...
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
When initialing the communication, the client changes the messages with the server. In binary encoding, "Hello Message" isthe first message sent from the client to server. The message defines the size of receiving and sending buffers and maximum size of messages that may be swapped during TCP communication between client and server. It also defines URL address of endpoint. The server will send "Acknowledge message", in which it will confirm the suggested parameters or modify them according to its limits.
...
The client will send next message "OpenSecureChannel message" . It helps to establish the communication channel to swap data. In this message, the client and server will agree what type of encrypting mode will be used (either "sign and encrypt" or "decrypt" only). OPCUA client in D2000 System supports only decrypted mode.
...
After establishing the communication channel, the client can send the message to create a session, "CreateSession Message". It is the connection on OSI application layer. After the server confirms the request, the session must be activated by message "ActivateSession Message". In this message, the client will agree the algorithm for signing and encoding with the server but only if the modes have been defined when establishing the communication channel.
...
From this moment, the server informs the client about the changes on the monitored objects by
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Communication line category: OPC UA Client
Host address: OPC UA server address. You may set the name according to UNC convention (e.g. "\\server" or "server", DNS names (e.g. "domain.com", "example.company.com") or IP address ("196.54.23.113").
TCP port: TCP port of OPC UA server (e.g. 4840).
EndpointUrl: Endpoint address (e.g. opc.tcp://localhost:4840)
Encoding type: Type of encoding that is used at dat exchange (currently only Binary encoding is supported).
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Full name | Description | Unit | Default value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Defines the time interval for server to send the information about the change of monitored items within the instance subscription by "Publish message". | mi:ss.mss | 00:05.000 | ||||||
| If the client does not send the request for data till the time defined by (Requested LifeTime Count*Requested Publishing Interval), the subscription expires. The value should be minimally 3 times higher than the "Requested Max KeepAlive Count". | Number | 1000 | ||||||
| If the objects of subscription are not changed, the server will send keep-alive message after elapsing the time (Max Notifications Per Publish * Requested Publishing Interval). The client will confirm this message when it sends a new request for data. | Number | 5 | ||||||
| Parameter defines the maximum number of notifications about the object change, which the server can send in one "Publish message". Zero indicates that the number of notifications is unlimited. | Number | 0 | ||||||
| Parameter enables/disables the publishing within the subscription. | YES/NO | 0 | ||||||
| It defines a relative priority of one subscription. If server should send more notifications, the subscription with higher priority is preferred. | 0-255 | 0 | ||||||
| This parameter enables to create the object queue with the defined length on OPC UA server's side for each monitored item in subscription. | Number | 0 |
...
| Name | Meaning | Unit | Default value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | The identifier in text format, which is, in dependence on ID type, converted to the required native type. | String | |||||||
| ID type | Enumerated types of identifiers. They help to access to the the objects in OPC UA address space. Numeric-1B ID: Identifier limited to 1-byte value (0-255) Numeric-2B ID: Identifier limited to 2-byte value (0-65535) Numeric-4B ID: 4-byte identifier String: Text identifier Guid -16B ID: 16-byte (128-bit) number that is usually divided into four parts. For example 3F2504E0-4F89-11D3-9A0C-0305E82C3301. ByteString: Identifier that is represented as a sequence of bytes. | Numeric-1B ID / Numeric-2B ID/ Numeric-4B ID/String/Guid -16B ID/ByteString | Undefined | ||||||
Namespace
| Numerical identifier of name space of OPC UA server. Each OPC UA server can have N name spaces. However, the object identifier must be unique in one name space. | Numeric | |||||||
| Variable type | Value type of objects that can be processed by OPC UA client. Variable type should be used only if I/O tag is intended for writing. As regards the reading of the object value, the information about type is sent together with the value. | Undefined / Boolean / Byte / SByte / Integer16 / Unsigned16 / Integer32 / Unsigned32 / Integer64 / Unsigned64 / Float / Double / String / UTC Time / Boolean array / Byte array / SByte array / Integer16 array / Unsigned16 array / Integer32 array / Unsigned32 array / Integer64 array / Unsigned64 array / Float array / Double array / String array / UTC Time array | Undefined | ||||||
| Array index | If the object value is represented as a value array (Boolean array / Byte array / SByte array / Integer16 array / Unsigned16 array / Integer32 array / Unsigned32 array / Integer64 array / Unsigned64 array / Float array / Double array / String array / UTC Time array), the parameter defines its range or value of a particular item. A text representation of array index may be in several formats:
| String | |||||||
| Write only | It sets if I/O tag is a part of subscription. Its value will be sent periodically from the server in "Publish message". | Unchecked/checked | Unchecked | ||||||
| Expanded Node ID | If it is checked, it enables to address the ExpandedNodeId. Unlike the classic identifier in the OPC UA address space, ExpandedNodeId is supplemented by NameSpace URI and Server index. | Unchecked/checked | Unchecked | ||||||
| NamespaceUri | Text identifier of name space of OPC UA server that is used instead of the numerical representation of namespace. | String | |||||||
| ServerIndex | Numerical identifier that address the server number when using the ExpandedNodeID identifier. | Numeric | 0 |
...
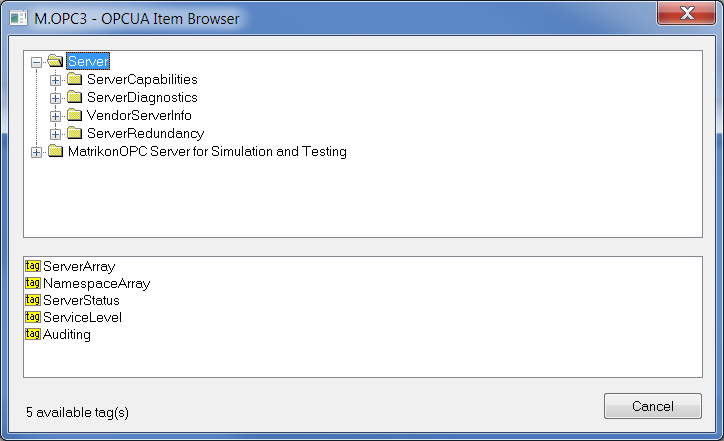
This dialog window is intended for browsing and inserting the OPC UA objects into the address parameter of I/O tag. The upper part contains the tree structure of address space. When clicking on the object, the lower part of window displays the direct descendents of the object.
Double click on one of the descendents transfers the address parameters of object to the address dialog window of I/O tag.
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...