...
The protocol is a modification of the protocol IEC 870-5-104 working on the basis of TCP network communication. The protocol has been modified specifically for redundant communication with the system Siemens Sinaut SpectrumSpectrum system. It supports the balanced mode and both active and passive establishing the establishment of the communication (a connecting party and a listening party) according to the station protocol parameters, and therefore allows to interconnect not only the D2000 system with the Sinaut system but also two D2000 systems.
Picture: the D2000 redundant system communicating with Sinaut redundant system in a redundant network
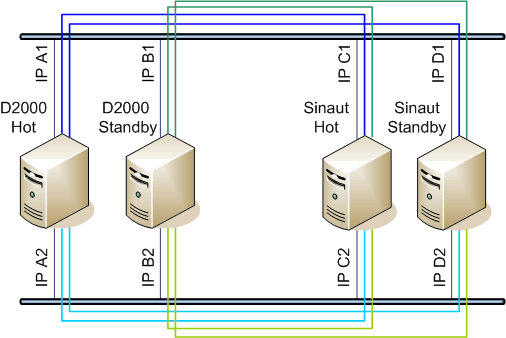
The picture above shown shows TCP connections - each process D2000 KOM (D2000 Hot, D2000 StandBy) with eachSinaut each Sinaut (Sinaut Hot, Sinaut StandBy)
...
- Originator ASDU address - is 1 byte, it is defined as a line number.
- ASDU address - is 2 bytes, it is defined as station address. Foe For each station on one line, there a different ASDU address must be defined different ASDU address.
| Kotva |
|---|
| NOTE_ASDUADDR |
|---|
| NOTE_ASDUADDR |
|---|
|
Note: Because of the Sinaut data model, the low and high address bytes are changed unlike exchanged (in contrast to the standard IEC 104 implementation), i.e. a big endian instead of a little endian is used.
Example:
station address=1, ASDU address is sent as bytes 0, 1 bytes
station address=513 (2*256+1), ASDU address is sent as 2, 1 bytes
For better orientation, station address may be defined in the form of ByteHI, ByteLO, i.e. address 2,1 is the same as 513 - Cause of transmission - is 2 bytes (it also contains Originator ASDU address)
- Information object address - 3 bytes, it is defined as I/O tag address
Note: Because of the Sinaut data model, the low and high address bytes are changed unlike are exchanged (in contrast to the standard IEC 104 implementation), i.e. a big endian instead of a little endian is used.
Example:
I/O tag address=1, ASDU address is sent as bytes 0, 0, 1 bytes.
I/O tag address=66051(1*65536+2*256+3), ASDU address is sent as bytes 1, 2, 3.
For better orientation, the I/O tag address may be defined in the form of ByteLO, ByteMIDDLE, ByteHI, i.e. address 1,2,3 is sent as bytes 1, 2, 3.
There are implemented the The following ASDU types in the monitoring direction of logging (from Sinaut system to D2000 system and also vice-versa in balanced mode) are implemented:
Table 1
| ASDU type | I/O tag types |
|---|
| 1 - Single-point information | Di, Qi (On/Off), Ai, Ci |
| 2 - Single-point information with a time tag | Di, Qi (On/Off), Ai, Ci |
| 3 - Double-point information | Qi, Ai, Ci |
| 4 - Double-point information with a time tag | Qi, Ai, Ci |
| 5 - Step position information | Ci, Ai * |
| 6 - Step position information with a time tag | Ci, Ai * |
| 7 - Bitstring of 32 bits | Ci, Ai |
| 8 - Bitstring of 32 bits with a time tag | Ci, Ai |
| 9 - Measured value, normalized value | Ai |
| 10 - Measured value, normalized value with time tag | Ai |
| 11 - Measured value, scaled value | Ci, Ai |
| 12 - Measured value, scaled value with time tag | Ci, Ai |
| 13 - Measured value, short floating point value | Ai |
| 14 - Measured value, short floating point value with time tag | Ai |
| 15 - Integrated totals | Ci, Ai |
| 16 - Integrated totals with time tag | Ci, Ai |
| 17 - Event of protection equipment with time tag | Ci, Ai, TiR ** |
| 18 - Packed start events of protection equipment with time tag | Ci, Ai, TiR *** |
| 20 - Packed single-point information with status change detection | Ci, Ai |
| 21 - Measured value, normalized value without quality descriptor | Ai |
| 30 - Single-point information with time tag CP56Time2a | Di, Qi (On/Off), Ai, Ci |
| 31 - Double-point information with CP56Time2a tag | Qi, Ai, Ci |
| 32 - Step position information with CP56Time2a tag | Ci, Ai * |
| 33 - Bitstring of 32 bits with CP56Time2a tag | Ci, Ai |
| 34 - Measured value, normalized value with CP56Time2a tag | Ai |
| 35 - Measured value, scaled value with CP56Time2a tag | Ci, Ai |
| 36 - Measured value, short floating point value with time tag CP56Time2a | Ai |
| 37 - Integrated totals with time tag CP56Time2a | Ci, Ai |
| 38 - Event of protection equipment with time tag CP56Time2a | Ci, Ai, TiR ** |
| 39 - Packed start events of protection equipment with time tag CP56Time2a | Ci, Ai, TiR *** |
| 40 - Packed output circuit information of protection equipment with time tag CP56Time2a | Ci, Ai, TiR *** |
Note: The individual bites of the quality byte that inform us on quality (SIQ for ASDU 1,2,30; DIQ for ASDU 3,4,31; QDS for 5..14,20,32..36) are mapped to the flags FLA (bit 0.bit), FLB (bit 1.bit) .. FLH (bit 7.bit).
For example:
for ASDU 4: FLA=DPI bit 0, FLB=DPI bit 1, FLC=0, FLD=0, FLE=BL bit, FLF=SB bit, FLG=NT bit, FLH=IV bit.
for ASDU 16: FLA..FLE = Sequence number bity bits 0..4, FLF=CY bit, FLG=CA bit, FLH=IV bit
Moreover:
- if a bit is set to IV (Invalid) bit is set, the value state status will be Invalid
- if some any of the bits are set to NT (Not topical), SB (Substituted), BL (Blocked), OV (Overflow), CA (Counter adjusted), CY (Counter overflow) bits are set for corresponding ASDU types, the value state status will be Weak.
* - T-bit of the value of these ASDUs is
in mapped to the
FI flag
FI, a number
within in range -64 .. +63
is in goes to a variable of Ci/Ai type
** -
ASDU 17 and
38: SEP byte is in the flags FLA (
bit 0
.bit), FLB (
bit 1
.bit) .. FLH (
bit 7
.bit), following 2 bytes (CP16Time2a) are in a variable of Ci/Ai type as a positive number (0-60 000) or they are in a variable of TiR type as a relative time (0-60 seconds)
The following ASDU types are implemented in the control
course direction (from D2000 system to Sinaut system and vice-versa in balanced mode):
...
| ASDU type | I/O tag type |
|---|
| 45 - Single command | Dout |
| 46 - Double command | Dout, Co |
| 47 - Regulating step command | Dout |
| 48 - Set point command, normalised value | Ao |
| 49 - Set point command, scaled value | Co |
| 50 - Set point command, short floating point value | Ao |
| 51 - Bitstring of 32 bit | Co |
| 58 - Single command with time tag CP56Time2a | Dout |
| 59 - Double command with time tag CP56Time2a | Dout, Co |
| 60 - Regulating step command with time tag CP56Time2a | Dout |
| 61 - Set point command, normalised value with time tag CP56Time2a | Ao |
| 62 - Set point command, scaled value with time tag CP56Time2a | Co |
| 63 - Set point command, short floating point value with time tag CP56Time2a | Ao |
| 64 - Bitstring of 32 bit with time tag CP56Time2a | Co |
To set the bites bits of the "status" byte (SCO for ASDU 45,58; DCO for ASDU 46,59; RCO for ASDU 47,60; QOS for ASDU 48..50,61..63), there are used the flags FLA (bit 0.bit), FLB (bit 1.bit) .. FLH (7.bit) are used except the bitesbits, which are directly set by the variable value ( SCO bit 0, DCO and RCS bites bits 0-1). Having received a response (positive/negative), the flags FLA .. FLH are set according to the bites bits of the "status" byte.
When sending commands (ASDU 45-64), the value of 6 [Activation] is used as CauseOfTransmission. Expecting Whether a response is expected from the controlled station depends on the parameter CMDC parameter. There are the following possibilitiesThese options are available:
- write writing is considered successful, if there is a packet with RSN confirming the SSN packet with the logwrite command
- write writing is considered finished, if there is a response with CauseOfTransmission=7 [Activation Confirmation] and/or 10 [Activation Termination]. Success/Unsuccess failure depends on the setting of the P/N bite in received CauseOfTransmission.
Redundant communication with Siemens Sinaut system - Basic features:
- One communication line of CP Redundant type TCP/IP-TCP Redundant type communicates with two redundant Sinaut partners Sinaut, where one of them is HOT, the other is STANDBY.
- Communication to with each of the partners is performed through two redundant networks (i.e. there are created two TCP connections are created for each Sinaut, together so altogether there are four TCP connections).
- Sending Only the HOT partner (D2000 or Sinaut) is allowed to send new values and replying reply to ASDU 100 [Interrogation Command] is allowed just HOT partner (D2000 eventually Sinaut). Having established the connection, the STANDBY partner only sends confirmations (S-frames) and test frames. The STANDBY partner may also send ASDU 100 [Interrogation Command].
- Each partner communicates to the other just through one a single TCP connection. It sends new values, command confirmations, ASDU 1000 100, and replies to ASDU 100 through the this connection. Second The second connection is standing not used (except for sending test frames through it) and it is only used when a failure on the first connection is detected.
Establishing a connection:
- In the active mode, the process D2000 KOM process connects to specified TCP ports. It sends to a StartDT Act U-frame to each of the ports an U-frame StartDT Act, and waits for StartDT Con as reply.
- In the passive mode, the process D2000 KOM waits on a specified TCP port (see the parameters SP, SH). When the clients are connected, the process waits for an a StartDT Act U-frame StartDT Act, and sends StartDT Con as reply.
- Further communication is completely symmetrical one. Both partners can send ASDU 100 [Interrogation Command] in order to read all current values and then the partners receive and sends changed values and commands.
Having established the connection, a partner may send I-frame with ASDU 100 [Interrogation Command] with CauseOfTransmission=6 [Activation] and with ASDUAddres=FFFF, whereby it requests the values of I/O tags for all stations. As a replay, the partner waits for:
- receiving an I-frame with ASDU 100 [Interrogation Command] and with CauseOfTransmission=7 and ASDUAddresASDU Address=FFFF
- receiving the current values of all I/O tags
- receiving an I-frame with ASDU 100 [Interrogation Command] and with CauseOfTransmission=10 and ASDUAddresASDU Address=FFFF
Forced disconnection: If all communication stations on the line are in the simulation mode or the communication is disabled for them, the communication line will be disconnected (closing communication sockets). If the simulation mode is not enabled and communication is not disabled for at least one station (the tab Parameters of object of Station type), the line will be reconnected (and Interrogation Command eventually Counter Interrogation Command will be send to the station). Then after enabling each next station, there is send an Interrogation Command or Counter Interrogation Command to the station; see the next point.
...
| Full name | Meaning | Unit | Default value |
|---|
| Command Confirm | Confirmation of control ASDUs.
If CMDC=0, the process D2000 KOM is not waiting for confirmation of control ASDUs from the partner station using backward sending ASDU with other CauseOfTransmission, ASDU is consider to be confirmed when a packet containg corresponding ReceiveSequenceNumber is received.
If CMDC=1, the process D2000 KOM is waiting for confirmation with CauseOfTransmission=7 (Activation Confirmation).
If CMDC=2, the process D2000 KOM is waiting for confirmation with CauseOfTransmission=10 (Activation Termination).
If CMDC=3, the process D2000 KOM is waiting for confirmation with CauseOfTransmission=7 or 10 (if both of them are received, just the first of them is taken into account).
Having received the corresponding confirmation means that writing is finished (the Transient attribute of written value is evaluated and the WTn timeout stops elapsing).
If there is received confirmation with other CauseOfTransmission as the process D2000 KOM expect for, it will be ignored.
Writing is successful if received ASDU contains the P/N bit set to 0. Otherwise, writing is unsuccessful.
The value from a received ASDU is backwardly written into the corresponding I/O tag and is sent to the system. E.g. if an ASDU of type 50 (short floating point) with the value of 1200.0 is sent and the partner station sends an ASDU of type 50 as reply, P/N bit=0, value of 999.0 (e.g. due to physical limitations of the given parameter), the the value is to be send by the process D2000 KOM to the system. | - | 3 |
| Debug Input | It is a mask for a debug level of the input data.
A meaning Meaning of the bits:- 1. bit - number of points received within General Interrogation
- 2. bit - a received values of I/O tags
- 3. bit - balanced mode: Interrogation command was received
- 4. bit - information about discarded values due to the setting of the Ignore Flagged parameter
| 0 .. 255 | 0 |
| Debug Output | It is a mask for a debug level of the output data.
A meaning of the bits:- 1.bit - balanced mode: a number of points sent within General Interrogation
- 2.bit - it shows a sent values of I/O tags
| 0 .. 255 | 0 |
| It allows a flag mapping which is compatible to Sinaut Spectrum ICCP OPC communication. For more information see ICCP compatible flag mapping. | YES/NO | NO |
| The parameter allows to specify the flags of values (data ASDU 1-40), which - if set - will cause the value to be discarded. The parameter was implemented when it was necessary to filter out the "Non-topical" flag values that came from the communication partner. The mapping of individual flags from ASDU to A..H flags is as follows: - A - Overflow (OV) - ASDU 5-14, 20, 32-36
- B - no mapping (according to standard this bit should be 0)
- C - no mapping (according to standard this bit should be 0)
- D - Elapsed Time Invalid (EI): ASDU 17-19, 38-40
- E - Blocked (BL) - ASDU 1-14, 17-20, 30-36, 38-40
- F - Substituted (SB) - ASDU 1-14, 17-20, 30-36; Counter overflow (CY) - ASDU 15, 16, 37
- G - Non-topical (NT) - ASDU 1-14, 17-20, 30-36; Counter adjusted (CA) - ASDU 15, 16, 37
- H - Invalid (IV) - ASDU 1-20, 30-40
| A..H | - |
| Ignore Unknown Addresses | If IUA=TRUE, the process D2000 KOM will not show an error on its console or write it into log files in case that incoming value has the address not matching any of the addresses of I/O tags defined in the D2000 system. | - | False |
| Interrogation Covers Counter Interrogation | As a reply to Interrogation, there are also sending ASDU 15,16,37 (Integrated Totals), which are standard requested by ASDU 101 [Counter Interrogation]. | - | True |
| K (max outstanding I APDUs) | Sending window size i.e. packet quantity, which is sent by the process D2000 KOM without receiving a confirmation (S-frame or I-frame). According to the standard, the default value is 12. | - | 12 |
| No Flags | If the parameter is True, then the status bit of incoming ASDUs is ignored and not saved into the flags FA...FH. Flags of output I/O tags are also ignored and they not set the status bit. | - | False |
| Order of IC | Order for sending ASDU 100 [Interrogation Command] when the station initializes to communicate or when creating a new station. If OIC<OCIC, ASDU 10 will be send before ASDU 101. If OIC=0, ASDU 100 will not be sent. The parameter can be set extra for each station. | - | 1 |
| Order of Counter IC | Order of sending ASDU 101 [Counter Interrogation Command] when initializing the connection. OCIC<OIC, ASDU 101 will be sent before ASDU 100. If OCIC=0, ASDU 101 will not be sent. The parameter can be set extra for each station. | - | 0 |
| Ping Count | Number of repetitions, after which the IP address not responding to ping is to be known as non-functional.
See the parameter PTO. | - | 3 |
| Ping TimeOut | If the parameter is other than zero, then defines the timeout (in milliseconds) of server response for ping (ICMP echo) packet. In the background, the process D2000 KOM sends ping packets to all defined IP addresses. If some of the addresses does not respond for PCNT-times, it is designated as non-functional and connection is terminated. If the parameter PTO= 0, sending ping packet to IP addresses is disabled. | - | 0 |
| Post Start Delay | When initializing the connection, delay between receiving StartDT Con response and sending Interrogation Command and/or Counter Interrogation Command. | ms | 0 |
| Initial SSN. According to the standard, after establishing the connection the SSN is set to 0, other than zero could be appropriate e.g. for testing. | - | 0 |
| Server Port, Server Host | The port number and IP address of the interface, where the process D2000 KOM is to be listening. If both the parameters are defined, the process D2000 KOM is working as passive (is waiting for connecting Sinaut clients). If the process should listen on all network interfaces, there must be set SH=ALL. | - |
|
| Standby Keep Open | If True, after changing the status of process D2000 Server (the process D2000 KOM is connected to) from Hot into Standby state (redundant system), connection with partner will not be closed. | - | True |
| Station Communication Error | Number of unsuccessful attempts to connect after communication breakdown. The station status is changed into the state St_CommErr after reaching the number. For redundant lines, the communication must be either failed for both TCP connections or a TCP connection with standby-server must be functioning (see the parameters ICF3 and IT), i.e. data from the server are ignored. | - | 2 |
| Station Hard Error | Number of unsuccessful attempts to connect after communication breakdown. The station status is changed into the state St_HardErr after reaching the number. For redundant lines, communication must be either failed for both TCP connections or working a TCP connection with standby-server must be functioning (see the parameters ICF3 and IT), i.e. data from the server are ignored. | - | 5 |
| Strict Redundancy Connection Signalisation | Number of TCP connections, which must be opened so that the line could be considered as OK. There are 4 connections (2x Sinaut, each of them has 2 network addresses). | - | 4 |
| Tcp Keep Init | The parameter is implemented for use on OpenVMS platforms only. If it is other than zero, then defines the timeout (in seconds) for opening a new connection to server. For OpenVMS, the default value is 75 seconds, for Windows it is 20 seconds. | - | 0 |
| TCP NoDelay | TND parameter sets a low-level parameter of TCP_NODELAY sockets which switch off a default packet linking. |
|
|
| W (ack after receiving W APDUs) | Quantity of received packets, after which the process D2000 KOM sends an S-frame confirmation. According to the standard, the default value is 8. There must be true W < K, the standard recommends W = 2/3 * K. | - | 8 |
| Wait Timeout T1 | Timeout for receiving the confirmation of a I-frame sent (either the confirmation within the I-frame or the S-frame itself) or a U-frame. If the process D2000 KOM does not get the confirmation in the time WT1, it closes the TCP connection. According to the standard, the WT1 default value is 15000 ms. | ms | 15 000 |
| Wait Timeout T2 | Timeout for sending the confirmation of a I-frame received. WT2 < WT1. If another I-frame (which confirms the I-frame received) is not sent in the time WT2 since the I-frame was received, so the process D2000 KOM sends an S-frame confirming the received I-frame to the partner. According to the standard, the WT2 default value is 10000 ms. | ms | 10 000 |
| Wait Timeout T3 | Timeout for sending test frames (U-frame TEST ACT). If no data are sent in any direction for a long time, an U-frame TEST ACT will be sent to the process D2000 KOM after expiration of the WT3 time and there is expected (in the WT1 time after sending) receiving a U-frame TEST CON. If the WT3 on the partner side is set to a lower value, it sends the test frames and the process D2000 KOM replies to them. According to the standard, the WT2 default value is 20000 ms. Setting the value to 0 disables sending test frames. | ms | 20 000 |
| Wait Timeout N | Timeout for receiving the confirmation of a value sent. Receiving e.g. S-frame with RSN (Receive Sequence Number) confirming, that the other party received previous I-frame doesn't mean, that the I-frame was processed. In the WTn time, the process D2000 KOM waits for receiving the response (e.g. after sending ASDU with TypeIdentificator=45 [Single Command] with CauseOfTransmission=6 [Activation] there is expected receiving Single Command with CauseOfTransmission=7 [Activation Confirmation].
After the expiration of the WTn time, the process D2000 KOM closes the TCP connection. | ms | 60 000 |
...
