GPIO protocol
Supported device types and versions
Communication line configuration
Communication station configuration
I/O tag configuration
Literature
Changes and modifications
Document revisions
Supported device types and versions
The protocol supports communication via inputs/outputs of Raspberry PI and computers built on an RPI Compute Module. Currently supported are:
- Raspberry PI (version 2, 3, and 4) based on a pigpio library - communication via GPIO (General Purpose I/O) pins
- Techbase NPE X500 M3 (DIN-mounted industrial computer built on RPI Compute Module 3 with industrial inputs and outputs)
The communication was tested with Raspberry PI (version 3) and NPE X500-M3-MAX-3G.
For Raspberry PI, the protocol supports reading of digital inputs (instantaneous values as well as counting signal changes with an optional time filter) and setting digital outputs to a constant value or pulse-width modulation (PWM).
For NPE X500 the protocol supports reading of digital and analog inputs and status of user button, writing to digital outputs, setting relay outputs, working with user LEDs, and a buzzer.
Note: On Raspberry PI, the KOM process must be run under the root user to gain access to the GPIO. It is possible to achieve by setting the setuid bit for the kom binary. Under the user pi, you can do the following:
cd /opt/d2000/bin
sudo chown root kom
sudo chmod 4755 kom
Note: On NPE X500, the KOM process must be run under the root user to gain access to the GPIO (see the previous note for Raspberry PI). An alternative is adding user d2000 to groups and setting appropriate access rights. Under the root user, you can do the following:
sudo usermod -a -G gpio d2000
For access to serial ports also:
sudo usermod -a -G dialout d2000
In order for the d2000 user to access the LEDs and the buzzer, it is necessary to set the rights for the respective files each time the computer starts up. Create a file d2000init in the /etc/init.d directory containing:
#!/bin/bash
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: script
# Required-Start: $all
# Required-Stop:
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop:
# Short-Description: D2000Kom
# Description: Support for D2000 KOM (work with leds/buzzer)
### END INIT INFO
DESC="Set permissions for LED/BUZZER for D2000 KOM"
chmod -R o+w /sys/class/leds/LED1
chmod -R o+w /sys/class/leds/LED2
chmod -R o+w /sys/class/leds/BUZZER
Then run:
chmod 755 /etc/init.d/d2000init
update-rc.d d2000init defaults
Communication line configuration
- communication line category: API.
- By default, a single line with a single station is configured for one device. If there is a need to stop communication with selected inputs/outputs, there may be several stations on one line. Due to the load distribution or for the rapid reading of the digital inputs, several lines with one or more stations per-line can be configured.
Communication line parameters
Communication line - configuration dialog box - the Protocol parameter tab.
Parameters defined in the field have an effect on some optional protocol parameters. The following line protocol parameters can be defined:
Table 1
| Full name | Description | Units / size | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
Device Type | Type of device. Currently supported are::
| - | Raspberry PI |
Library Name | Name of the library with communication functions for a particular device. The used values are:
| - | - |
Read Delay Ms | Delay after one reading of the values of all I/O tags. Using this parameter, it is possible to control the reading frequency more finely than using the polling parameters in the configuration of the time parameters of the station. | ms | 1 |
Communication station configuration
- Communication protocol: GPIO Protocol.
- Station address: n/a.
I/O tag configuration
Possible I/O tag types: Ai, Ao, Ci, Co, Di, Do.
The address format of the I/O tag depends on the device type.
I/O tag addresses for Raspberry PI
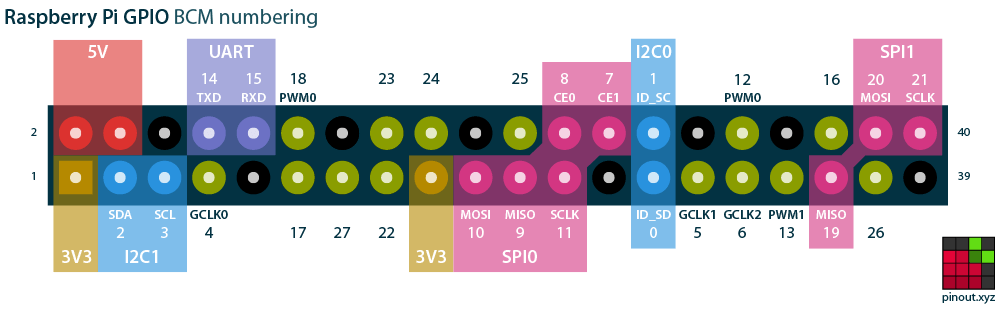
In the following table, id defines the number of ping in BCM (Broadcom) numbering.
Following image copied from http://pinout.xyz shows the BCM pin numbering on the GPIO connector:
| Address | Description | I/O tag type | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
DI,id | The GPIO pin will be configured as a digital input. If the voltage of 3.3V is applied to it, the value of input will be 1. If 0V (ground) voltage is applied to it, the value of input will be 0. | Di, Ci, Ai | DI,25 DI_UP,24 |
DO,id | The GPIO pin will be configured as a digital output. If a value of 1 is written to it, the output will be 3.3V. If 0 is written, the output voltage will be 0V (ground). | Dout, Co, Ao | DO,24 |
| TRIGGER_TOON,id[,filter] TRIGGER_TOON_UP,id[,filter] TRIGGER_TOON_DOWN,id[,filter] TRIGGER_TOOFF,id[,filter] TRIGGER_TOOFF_UP,id[,filter] TRIGGER_TOOFF_DOWN,id[,filter] TRIGGER,id[,filter] TRIGGER_UP,id[,filter] TRIGGER_DOWN,id[,filter] | The GPIO pin will be configured as a counter of input events with an optional filter. The counter can register rising signal edges 0V → 3.3V (TOON), falling edges 3.3V → 0V (TOOFF), and any signal changes (without TOON/TOOFF). | Ci, Ai | TRIGGER,24 |
| PWM,id | The GPIO pin will be configured as PWM (pulse width modulation) output. It is then possible to write values 0-255 controlling the width of the pulse from fully off to fully on. | Dout, Co, Ao | PWM,12 |
| REVISON | The revision of the hardware (the number from the "Revision" line from the /proc/cpuinfo file. For example, for RPI 3 this file contains a row | Ci | REVISON |
I/O tag addresses for NPE X500
In the following table, id defines the number of input/output (e.g. DI, DO, AO). The number of inputs and outputs depends on the particular model. The notes are referring to the NPE X500-M3-MAX-3G that was tested.
Note 1: Output points whose addresses contain _BUF use buffered writing. This allows the values of such objects not only to be written but also to be read, which can be useful, for example, after the start of the KOM process.
Note 2: With the tested model, the reading of the digital input took less than 1 ms, while the reading of the analog input took approximately 20 ms.
| Address | Description | I/O tag type | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
DI,id | Digital input (DI) | Di, Ci, Ai | DI,1 DI,2 |
DO,id | Digital output (DO). If buffered (DO_BUFF), the value is also read (during startup and periodically). | Dout, Co, Ao | DO,1 |
| DIO,id DIO_BUF,id | Digital input/output. Based on the I/O tag type, the GPIO port is configured as input (Di, Ci, Ai) or output (Dout, Co, Ao). | Input: Di, Ci, Ai Output: Dout, Co, Ao | DIO,2 DIO_BUF,3 |
| RELAY,id RELAY_BUF,id | Relay output. If buffered (RELAY_BUFF), the value is also read (during startup and periodically). | Dout, Co, Ao | RELAY,1 RELAY_BUF,2 |
| AI,id | Analog input (AI). | Ci, Ai | AI,1 |
| LED,id LED_BUF,id | LED output. If buffered (LED_BUFF), the value is also read (during startup and periodically). | Dout, Co, Ao | LED,1 LED_BUF,2 |
| BUZZER BUZZER_BUF | Buzzer. If buffered (BUZZER_BUFF), buzzer status is also read (during startup and periodically). | Dout, Co, Ao | BUZZER BUZZER_BUF |
| BUTTON BUTTON_BUF | User button status. | Di, Ci, Ai | BUTTON |
Literature
Blog
You can read a blog about GPIO protocol: GPIO protocol is here to help
Changes and modifications
Document revisions
- Ver. 1.0 - August 30th, 2018 – Document created
Related pages:
0 komentárov