...
| Full name | Description | Unit | Default value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Defines the time interval for the server to send the information about the change of monitored items within the instance subscription by "Publish message". | mi:ss.mss | 00:05.000 | ||||||
| If the client does not send the request for data till the time defined by (LifeTime Count * Publishing Interval), the subscription expires. The value should be minimally 3 times higher than the "Requested Max KeepAlive Count". | Number | 1000 | ||||||
| If the objects of subscription are not changed, the server will send a keep-alive message after elapsing the time (Max Notifications Per Publish * Publishing Interval). The client will confirm this message when it sends a new request for data. | Number | 5 | ||||||
| The parameter defines the maximum number of notifications about the object change, which the server can send in one "Publish message". Zero indicates that the number of notifications is unlimited. | Number | 0 | ||||||
| The parameter enables/disables the publishing within the subscription. | YES/NO | YES | ||||||
| It defines a relative priority of a subscription. If the server should send more notifications, the subscription with higher priority is preferred. | 0-255 | 0 | ||||||
| This parameter enables creating an object queue with the defined length on the OPC UA server's side for each monitored item in a subscription. | Number | 0 | ||||||
| Timestamps used while reading a value:
| - | Server | ||||||
| Timestamps used to write a value:
Note: If the OPC server does not support the writing of timestamps, according to the standard it should return the Bad_WriteNotSupported (2155020288) error code. | - | None | ||||||
| StatusCode item will be used when writing. Note: According to the standard, the OPC UA Wrapper returns the Bad_WriteNotSupported (2155020288) error code if the StatusCode entry is used when writing to the OPC DA Server version 2.05a. | YES/NO | YES | ||||||
| When an item of an array is written, the entire array is read first and then written. If this parameter is set to NO, only a specific array item is written, Note: According to the standard, if the OPC server does not support writing a specific array item, it should return the Bad_WriteNotSupported (2155020288) error code. Note: If this parameter is active, the "Write only" parameter must not be set at the I/O tag which addresses an item of the array. | YES/NO | NO | ||||||
| A way of reading values:
Note: The Subscribe+Read and Read modes should only be used if there is a problem with standard communication, as they are less efficient and have a higher overhead. | Subscribe Subscribe+Read Read | Subscribe | ||||||
| Ignoring filter parameters in the I/O tag configuration (Sampling type, DeadBand type, Trigger type). In the specific case, the OPC UA server did not work correctly if monitored items with the specified filter parameters were inserted into the subscription. | YES/NO | NO |
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Name | Meaning | Unit | Default value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | The identifier in text format, which is, in dependence on ID type, converted to the required native type. Note: if an identifier %IGNORE is specified for ID type=String, the I/O tag is ignored. | String | |||||||
| ID type | Enumerated types of identifiers. They help to access the objects in OPC UA address space. Numeric-1B ID: Identifier limited to 1-byte value (0-255) Numeric-2B ID: Identifier limited to 2-byte value (0-65535) Numeric-4B ID: 4-byte identifier String: Text identifier Guid -16B ID: 16-byte (128-bit) number that is usually divided into four parts. For example 3F2504E0-4F89-11D3-9A0C-0305E82C3301. ByteString: Identifier that is represented as a sequence of bytes. | Numeric-1B ID / Numeric-2B ID/ Numeric-4B ID/String/Guid -16B ID/ByteString | Undefined | ||||||
Namespace
| Numerical identifier of the namespace of OPC UA server. Each OPC UA server can have N namespaces. However, the object identifier must be unique in one namespace. | Numeric | |||||||
| Variable type | The value type of objects that can be processed by OPC UA client. Variable type should be used only if the I/O tag is intended for writing. As regards the reading of the object value, the information about type is sent together with the value. | Undefined / Boolean / Byte / SByte / Integer16 / Unsigned16 / Integer32 / Unsigned32 / Integer64 / Unsigned64 / Float / Double / String / UTC Time / Boolean array / Byte array / SByte array / Integer16 array / Unsigned16 array / Integer32 array / Unsigned32 array / Integer64 array / Unsigned64 array / Float array / Double array / String array / UTC Time array / LocalizedText / LocalizedText array | Undefined | ||||||
| Array index | If the object value is represented as a value array (Boolean array / Byte array / SByte array / Integer16 array / Unsigned16 array / Integer32 array / Unsigned32 array / Integer64 array / Unsigned64 array / Float array / Double array / String array / UTC Time array), the parameter defines its range or value of a particular item. The first element of array is identified by index 0. A text representation of array index may be in several formats:
Note: Writing is only supported for I/O tags with a specific index, not for ranges. | String | |||||||
| Write only | It controls if the I/O tag is a part of the subscription. Its value will be sent periodically from the server in "Publish message". | Unchecked/checked | Unchecked | ||||||
| Expanded Node ID | If it is checked, it enables addressing the ExpandedNodeId. Unlike the classic identifier in the OPC UA address space, ExpandedNodeId is supplemented by NameSpace URI and Server index. Note: ExpandedNodeId is not yet supported in the KOM process. | Unchecked/checked | Unchecked | ||||||
| NamespaceUri | Text identifier of the namespace of the OPC UA server that is used instead of the numerical representation of a namespace. | String | |||||||
| ServerIndex | A numerical identifier that addresses the server number when using the ExpandedNodeID identifier. | Numeric | 0 |
...
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Name | Meaning | Unit | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling type | The parameter defines a sampling frequency of the monitored objects. When using the "Publishing rate", the frequency is equivalent to time Requested Publishing Interval, which is set on the communication station level. "Practical fastest rate" sets the sampling frequency on the maximum value. "Custom rate" enables to specify the custom sampling interval, which may be defined in "Sampling Time". | Publishing rate/Practical fastest rate/Custom rate | Publishing rate |
| Sampling time | The parameter allows you to set the custom sampling frequency if "Sampling type" is "Custom rate". | ss.ms | 0.0 |
| DeadBand type | Deadband is a band in which the change of value does not cause Data Change Notification, which is the part of Publish Message. When using "None", this band is ignored. Otherwise, there is used the relative or absolute value ("Percent"/"Absolute") from "DeadBand value". | None/Absolute/Percent | None |
| DeadBand value | The parameter defines the custom value of a deadband if you chose the relative/absolute value ("Percent"/"Absolute"). | 0.0 | |
| Trigger type | The parameter specifies the condition which causes Data Change Notification. When using "Status", only the status change is reported. Change of value and timestamp are ignored. When using "Status,Value", the change of timestamp is ignored. "Status,Value,Timestamp" ensures the reporting in all options, i.e. when changing the status, value, or timestamp. Note: a specific Simatic S7-1500 did not send value changes if this parameter was set to default "Status, Value, Timestamp" - changing it to "Status, Value" helped. | Status/Status,Value/Status,Value,Timestamp | Status,Value,Timestamp |
...
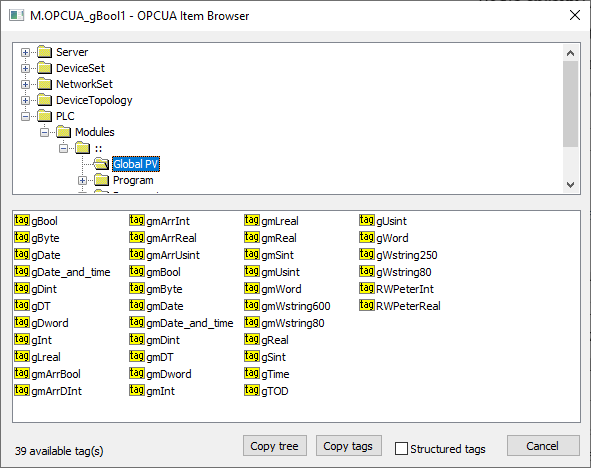
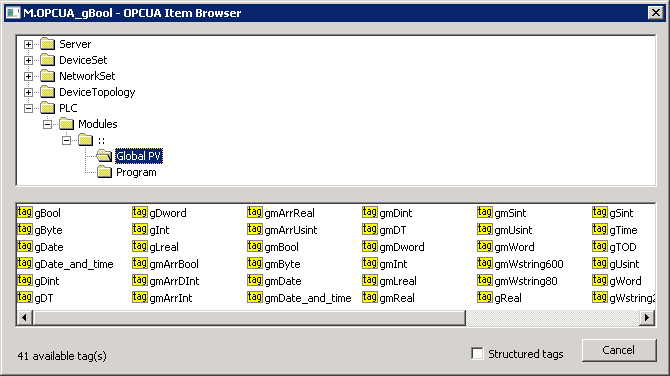
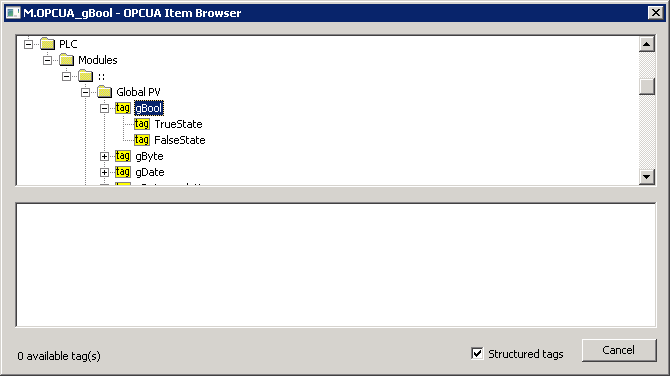
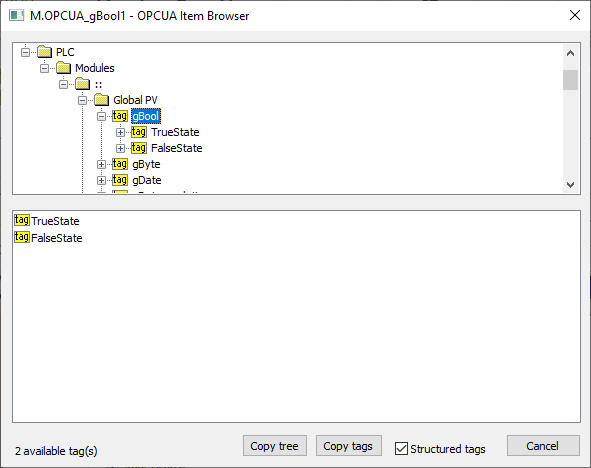
This dialog window is intended for browsing and inserting the OPC UA objects into the address parameter of the I/O tag. The upper part contains the tree structure of the address space. When clicking on the object, the lower part of the window displays the direct descendants of the object (variables, tags).
Double click on one of the descendants transfers the address parameters of an object to the address dialog window of the I/O tag.
Note: Using Ctrl+C it is possible to copy a list of displayed descendants into the Windows clipboard. All descendants will be copied unless a specific descendant is selected.Note: In versions from 17th December 2018 and newer, the recycling of browser dialog has been implemented. If the dialog is closed by the Close button or after selecting a tag, it is actually only hidden and it is available for browsing by another I/O tag within the same station so that the tree structure of the browsed objects is preserved. Clicking on the close icon at the top right corner will cause the dialog to be really closed.
"Copy tags" button or a keyboard shortcut Ctrl+C copies the names of tags in a selected branch into the Windows clipboard. All tags will be copied unless a specific tag is selected.
"Copy tree" button or a keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Shift+C copies the names of tags and their addresses in all browsed branches into the Windows clipboard.
Checking the "Structured tags" option causes the variables (tags) to appear in the tree structure in addition to the objects, and the KOM process also attempts to read their descendants. This is useful for browsing OPC UA servers that support structured tags. You can also insert a tag into the address dialog window of the I/O tag by double-clicking the tag name in the tree structure.
| Kotva | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...