, there are displayed the possible object value states are displayed. This list is different for various kinds of specific types of objects. The archiving start condition will be valid , if the object is in the chosen selected state. If the option Inverse function is enabled, the condition is valid, if the object is in a status other than the chosen state.
...
Defining the condition that causes stopping the archiving of the given historical value.
The object representing the archiving stop condition may be defined by in several ways:
- by writing the object name into the input field,
- by selecting the object from the list of objects - the list is opened by clicking the button right from the input field,
- by creating a new object - the "Create new object button" button.
Also, it is necessary to define, for what state of the given object is the condition is valid. In the list under the object entry field, there are displayed the possible object value states are displayed. This list is different for various kinds of specific types of objects. The archiving stop start condition will be valid , if the object is in the chosen selected state. If the option Inverse function is enabled, the condition is valid, if the object is in a status other than the chosen state.
...
When archiving into the statistical archive, it is possible to use these implemented functions.
| Function | Meaning |
|---|---|
| None | No function. |
| Average * | Arithmetical average of all archive object values. |
| W-Average * | Weighted arithmetical average of all archive object values. |
| Integral | Time is integral of to historical values. |
| Sum | Sum of archive object values. |
| Maximum | Maximum of archive object values. |
| Minimum | Minimum of archive object values. |
| Count | Number The number of archive object values. |
| Filter | Applying a filter for value storing into in the statistical archive. |
| Increment | If the newer value is greater than the older one, then the difference between the values, otherwise the newer value (the function is useful to process counter values that oveflow overflow and start from zero again). |
| Delta | Delta between values. Parameter (Compare value) – the weight of impulse. The result will be the impulse multiplied by its weight. Weight A weight of 1 will ensure standard behaviour. |
| EcoAvg | Average of the object values within the elapsed time period (Period parameter in Time parameters tab) according to the methodology based on flags of individual values entering the statistic. The same purpose is fulfilled by the function %EcoAveR, that which is implemented for eval tags. |
| GT Time (>) | The function calculates the time, during which the value of the historical value was greater than the entered constant (Compare value). |
| GE Time (>=) | The function calculates the time, during which the value of the historical value was greater or equal to the entered constant (Compare value). |
| LT Time (<) | The function calculates the time, during which the value of the historical value was lower then than the entered constant (Compare value). |
| LE Time (<=) | The function calculates the time, during which the value of the historical value was lower or equal to the entered constant (Compare value). |
| Maximum in the time interval | Obsolete - do not use! |
| Minimum in the time interval | Obsolete - do not use! |
| Number of local maximums | The number of local maximums in a given time interval. |
| Number of local minimums | The number of local minimums in a given time interval. |
| Sum of positive values | Sum of positive values of the historical value. |
| Sum of negative values | Sum of negative values of the historical value. |
| Average of positive values | Arithmetical average of positive values of the historical value. |
| Average of negative values | Arithmetical average of negative values of the historical value. |
| Sum of increments | Sum of increments for a given time interval. If the new value is less than the old value, the increment is 0. Parameter (Compare value) – the weight of impulse. The result will be the impulse multiplied by its weight. Weight A weight of 1 will ensure standard behaviour. |
| Time slice** | Object value in given time moments. |
| Sample standard deviation | The function calculates the sample standard deviation of all values of the archive object. |
...
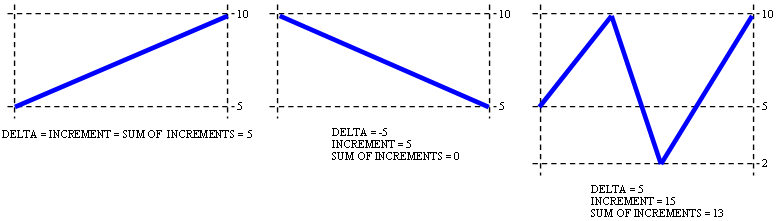
The difference among the functions INCREMENT, DELTA, and SUM OF INCREMENTS is shown in the following figures.
...
- DELTA = 5-10 = -5
- INCREMENT = 5 (because 5 <105<10)ADDITIONAL AMOUNT
- SUM OF INCREMENTS = 0 (because 5 <105<10)
In the third case
- DELTA = (10 - 5) + (2 - 10) + (10 - 2) = 5
- INCREMENT = (10-5) + 2 (because 5 <105<10) + (10-2) = 15
- ADDITIONAL AMOUNT SUM OF INCREMENTS = (10-5) + 0 (because 5 <105<10) + (10 - 2) = 13
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
- Continuous - continuous (on the fly) calculation. Result values are calculated on the fly and they are automatically available (in dependence depending on the system load). A disadvantage of the method is a higher demand on the for computing power (especially for frequent changes of primary historical values that enter into the expression).
- On demand - the calculation is executed and the result is stored to in the archive on demand. The demand can be generated by the the CALCONDEMANDSTAT action CALCONDEMANDSTAT or by the Tell command RECALC command ).
Note: historical value values calculated "on-demand" should not have any depending on historical values calculated continuously, because the result because their results would be wrong. - On read - the calculation is executed as a result of a read request. An advantage of the this method is that values are not stored in the database so they don't occupy any disk space. There is no chance possibility of wrong re-calculation in case of writing delayed data into the archive. A disadvantage is a the necessity to read source data and calculate it for each read demandrequest. This method should be used for objects whose values are rarely needed.
Note: historical value calculated "on-read" should not have any depending historical values calculated continuously or "on-demand", because the result could be wrong in some cases (due to delayed data) or the calculation could be ineffective (multiple calculations of a single "on-read" object if it is used by several other historical values).
...
The value of the parameter Validation criteria defines the value percentage in the primary archive (used fro for the calculation of values stored into in the statistical archive) that has to be valid, in order to acquire a valid result. If there were less fewer valid values than stated in the Validity criteria, the result will be Weak_Value.
...
Statistical time period defines the time interval, the set of historical values, that will be processed by the particular statistical function. By default, the interval is equal with to the archiving period. If it is necessary to enter a different period, check the option Time interval different from archiving period and enter the required period into the parameter Interval. The time period must be greater than 0 [s].
...
- Hours - hour integral
- Minutes - minute integral
Kotva filter filter Seconds - second integral
| Kotva |
|---|
...
|
This parameter (available from D2000 version 22) determines whether a value with interval start/end time enters the calculation. The parameter is configurable for functions:
- Average
- Sum
- Maximum
- Minimum
- Count
- EcoAvg
- Maximum in the time interval
- Minimum in the time interval
- Sum of positive values
- Sum of negative values
- Average of positive values
- Average of negative values
- Sample standard deviation
It cannot be configured for other functions:
- W-Average
- Integral
- Filter
- Increment
- Delta
- GT Time (>)
- GE Time (>=)
- LT Time (<)
- LE Time (<=)
- Number of local maximums
- Number of local minimums
- Sum of increments
- Time slice
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
The system allows archiving of significant changes in the values of the archived object. This method of archiving represents the definition of three sensitivity bands in which it is possible to enter different values of a significant changeThe system allows to archive considerable value changes of the archive object. This archiving method represents defining of three deadband levels, that are possible to set various values of significant changes.
Values of filtering:
- High limit - defining the high limit for filtering.
- Low limit - defining the low limit for filtering.
- Above limit - defines a significant change of the archive object for value above the high limit.
- In limit - defines a significant change of the archive object for value within the the lower and high limits.
- Below limit - defines a significant change of the archive object for value below the low limit.
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
...