...
I/O tag address. The address type depends on the communication protocol of the station, which is the parent of a particular I/O tag. The address is stored in the configuration database in a text form. A specific communication protocol converts this address into a binary form. For internal communication protocols of the D2000 system, a protocol-dependent dialog box with the validity check of a specified address is used during the I/O tag address configuration. For external communication protocols (OEM Protocol 1 up to OEM Protocol 16) of the D2000 system, the address is entered directly in text form.
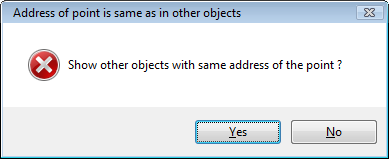
During the saving of the I/O tag configuration, the uniqueness of its address is tested. If the address of the I/O tag is not unique (within a parent station), the system will inform you about the error.
By choosing the option Yes, a new CNF dialog window opens. Only I/O tags with conflicting addresses sharing a common parent are displayed in this window. The user can (but does not have to) change the address of these I/O tags.
...
If a new value is less than the Min value, the system will assign the Min value to this new value. If a new value is greater than the Max value, the system will assign the Max value to this new value. This filter may be used to eliminate values, which technically may not break given limits (e.g. throttle stops), but the particular sensor (converter) may also generate values out of limits
...
If a new value is less than the Min value or greater than the Max value, it will be discarded.
...
Therefore for I/O tags of output type (Ao, Co, and ToR), it's possible to configure only the linear conversion because only in this case there is an unambiguous inverse function used during value writing into a particular device.
...
- If the option is enabled, then a value must be entered into the Start value input box and a control object must be defined - Control object input box. The valid mode is defined by means of Manual/Auto radio buttons. A mode may be changed in the D2000 HI process and its changes will be stored in the system database. The operator can change the required value in Manual mode. Its change is also stored in the system database.
- If the option is disabled, then only one of the Auto or Manual modes may be enabled. The operator's right to change the required value is defined by means of their access rights. Changing a required value in the D2000 HI process is allowed to an operator with Control access right level (or higher).
...
- Value - I/O tag with its own value acquired from the communication. Writing a new value of the I/O tag into a particular device is accompanied by a transient state. The new value is confirmed after the communication verifies the writing.
- Command - Output I/O tag, that may not have its own value (cannot acquire it by means of the communication with a particular device). A new value written into the device does not go through the transient state. Control windows in the D2000 HI process also allow writing the same value several times (e.g. enabled ON and OFF buttons at the same time - unlike the value output tags where only the button of the opposite value than the current one is enabled).
...
Maximum step size for a change
The parameter parameter "Maximum step size for a change" allows limiting the maximum change of value for manual control. This limitation has the character of a recommendation and a user is able to override it.
...
The default value allows replacing an I/O tag value acquired by the D2000 KOM process by , with another one in some cases, (e.g. the sensor device breakaway, a failure of the communication with the device). An I/O tag value may be replaced by a value of another object (so-called control object) or adjusted manually by the operator of the D2000 HI process via the control window.
...
The default value is stored in text form. It is converted to a required value type and then is used as the value of the I/O tag.
If it is not defined or conversion has failed, the initialization of the values of the output I/O tag will not be executed (more info...).
...
- Writing a verified output I/O tag is successful if a new value of the verifying object that confirms the value written will come within the execution timeout (the Output control tab). Values of the verifying object, which do not meet the condition, will not cause any action (i.e. they do not cause unsuccessful writing).
- If the execution timeout is 0, waiting is not time-limited.
- If the execution timeout expires, writing to the output I/O tag is considered to be unsuccessful and the alarm ErrorWriteCmd occurs, if it is configured.
- Within the execution timeout, several values of the verifying object may come. The values, which are not equal to the value written (with the Delta tolerance) do not cause the writing to be treated as unsuccessful, i.e. writing to the I/O tag is unsuccessful only after the execution timeout exceeds.
- If the value of the verifying object is equal to the written value of the output I/O tag (with the Delta tolerance) when the value was written, the writing is acting as if the verification is not enabled, i.e. it does not wait for a new value of the verifying object, but writing is successful immediately after sending the value to the communication (and after confirmation, if the protocol supports it).
...